Abstract
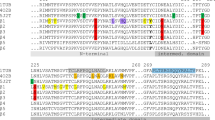
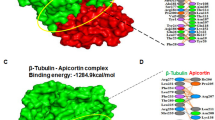
Albendazole is a benzimidazole drug which can be used to treat liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) infections. Its mode of action is believed to be the inhibition of microtubule formation through binding to β-tubulin. However, F. hepatica expresses at least six different isotypes of β-tubulin, and this has confused, rather than clarified, understanding of the molecular mechanisms of benzimidazole drugs in this organism. Recombinant F. hepatica β-tubulin proteins were expressed in, and purified from, Escherichia coli. These proteins were then used in pull-down assays in which albendazole was covalently linked to Sepharose. β-Tubulin isotype 2 was pulled down in this assay, and this interaction could be reduced by adding competing albendazole. Molecular modelling of β-tubulin isotypes suggests that changes in the side change conformations of residue 200 in the putative albendazole binding site may be important in determining whether, or not, a particular isotype will bind to the drug. These results, together with previous work demonstrating that albendazole causes disruption of microtubules in the liver fluke, strongly suggest that β-tubulin isotype 2 is one of the targets of this drug.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABZ:
-
Albendazole
- ABZ.SO:
-
Albendazole sulphoxide
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside
- rmsd:
-
Root mean square deviation
- TCBZ:
-
Triclabendazole
- VdW:
-
Van der Waal’s
References
Alvarez L, Moreno G, Moreno L, Ceballos L, Shaw L, Fairweather I, Lanusse C (2009) Comparative assessment of albendazole and triclabendazole ovicidal activity on Fasciola hepatica eggs. Vet Parasitol 164:211–216
Arguello-Garcia R, Cruz-Soto M, Romero-Montoya L, Ortega-Pierres G (2009) In vitro resistance to 5-nitroimidazoles and benzimidazoles in Giardia duodenalis: variability and variation in gene expression. Infect Genet Evol 9:1057–1064
Boray JC (1994) Diseases of domestic animals caused by flukes. F.A.O, Rome, pp 1–32
Brennan GP, Fairweather I, Trudgett A, Hoey E, McCoy M, McConville M, Meaney M, Robinson M, McFerran N, Ryan L, Lanusse C, Mottier L, Alvarez L, Solana H, Virkel G, Brophy PM (2007) Understanding triclabendazole resistance. Exp Mol Pathol 82:104–109
Buchanan JF, Fairweather I, Brennan GP, Trudgett A, Hoey EM (2003) Fasciola hepatica: surface and internal tegumental changes induced by treatment in vitro with the sulphoxide metabolite of albendazole ('Valbazen'). Parasitology 126:41–153
Chambers E, Hoey EM, Trudgett A, Fairweather I, Timson DJ (2010) Binding of serum albumin to the anthelmintic drugs albendazole, triclabendazole and their sulphoxides. Vet Parasitol 171(1–2):172–175
Chu SW, Badar S, Morris DL, Pourgholami MH (2009) Potent inhibition of tubulin polymerisation and proliferation of paclitaxel-resistant 1A9PTX22 human ovarian cancer cells by albendazole. Anticancer Res 29:3791–3796
Cline GW, Hanna SB (1987) The aminolysis of N-hydroxysuccinimide esters. A structure-reactivity study. J Am Chem Soc 109:3087–3091
Cruz MC, Edlind T (1997) β-Tubulin genes and the basis for benzimidazole sensitivity of the opportunistic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiology 143:2003–2008
Elard L, Comes AM, Humbert JF (1996) Sequences of β-tubulin cDNA from benzimidazole-susceptible and -resistant strains of Teladorsagia circumcincta, a nematode parasite of small ruminants. Mol Biochem Parasitol 79:249–253
Fairweather I (2005) Triclabendazole: new skills to unravel an old(ish) enigma. J Helminthol 79:227–234
Fairweather I (2009) Triclabendazole progress report, 2005–2009: an advancement of learning? J Helminthol 83:139–150
Fetterer RH (1986) The effect of albendazole and triclabendazole on colchicine binding in the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 9:49–54
Ghisi M, Kaminsky R, Maser P (2007) Phenotyping and genotyping of Haemonchus contortus isolates reveals a new putative candidate mutation for benzimidazole resistance in nematodes. Vet Parasitol 144:313–320
Halferty L, Brennan GP, Trudgett A, Hoey L, Fairweather I (2009) Relative activity of triclabendazole metabolites against the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 159:126–138
Henriquez FL, Ingram PR, Muench SP, Rice DW, Roberts CW (2008) Molecular basis for resistance of Acanthamoeba tubulins to all major classes of antitubulin compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:1133–1135
Hoti SL, Subramaniyan K, Das PK (2003) Detection of codon for amino acid 200 in isotype 1 β-tubulin gene of Wuchereria bancrofti isolates, implicated in resistance to benzimidazoles in other nematodes. Acta Trop 88:77–81
Jimenez-Gonzalez A, De Armas-Serra C, Criado-Fornelio A, Casado-Escribano N, Rodriguez-Caabeiro F, Diez JC (1991) Preliminary characterization and interaction of tubulin from Trichinella spiralis larvae with benzimidazole derivatives. Vet Parasitol 39:89–99
Kenyon F, Sargison ND, Skuce PJ, Jackson F (2009) Sheep helminth parasitic disease in south eastern Scotland arising as a possible consequence of climate change. Vet Parasitol 163:293–297
Kwa MS, Veenstra JG, Roos MH (1994) Benzimidazole resistance in Haemonchus contortus is correlated with a conserved mutation at amino acid 200 in β-tubulin isotype 1. Mol Biochem Parasitol 63:299–303
Lacey E, Prichard RK (1986) Interactions of benzimidazoles (BZ) with tubulin from BZ-sensitive and BZ-resistant isolates of Haemonchus contortus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 19:171–181
