Abstract
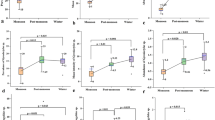
Parasite intensity dynamics can be strongly affected by ecosystem abiotic components. We conducted this study to investigate how the intensity of Argulus sp. is influenced by physicochemical factors in three water bodies — river, fish farm, and reservoir — and to find the occurrence of Argulus sp. under different conditions. Argulus sp. specimens were collected using different methods — gill-netting 30 × 1.5 m, 40 mm mesh monofilament net and set from a small boat, beach seining and plankton net — from July 2010 until Jun 2011 at Guangdong province, China. Main water parameters taken for the assessment consisting of temperature, pH, DO, biochemical oxygen demand of 5 days (BOD5), chemical oxygen demand (COD), NH +4 , total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP). The results show that the ratio of female to male Argulus sp. during the studied period was 2.3:1. The presence and intensity of Argulus sp. were temperature-dependent and variable; pH values were lower than standers with high intensity of Argulus sp. Argulus sp. has the ability to live in low dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration. Relatively high concentrations of BOD5, COD, NH +4 , TN and TP were detected with related variable intensity of Argulus sp., which is supposed to be a freshwater fish ectoparasite found in polluted ecosystems. It is concluded that the fish ectoparasite Argulus sp. have a strong potency of genetic adaptation impacted by environmental factors. However, this needs further study in order to gain insight into the question of the likelihood of adaptation to abiotic factors’ variation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA and WCPE (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA
Bagarinao T (1992) Sulfide as an environmental factor and toxicant: tolerance and adaptations in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 24(1–2):21–62
Bandilla M, Hakalahti T, Hudson PJ, Valtonen ET (2005) Aggregation of Argulus coregoni (Crustacea: Branchiura) on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): a consequence of host susceptibility or exposure? Parasitology 130:1–8
Banerjee S, Bandyopadhyay PK (2010) Observation on prevalence of ectoparasites in carp fingerlings in two districts of West Bengal. J Parasit Dis 34(1):44–47
Bulgakov NG (2004) Ecologically tolerable impact levels of abiotic factors in water bodies in russia and neighboring countries: dependence on the geographic and climatic conditions. Water Resour 31(2):174–179
Chomicki KM, Schiff SL (2008) Stable oxygen isotopic fractionation during photolytic O2 consumption in stream waters. Sci Total Environ 404(2–3):236–244
Crear BJ, Forteath GNR (2000) The effect of extrinsic and intrinsic factors on oxygen consumption by the southern rock lobster, Jasus edwardsii. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 252(1):129–147
Fisenko AI, Malomuzh NP (2009) To what extent is water responsible for the maintenance of the life for warm-blooded organisms? Int J Mol Sci 10:2383–2411
Gasnier N, Cabaret J (1998) Stable and unstable environments influence the genetic diversity of the nematode Teladorsagia circumcincta, a parasite of small ruminants. Parasitol Res 84:676–681
Gault NFS, Kllpatrick DJ, Stewart MT (2002) Biological control of the fish louse in a rainbow trout fishery. J Fish Biol 60(1):226–237
Grillo V, Jackson F, Cabaret J, Gilleard JS (2007) Population genetic analysis of the ovine parasitic nematode Teladorsagia circumcincta and evidence for a cryptic species. Int J Parasitol 37(3–4):435–447
Guangdong Environmental Protection Bureau (2008) Guangdong provincial Bulletin on Status of the Environment. Guangdong Environmental Protection commission, Guangdong
Hakalahti-Sirén T, Lankinen Y, Valtonen ET (2004) Efficacy of emamectin benzoate in the control of Argulus coregoni (Crustacea: Branchiura) on rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dis Aquat Org 60:197–204
Hakalahti-Sirén T, Mikheev VN, Valtonen ET (2008) Control of freshwater fish louse Argulus coregoni: a step towards an integrated management strategy. Dis Aquat Org 82(1):67–77
