Abstract
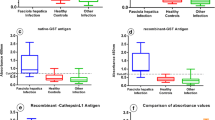
The utility of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to determine the sensitization against the trematode Fasciola hepatica in horses from an endemic area (NW Spain) was assessed. Blood samples were collected from 536 horses and tested against a 2.9-kDa recombinant surface protein (FhrAPS) to estimate the presence of IgG antibodies. Data were analysed regarding several intrinsic (age, gender and breed) and extrinsic factors (aptitude and housing). The farm size (number of horses/farm) was also considered. Sixty percent (95% CI 56, 64) of the horses were positive to the FhrAPS-ELISA, with a significantly higher seroprevalence in the mares (67%). Foals reached the lowest percentage of sensitization against the trematode (12%), and a significant positive correlation between the seroprevalence of fasciolosis and the age of the horses was established. When considering all the factors together, the seroprevalence of fasciolosis was initially classified into two groups (nodes) regarding the age of the horses. The node composed of the horses older than 1 year was then divided into two other clusters according to their gender. The mares were finally classified and grouped into two nodes regarding their breed. We concluded that the FhrAPS-ELISA is very useful for the demonstration of specific equine IgG antibodies against F. hepatica. An elevated risk of exposition to this trematode in horses maintained in endemic areas was proven. The possible role of horses as reservoirs for F. hepatica infections is discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaino H, Apt W, Vega F, Gorman T, Apt P (1992) Fasciolasis animal en la VII Región de Chile: áreas de distribución e infección en caballos y conejos silvestres. Parasitol al Día 16:11–16
Apt W, Aguikra X, Flavio I, Alcaíno H, Zulantq I, Patia AP, González V, Retamal C, Rodríguez J, Sandoval J (1993) Prevalencia de fascioliasis en humanos, caballos, cerdos y conejos silvestres, en tres provincias de Chile. Bol Of Sanit Panam 11:405–414
Arias M, Morrondo P, Hillyer GV, Sánchez-Andrade R, Suárez JL, Lomba C, Pedreira J, Díaz P, Díez-Baños P, Paz-Silva A (2007) Immunodiagnosis of current fasciolosis in sheep naturally exposed to Fasciola hepatica by using a 2.9 kDa recombinant protein. Vet Parasitol 146:46–49
Arias MS, Suárez JL, Hillyer GV, Francisco I, Calvo E, Sánchez-Andrade R, Díaz P, Francisco R, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P, Paz-Silva A (2009) A recombinant-based ELISA evaluating the efficacy of netobimin and albendazole in ruminants with naturally acquired fascioliasis. Vet J 182:73–78
Arias M, Piñeiro P, Hillyer GV, Suárez JL, Francisco I, Cortiñas FJ, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P, Sánchez-Andrade R, Paz-Silva A (2010) An approach of the laboratory to the field: assessment of the influence of cattle management on the seroprevalence of fascioliasis by using polyclonal- and recombinant-based ELISAs. J Parasitol 96:626–631
Arias M, Lomba C, Dacal V, Vázquez L, Pedreira J, Francisco I, Piñeiro P, Cazapal-Monteiro C, Suárez JL, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P, Sánchez-Andrade R, Paz-Silva A (2011) Prevalence of mixed trematode infections in an abattoir receiving cattle form northern Portugal and north-west Spain. Vet Rec 168:408–412
Carnevale S, Rodríguez M, Guarnera EA, Carmona C, Tanos T, Angel S (2001) Immunodiagnosis of fasciolosis using recombinant procathepsin L cystein proteinase. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 41:43–49
Espino AM, Díaz A, Pérez A, Finlay CM (1998) Dynamics of antigenemia and coproantigens during a human Fasciola hepatica outbreak. J Clin Microbiol 36:2723–2726
Gajewska A, Smaga-Kozłowska K, Wiśniewski M (2005) Pathological changes of liver in infection of Fasciola hepatica. Wiad Parazytol 51:115–123
Getachew M, Innocent GT, Trawford AF, Reid SWJ, Love S (2010) Epidemiological features of fasciolosis in working donkeys in Ethiopia. Vet Parasitol 169:335–339
Gorman T, Aballay J, Fredes F, Silva M, Aguillón JC, Alcaíno HA (1997) Immunodiagnosis of fasciolosis in horses and pigs using western blots. Int J Parasitol 27:1429–1432
Haridy FM, Morsy TA, Gawish NI, Antonios TN, Abdel Gawad AG (2002) The potential reservoir role of donkeys and horses in zoonotic fascioliasis in Gharbia Governorate, Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 32:561–570
Khan MK, Sajid MS, Khan MN, Iqbal Z, Iqbal MU (2009) Bovine fasciolosis: prevalence, effects of treatment on productivity and cost benefit analysis in five districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Res Vet Sci 87:70–75
