Abstract
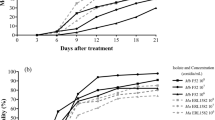
In view of the need to combat the generalized spread of resistance in ticks to commercial acaricides, the objective of this study was to evaluate the action of entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernema carpocapsae, strains Santa Rosa and ALL) on engorged female Anocentor nitens. Five ticks per Petri dish were exposed to concentrations of 500, 5,000, or 25,000 infective juveniles of S. carpocapsae for 72 h. After transferring the ticks to clean plates, biological parameters were analyzed. Related to strains Santa Rosa, the period of pre-oviposition (p = 0.0001), oviposition (p = 0.041), and the mass weight of eggs (p = 0.005) showed significant differences between the control group and treated group. When the strain ALL was tested, the control and treated groups differed between the periods of pre-oviposition (p = 0.001), oviposition (p = 0.001), and egg mass weight (p = 0.01). The egg mass conversion was less significant in the groups when exposed to strains Santa Rosa (p = 0.002) and ALL (p = 0.001) relative to the control. The efficacy of both entomopathogenic nematode strains used in this study was comparable to other biological control agents, showing their potential against A. nitens in the laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo JPM, López NJC (2002) Desplazamiento y parasitismo de los entomonematodos Steinernema feltiae (Rhabdiida: Steinernematidae) y Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditidae) hacia frutos infestados con la broca del café Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari) (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Rev Colomb Entomol 28:145–151
Adams BJ, Nguyen KB (2002) Taxonomy and systematics. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CABI, New York, pp 1–33
Aragão H, Fonseca F (1961) Notas de ixodologia. VIII. Lista e chave para os representantes da fauna ixodológica brasileira. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 59:115–129
Ávila CJ, Melhorança AL (1999) Eficiência do vírus de poliedrose nuclear de Anticarsia gemmatalis Hubner (Lepdoptera: Noctuidade), em mistura com herbicidas pós-emergentes, no controle do inseto, em soja. Rev Agric 28:339–341
Bennett GF (1974) Oviposition of Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) (Acari: Ixodidae). III. Oviposition pattern of acaricide resistant cepa. Acarologia 16:694–396
Bittencourt VRCP (1997) Avaliação da eficácia in vitro de dois isolados do fungo entomopatogênico Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) em fêmeas ingurgitadas de Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1887). Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 6:42–52
Brum JGW, Teixeira MO (1992) Acaricidal activity of Cedecea lapagei on engorged females of Boophilus microplus exposed to environment. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 44:543–544
Burnell AM, Stock P (2000) Heterorhabditis, Steinernema and their bacterial symbionts—lethal pathogens of insects. Nematology 2:31–42
Castro MEB, Ribeiro ZMA, Souza ML (2001) Estudo de Especificidade do Vírus da Lagarta da Soja (AgMNPV) em Cultura de Células. Ruralnet-Trabalhos Científicos 20 nov
Forst S, Clarke D (2002) Bacteria–nematode symbiosis. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CABI, New York, pp 57–77
Freitas-Ribeiro GM, Furlong J, Vasconcelos VO, Dolinski C, Loures-Ribeiro A (2005) Analysis of biological parameters of Boophilus microplus Canestrini, 1887 exposed to entomopathogenic nematodes Steinernema carpocapsae Santa Rosa and All Cepas (Steinernema: Rhabditida). Braz Arch Biol Technol 48:911–919
Kaaya GP, Samish M, Glazer I (2000) Laboratory evaluation of pathogenicity of entomogenous nematodes to African ticks species. Ann N Y Acad Sci 916:303–308
Kocan KM, Pidherney MS, Blouin EF, Claypool PL, Samish M, Glazer I (1998) Entomopathogenic nematodes as a potential biological control method of ticks. Ann N Y Acad Sci 9:355–364
Lindegren JE, Valero KA, Mackey BE (1993) Simple in vivo production and storage methods for Steinernema carpocapsae infective juvenile. J Nematol 25:193–197
Maulèon H, Barré N, Panoma S (1993) Pathogenicity of 17 isolates of entomophagous nematodes (Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) for the ticks Amblyomma variegatum (Fabricius), Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) and Boophilus annulatus (Say). Exp Appl Acarol 17:831–838
Pacheco DJP, Corrêa-Ferreira BS (2000) Parasitismo de Telenomus podisi Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) em populações de percevejos pragas da soja. An Soc Entomol Bras 29:295–302
Pfeifer BI (1995) Epidemiological aspects of equine babesioses in a herd of horses in Brazil. Vet Parasitol 58:1–8
Samish M, Glazer I (1991a) Pathogenicity of parasitic nematodes to ticks. Modern acarology, vol. 2. Academia, Prague, pp 629–632
Samish M, Glaze I (1991b) Killing ticks with parasitic nematodes of insects. J Invertebr Pathol 58:281–282
Samish M, Glazer I (1992) Infectivity of entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) to female ticks of Boophilus annulatus (Acari: Ixodidae). Entomol Soc Am 29:614–618
Samish M, Glazer I (2001) Entomopathogenic nematodes for the biocontrol of ticks. Trends Parasitol 17:368–371
Schulze P (1937) Anocentos columbianus. Zool Anzeiger 120(1-2): 24–27
Sutherst RW, Wilson LJ, Cook IM (2000) Predation of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) (Acarina: Ixodidae), in three pastures Australian. Aust J Entomol 39:70–77
Vasconcelos VO, Furlong J, Freitas GM, Dolinski C, Mendonça AM, Devitte RCR, Prata M (2004) Steinernema glaseri Santa Rosa cepa (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) and Heterorhabditis bacteriophora CCA Cepa (Rhabditida: Heterorhabditldae) as biological control agents of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 94:201–206
Zhioua E, Brun RA, Ginsberg HS, Aeschlimann A (1995) Pathogenicity of Steinernema carpocapsae and Steinernema glaseri (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) to Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 32:900–905
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freitas-Ribeiro, G.M., Vasconcelos, V.O., Furlong, J. et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of strains of Steinernema carpocapsae Santa Rosa and ALL (Steinernematidae: Rhabditida) to control engorged female Anocentor nitens (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 104, 1203–1206 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1313-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1313-9