Hoffman GL (1977) Argulus, a Branchiuran parasite of freshwater fishes. US Fish Wildl Serv Fish Dis Leafl 49:9
Hsiao SC (1950) Copepods from Lake Erh Hai, China. Proc US Nat Mus 100:161–200
Julio AC, Álvaro A (2006) Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: a global assessment. Environ Int 32(6):831–849
Knapen D, Bervoets L, Verheyen E, Blust R (2004) Resistance to water pollution in natural gudgeon (Gobio gobio) populations may be due to genetic adaptation. Aquat Toxicol 67(2):155–165
Koprivnikar J et al (2010) Effects of temperature, salinity, and pH on the survival and activity of marine cercariae. Parasitol Res 106(5):1167–1179
Kozlov VM, Zvereva LE (2011) A second life for old data: global patterns in pollution ecology revealed from published observational studies. Environ Pollut 159(5):1067–1075
Kuang PR, Qian JH (1991) Economic fauna of China, parasitic crustacean of freshwater fishes. Science Press, Beijing, 210 pp
Leignel V, Humbert JF (2001) Mitochondrial DNA variation in benzimidazole-resistant and -susceptible populations of the small ruminant parasite Teladorsagia circumcincta. J Hered 92:503–506
Lisichkin YV, Novikov AG, Fomichev NK (1989) Vibration and configuration contributions to the heat capacity of water according to data of the inelastic cold neutron scattering. J Phys Chem 63:833–835
Nagasawa K, Katahira H, Mizuno K (2010) New host and locality of the fish ectoparasite Argulus japonicas (Crustacea, Branchiura, Argulidae) in Japan, with a note on its heavy infection. Biogeography 12:17–20
Nianqing Zh et al (2011) A coupling simulation based on a hydrodynamics and water quality model of the Pearl River Delta, China. J Hydrol 396:267–276
Poly WJ (1997) Host and locality records of the fish ectoparasite, Argulus (Branchiura), from Ohio (U.S.A.). Crustaceana 70(8):867–874
Ramos AT, de Souza Machado AA, Bianchini A (2011) Chitobiase of planktonic crustaceans from South Atlantic coast (Southern Brazil): characterization and influence of abiotic parameters on enzyme activity. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 407(2):323–329
Rosas C, Martinez E, Gaxiola G, Brito R, Sánchez A, Soto L (1999) The effect of dissolved oxygen and salinity on oxygen consumption, ammonia excretion and osmotic pressure of Penaeus setiferus (Linnaeus) juveniles. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 234(1):41–57
Saurabh Sh, Mohanty BR, Sahoo PK (2011) Expression of immune-related genes in rohu Labeo rohita (Hamilton) by experimental freshwater lice Argulus siamensis (Wilson) infection. Vet Parasitol 175:119–128
Shimura S (1983) Seasonal occurrence, sex ratio and site preference of Argulus coregoni Thorell (Crustacea: Branchiura) parasitic on cultured freshwater salmonids in Japan. Parasitology 86:537–552
Stammer J (1959) Beiträge zu Morphologie, Biologie und Bekämpfung der Karpfenläuse. Z Parasitenkunde 19:135–208
OECD Territorial Reviews: Guangdong, China 2010. OECD Publishing, 310 pp
The World Bank (2006) Guangdong Pearl River delta urban environment, Project2 — Foshan subproject, design review and advisory services, El 399, Vol. 3. World Bank, April, 2006, 87 pp
Wadeh H, Alsarakibi M, Guoqing L (2010) Analysis of genetic variability within Argulus japonicus from representatives of Africa, Middle East, and Asia revealed by sequences of three mitochondrial DNA genes. Parasitol Res 107:547–553
Wegner KM, Kalbe M, Milinski M, Reusch TH (2008) Mortality selection during the 2003 European heat wave in three-spined sticklebacks: effects of parasites and MHC genotype. BMC Evol Biol 8:124
WHO, 2011. Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th ed. WHO Press, Geneva, Switzerland, 541 pp
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30972179) and the Ph. D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (200805640004). The authors are thankful to Dr. Ahmad Katsha, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA, for his valuable advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsarakibi, M., Wadeh, H. & Li, G. Freshwater abiotic components’ impact on the viability of fish lice, Argulus sp., in Guangdong province, China. Parasitol Res 111, 331–339 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2844-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2844-7