Abstract
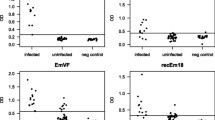
In 1997, an outbreak of alveolar echinococcosis in Japanese monkeys (Macaca fuscata) occurred in a zoo in Hokkaido, Japan. Twelve infected monkeys from a colony (n = 57) were diagnosed serologically by Western blotting, and ultrasonography showed the presence of tumor-like tissue in the livers of nine monkeys. The 12 infected monkeys have been treated with albendazole for 10 years without surgical resection. Ten of these monkeys have died so far; diagnoses were confirmed histopathologically through autopsy. Two of these monkeys are still alive. Recently, a significant difference between the two living monkeys was recognized. A difference in curative effect was demonstrated between the two living monkeys by radiography, contrast enhanced computed tomography, and contrast ultrasound. One showed metastasis to various organs, and the other appeared to be almost cured, as demonstrated by size reduction and calcification of the lesion after albendazole treatment for 10 years. This time, serological reexamination was performed to corroborate this apparent difference. The serological tests supported the preliminary imaging findings. In addition, the presence of albendazole metabolites in sera was confirmed by high-performance liquid chromatography. In this study, it was demonstrated that tests which have been used in human cases were also effective for diagnosing alveolar echinococcosis and for assessing curative effects in nonhuman primates such as M. fuscata.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann RW, Renner EC, Gottstein B, Grimm F, Eckert J, Renner EL, Swiss Echinococcosis Study Group (2004) Immunosurveillance of alveolar echinococcosis by specific humoral and cellular immune tests: long-term analysis of the Swiss chemotherapy trial (1976–2001). J Hepatol 41:551–559
Bacciarini LN, Gottstein B, Pagan O, Rehmann P, Gröne A (2004) Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Vet Pathol 41:229–234
Chonan T, Nishimura K, Hirama Y (2000) Rapid determination of residues of five kinds of veterinary drugs in livestock products by HPLC. J Food Hyg Soc Japan (Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi) 41:326–329 in Japanese, with English abstract
Fujimoto Y, Ito A, Ishikawa Y, Inoue M, Suzuki Y, Ohhira M, Ohtake T, Kohgo Y (2005) Usefulness of recombinant Em18-ELISA to evaluate efficacy of treatment in patients with alveolar echinococcosis. J Gastroenterol 40:426–431
Gottstein B, Bettens F, Parkinson AJ, Wilson F (1996) Immunological parameters associated with susceptibility or resistance to alveolar hydatid disease in Yupiks/Inupiats. Arctic Med Res 55:14–19
Ito A, Sako Y, Yamasaki H, Mamuti W, Nakaya K, Nakao M, Ishikawa Y (2003) Development of Em18-immunoblot and Em18-ELISA for specific diagnosis of alveolar echinococcosis. Acta Tropica 85:173–182
Kimura H, Furuya K, Kawase S, Sato C, Yamano K, Takahashi K, Uraguchi K, Ito T, Yagi K, Sato N (1999) Recent epidemiologic trends in alveolar echinococcosis prevalence in humans and animals in Hokkaido. J J A Inf D 52:117–120
Kishimoto M, Yamada K, Yamano K, Shimizu J, Lee K, Kobayashi N, Fujimoto S, Iwasaki T, Miyake Y (2009) Significance of imaging features of alveolar echinococcosis in studies on nonhuman primates. Am J Trop Med Hyg 81:540–544
Kondo H, Wada Y, Bando G, Kosuge M, Yagi K, Oku Y (1996) Alveolar hydatidosis in a gorilla and a ring-tailed lemur in Japan. J Vet Med Sci 58:447–449
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Ma L, Ito A, Liu YH, Wang XG, Yao YQ, Yu DG, Chen YT (1997) Alveolar echinococcosis: Em2plus-ELISA and Em18-western blots follow-up after treatment with albendazole. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 91:476–478
Rehmann P, Gröne A, Gottstein B, Völlm J, Sager H, Janovsky M, Bacciarini LN (2005) Detection of Echinococcus multilocularis infection in a colony of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) using serology and ultrasonography. J Vet Diagn Invest 17:183–186
Sato H, Mitamura H, Arai J, Kumagai M (1983) Serological diagnosis of human hydatid diseases by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Part 1) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay by multilocular Echinococcus antigen. Rep Hokkaido Inst Public Health 33:8–15 in Japanese, with English abstract
Sato C, Kawase S, Yano S, Nagano H, Fujimoto S, Kobayashi N, Miyahara K, Yamada K, Sato M, Kobayashi Y (2005) Outbreak of larval Echinococcus multilocularis infection in Japanese monkey (Macaca fuscata) in a zoo, Hokkaido: western blotting patterns in the infected monkeys. J Vet Med Sci 67:133–135
Tappe D, Brehm K, Frosch M, Blankenburg A, Schrod A, Kaup FJ, Mätz-Rensing K (2007) Echinococcus multilocularis infection of several old world monkey species in a breeding enclosure. Am J Trop Med Hyg 77:504–506
Torgerson PR, Budke C (2003) Echinococcosis—an international public health challenge. Res Vet Sci 74:191–202
Torgerson PR, Schweiger A, Deplazes P, Pohar M, Reichen J, Ammann RW, Tarr PE, Halkik N, Müllhaupt B (2008) Alveolar echinococcosis: from a deadly disease to a well-controlled infection. Relative survival and economic analysis in Switzerland over the 35 years. J Hepatol 49:72–77
Wen H, New RRC, Craig PS (1993) Diagnosis and treatment of human hydatidosis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 35:565–574
Yamano K, Hada N, Yamamura T, Takeda T, Honma H, Sawada Y (2006) Serodiagnostic potential of chemically synthesized glycosphingolipid antigens in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for alveolar echinococcosis. J Helminthol 80:387–391
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Dr. T. Chonan and Dr. T. Tazawa for a gift of chemicals used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamano, K., Kanetoshi, A., Goto, A. et al. Japanese monkey (Macaca fuscata) with alveolar echinococcosis after treatment with albendazole for 10 years: serodiagnosis and determination of albendazole metabolites. Parasitol Res 106, 69–74 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1627-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1627-2