Lowe J, Li H, Downing KH, Nogales E (2001) Refined structure of αβ-tubulin at 3.5 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 313:1045–1057
Lubega GW, Prichard RK (1990) Specific interaction of benzimidazole anthelmintics with tubulin: high-affinity binding and benzimidazole resistance in Haemonchus contortus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 38:221–232
Lubega GW, Prichard RK (1991) Interaction of benzimidazole anthelmintics with Haemonchus contortus tubulin: binding affinity and anthelmintic efficacy. Exp Parasitol 73:203–213
MacDonald LM, Armson A, Thompson AR, Reynoldson JA (2004) Characterisation of benzimidazole binding with recombinant tubulin from Giardia duodenalis, Encephalitozoon intestinalis, and Cryptosporidium parvum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 138:89–96
Marshak DR, Watterson DM, Van Eldik LJ (1981) Calcium-dependent interaction of S100b, troponin C, and calmodulin with an immobilized phenothiazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:6793–6797
Mas-Coma S, Valero MA, Bargues MD (2009a) Chapter 2. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv Parasitol 69:41–146
Mas-Coma S, Valero MA, Bargues MD (2009b) Climate change effects on trematodiases, with emphasis on zoonotic fascioliasis and schistosomiasis. Vet Parasitol 163:264–280
McConville M, Brennan GP, McCoy M, Castillo R, Hernandez-Campos A, Ibarra F, Fairweather I (2006) Adult triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: surface and subsurface tegumental responses to in vitro treatment with the sulphoxide metabolite of the experimental fasciolicide compound alpha. Parasitology 133:195–208
Moll L, Gaasenbeek CP, Vellema P, Borgsteede FH (2000) Resistance of Fasciola hepatica against triclabendazole in cattle and sheep in The Netherlands. Vet Parasitol 91:153–158
Nogales E, Wolf SG, Downing KH (1998) Structure of the αβ tubulin dimer by electron crystallography. Nature 391:199–203
Oxberry ME, Geary TG, Winterrowd CA, Prichard RK (2001) Individual expression of recombinant α- and β-tubulin from Haemonchus contortus: polymerization and drug effects. Protein Expr Purif 21:30–39
Pathmanathan S, Elliott SF, McSwiggen S, Greer B, Harriott P, Irvine GB, Timson DJ (2008) IQ motif selectivity in human IQGAP1: binding of myosin essential light chain and S100B. Mol Cell Biochem 318:43–51
Prichard R (2001) Genetic variability following selection of Haemonchus contortus with anthelmintics. Trends Parasitol 17:445–453
Robinson MW, Dalton JP (2009) Zoonotic helminth infections with particular emphasis on fasciolosis and other trematodiases. Phil Trans R Soc B 364:2763–2776
Robinson MW, Hoey EM, Fairweather I, Dalton JP, McGonigle S, Trudgett A (2001) Characterisation of a β-tubulin gene from the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Int J Parasitol 31:1264–1268
Robinson MW, Trudgett A, Hoey EM, Fairweather I (2002) Triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: β-tubulin and response to in vitro treatment with triclabendazole. Parasitology 124:325–338
Robinson MW, Trudgett A, Hoey EM, Fairweather I (2003) The effect of the microtubule inhibitor tubulozole-C on the tegument of triclabendazole-susceptible and triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 91:117–129
Robinson MW, McFerran N, Trudgett A, Hoey L, Fairweather I (2004) A possible model of benzimidazole binding to β-tubulin disclosed by invoking an inter-domain movement. J Mol Graph Model 23:275–284
Ryan LA, Hoey E, Trudgett A, Fairweather I, Fuchs M, Robinson MW, Chambers E, Timson DJ, Ryan E, Feltwell T, Ivens A, Bentley G, Johnston D (2008) Fasciola hepatica expresses multiple α- and β-tubulin isotypes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 159:73–78
Schwab AE, Boakye DA, Kyelem D, Prichard RK (2005) Detection of benzimidazole resistance-associated mutations in the filarial nematode Wuchereria bancrofti and evidence for selection by albendazole and ivermectin combination treatment. Am J Trop Med Hyg 73:234–238
Schwenkenbecher JM, Kaplan RM (2009) Real-time PCR assays for monitoring benzimidazole resistance-associated mutations in Ancylostoma caninum. Exp Parasitol 122:6–10
Sellick CA, Reece RJ (2003) Modulation of transcription factor function by an amino acid: activation of Put3p by proline. EMBO J 22:5147–5153
Solana HD, Teruel MT, Najle R, Lanusse CE, Rodriguez JA (1998) The anthelmintic albendazole affects in vivo the dynamics and the detyrosination-tyrosination cycle of rat brain microtubules. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Ther Latinoam 48:199–205
Thomas I, Coles GC, Duffus K (2000) Triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica in southwest Wales. Vet Rec 146:200
Upcroft J, Mitchell R, Chen N, Upcroft P (1996) Albendazole resistance in Giardia is correlated with cytoskeletal changes but not with a mutation at amino acid 200 in β-tubulin. Microb Drug Resist 2:303–308
Acknowledgements
EC and LAR were in receipt of PhD studentships from the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (Northern Ireland).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chambers, E., Ryan, L.A., Hoey, E.M. et al. Liver fluke β-tubulin isotype 2 binds albendazole and is thus a probable target of this drug. Parasitol Res 107, 1257–1264 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1997-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1997-5