Abstract
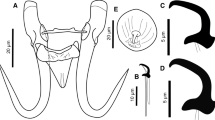
Three species of cyathostomes—Cylicocyclus ashworthi, Cylicostephanus bidentatus, and Cylicostephanus hybridus were identified recently in horses in Kentucky. General characteristics and distinguishing description of these species are presented. Distribution of these species and their role in the horse strongylid community are discussed. The importance of examining the entire contents of the large intestine or alternatively a high number of specimens in order to recover and identify species residing in low numbers is stressed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baruš V (1962) Helmintofauna koni v Československu. Česk Parasitol 9:15–94
Braide EI, Georgi JR (1974) Numbers of external leaf crown elements of 18 species of equine cyathostomes. Cornell Vet 64:233–239
Čerňanská D, Paoletti B, Králová-Hromadová I, Iorio R, Čudeková P, Milillo P, Traversa D (2009) Application of a reverse line blot hybridisation assay for the species specific identification of cyathostomins (Nematoda, Strongylida) from benzimidazole-treated horses in the Slovak Republic. Vet Parasitol 160:171–174
Chapman MR, French DD, Klei TR (2001) Seasonal transmission of gastrointestinal parasites of equids in Southern Louisiana. J Parasitol 87:1371–1378
Chapman MR, French DD, Klei TR (2002) Gastrointestinal helminths of ponies in Louisiana: a comparison of species currently prevalent with those present 20 years ago. J Parasitol 88:1130–1134
Chapman MR, French DD, Klei TR (2003a) Prevalence of strongyle nematodes in naturally infected ponies of different ages and during different seasons of the year in Louisiana. J Parasitol 89:309–314
Chapman MR, Kearney MT, Klei TR (2003b) Equine cyathostome populations: accuracy of species composition estimations. Vet Parasitol 116:15–21
Dikmans G (1945) Check list of the internal and external animal parasites of domestic animals in North America. Am J Vet Res 6:211–241
Drudge JH, Lyons ET (1977) Methods in the evaluation of antiparasitic drugs in the horse. Am J Vet Res 38:1581–1586
Dvojnos GM, Kharchenko VA (1994) Strongilidy dikikh i domashnikh loshadej. [Strongylida of wild and domestic horses]. Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 234 (in Russian)
Foster AO (1936) A quantitative study of the nematodes from a selected group of equines in Panama. J Parasitol 22:479–510
Foster AO, Ortiz PO (1937) A further report on the parasites of selected group of equines in Panama. J Parasitol 23:360–364
Gawor JJ (1995) The prevalence and abundance of internal parasites in working horses autopsied in Poland. Vet Parasitol 58:99–108
Hodgkinson JE, Freeman KL, Lichtenfels JR, Palfreman S, Love S, Matthews JB (2005) Identification of strongyle eggs from anthelmintic-treated horses using a PCR-ELISA based on intergenic DNA sequences. Parasitol Res 95:287–292
Hung GC, Chilton NB, Beveridge I, McDonnell A, Lichtenfels JR, Gasser RB (1997) Molecular delineation of Cylicocyclus nassatus and C. ashworthi (Nematoda: Strongylidae). Int J Parasitol 27:601–607
Ionita M, Howe DK, Lyons ET, Tolliver SC, Kaplan RM, Mitrea IL, Yeargan M (2010) Use of a reverse line blot assay to survey small strongyle (Strongylida: Cyathostominae) populations in horses before and after treatment with ivermectin. Vet Parasitol 168:332–337
Kaye JN, Love S, Lichtenfels JR, McKeand JB (1998) Comparative sequence analysis of the intergenic spacer region of cyathostome species. Int J Parasitol 28:831–836
Kuzmina TA, Kharchenko VA, Starovir AI, Dvoinos GM (2005) Analysis of the strongylid nematodes (Nematoda: Strongylidae) community after deworming of brood horses in Ukraine. Vet Parasitol 131:283–290
Kuzmina TA, Kharchenko VA, Zvegintsova NS (2007) Comparative study of the intestinal strongylid communities of equidae in the Askania-Nova biosphere reserve, Ukraine. Helminthologia 44:62–69