Knubben-Schweizer G, Deplazes P, Torgerson PR, Rapsch C, Meli ML, Braun U (2010) Bovine fasciolosis in Switzerland: relevance and control. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd 152:223–229
Lean I, Westwood C, Playford M (2008) Livestock disease threats associated with intensification of pastoral dairy farming. N Z Vet J 56:261–269
Morsy TA, Salem HS, Haridy FM, Rifaat MM, Abo-Zenadah NY, Adel El-Kadi M (2005) Farm animals' fascioliasis in Ezbet El-Bakly (Tamyia Center) Al-Fayoum Governorate. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 35:825–832
Paz-Silva A, Sánchez-Andrade R, Suárez JL, Pedreira J, Arias M, López C, Panadero R, Díaz P, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2003) Prevalence of natural ovine fasciolosis shown by demonstrating the presence of serum circulating antigens. Parasitol Res 91:328–331
Paz-Silva A, Hillyer GV, Sánchez-Andrade R, Rodríguez-Medina JR, Arias M, Morrondo P, Díez-Baños P (2005) Isolation, identification and expression of a Fasciola hepatica cDNA encoding a 2.9-kDa recombinant protein for the diagnosis of ovine fascioliasis. Parasitol Res 95:129–135
Paz-Silva A, Hillyer GV, Arias MS, Sánchez-Andrade R, Pedreira J, Suárez JL, Lomba C, Díaz P, Francisco I, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2007) A cross-sectional study of fascioliasis in autochthonous cattle from NW Spain by using a 2.9-kDa recombinant protein. Int J Appl Res Vet Med 5:52–56
Paz-Silva A, Arias M, Francisco I, Cortiñas FJ, Francisco R, Mochales E, Suárez JL, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P, Sánchez-Andrade R (2010) Cross-immunity and interpretation of the diagnostics of parasitic trematodosis in ruminants by means of immunoenzymatic probes. In: LaMann GV (ed) Veterinary parasitology. Nova, New York, pp 289–302
Perrucci S, Pinello E, Fichi G, Ciardi E, Bàrberi P, Moonen C, Ragaglini G, Bibbiani C (2007) Parasitic infections in an organic grazing cattle herd in Tuscany using geographic information systems to determine risk factors. Vet Ital 43:415–424
Phiri IK, Phiri AM, Harrison LJ (2006) Serum antibody isotype responses of Fasciola-infected sheep and cattle to excretory and secretory products of Fasciola species. Vet Parasitol 141:234–242
Rodríguez-Pérez J, Hillyer GV (1995) Detection of excretory-secretory circulating antigens in sheep infected with Fasciola hepatica and with Schistosoma mansoni and Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 56:57–66
Rogan WJ, Gladen B (1978) Estimating prevalence from the results of a screening test. Am J Epidemiol 107:71–76
Ross JG (1977) A five-year study of the epidemiology of fascioliasis in the north, east and west of Scotland. Br Vet J 133:263–272
Sánchez-Andrade R, Paz-Silva A, Suárez J, Panadero R, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2000) Use of a sandwich-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (SEA) for the diagnosis of natural Fasciola hepatica infection in cattle from Galicia (NW Spain). Vet Parasitol 93:39–46
Sánchez-Andrade R, Paz-Silva A, Suárez JL, Panadero R, Pedreira J, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2001) Effect of fasciolicides on the antigenaemia in sheep naturally infected with Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 87:609–614
Sánchez-Andrade R, Paz-Silva A, Suárez JL, Panadero R, Pedreira J, López C, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2002) Influence of age and breed on natural bovine fasciolosis in an endemic area (Galicia, NW Spain). Vet Res Commun 26:361–370
Soulé C, Boulard C, Levieux D, Barnouin J, Plateau E (1989) Experimental equine fascioliasis: evolution of serologic, enzymatic and parasitic parameters. Ann Rech Vet 20:295–307
Spithill TW, Smooker PM, Copeman DB (1999) Fasciola gigantica: epidemiology, control, immunology and molecular biology. In: Dalton JP (ed) Fasciolosis. CABI Pub, Wallingford, Oxon, pp 465–525
Thrusfield M (2005) Veterinary epidemiology. Blackwell, Oxford, p 584
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Projects XUGA PGIDT06RAG26102PR and 07MDS021261PR (Xunta de Galicia, Spain), and complies with the current laws for Animal Health Research in Spain. Dr. Arias has received a fellowship from the “Ángeles Alvariño” Research Program (XUGA, Spain). We are in debt to Mrs. B. Valcárcel for preparing and editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arias, M.S., Piñeiro, P., Hillyer, G.V. et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of equine antibodies specific to a recombinant Fasciola hepatica surface antigen in an endemic area. Parasitol Res 110, 1001–1007 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2587-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2587-x