Lichtenfels JR (1975) Helminths of domestic equids. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 42:1–92
Lichtenfels JR, Klei TR (1988) Cylicostephanus torbertae sp. n. (Nematode: Strongyloidea) from Equus caballus with a discussion of the genera Cylicostephanus, Petrovinema and Skrjabinodentus. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 55:165–170
Lichtenfels JR, Kharchenko VA, Sommer C, Ito M (1997) Key characters for the microscopical identification of Cylicocyclus nassatus and of Cylicocyclus ashworthi (Nematoda: Cyathostominae) of the horse, Equus caballus. J Helminthol Soc Wash 64:120–127
Lichtenfels JR, McDonnell A, Love S, Matthews JB (2001) Nematodes of the tribe Cyathostominea(Strongylidae) collected from horses in Scotland. Comp Parasitol 68:265–269
Lichtenfels JR, Kharchenko VA, Dvojnos GM (2008) Illustrated identification keys to strongylid parasites (Strongylidae: Nematoda) of horses, zebras and asses (Equidae). Vet Parasitol 156:4–161
Lyons ET, Tolliver SC (2009) Some historic aspects of small strongyles and ascarids in equids featuring drug resistance with notes on ovids. Agricultural Experiment Station. Bulletin SR- 102. University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Lexington, KY
Lyons ET, Tolliver SC, Kuzmina TA, Collins SS (2010) Critical tests evaluating efficacy of moxidectin against small strongyles in horses from a herd for which reduced activity had been found in field tests in Central Kentucky. Parasitol Res 107(6):1495–1498. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-2025-5
Mfitilodze M, Hutchinson G (1990) Prevalence and abundance of equine strongyles (Nematoda: Strongyloidea) in tropical Australia. J Parasitol 76:487–494
Ogbourne CP (1976) The prevalence, relative abundance and site distribution of nematodes of the subfamily Cyathostominae in horses killed in Britain. J Helminthol 50:203–214
Osterman Lind E, Kuzmina T, Uggla A, Waller PJ, Höglund J (2007) A field study on the effect of some anthelmintics on cyathostomins of horses in Sweden. Vet Res Comm 31:53–65
Silva AVM, Costa HMA, Santos HA, Carvalho RO (1999) Cyathostominae (Nematoda) parasites of Equus caballus in some Brazilian states. Vet Parasitol 86:15–21
Slivinska K, Gawor J, Jaworski Z (2009) Gastro-intestinal parasites in yearlings of wild Polish primitive horses from the Popielno Forest Reserve, Poland. Helminthologia 46:9–13
Stancampiano L, Mughini Gras L, Poglayen G (2010) Spatial niche competition among helminth parasites in horse’s large intestine. Vet Parasitol 170:88–95
Tolliver SC (2000) A practical method of identification of the North American cyathostomes (small strongyles) in equids in Kentucky. University of Kentucky, Lexington, p 37, SR- 2001, Monograph
Traversa D, Iorio R, Klei TR, Kharchenko VA, Gawor J, Otranto D, Sparagano AO (2007) New method for simultaneous species-specific identification of equine strongyles (Nematoda Strongylida) by reverse line blot hybridisation. J Clin Microbiol 45:2937–2942
Acknowledgments
This investigation (Paper No. 10-14-114) was made in connection with a project of the University of Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station and is published with the approval of the director.
Authors express sincere thanks to Dr. Yury (Iurii) Kuzmin, Institute of Zoology NAS of Ukraine, for his assistance in preparation of the pictures. Appreciation is expressed to the Albert and Lorraine Clay Fellowship for partial financial support for one of the authors, Tetiana Kuzmina, to come as a visiting scientist from the Ukraine to the University of Kentucky to study parasites of equids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzmina, T.A., Tolliver, S.C. & Lyons, E.T. Three recently recognized species of cyathostomes (Nematoda: Strongylidae) in equids in Kentucky. Parasitol Res 108, 1179–1184 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2160-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2160-z