Abstract
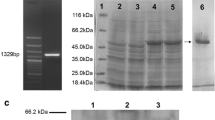
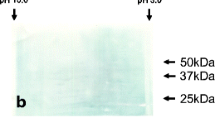
Tubulins are heterodimeric molecules responsible for the polymerization of microtubules in apicomplexan parasites. The α-tubulin, a subcellular structural protein of Eimeria acervulina, was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli as an α-tubulin-GST fusion protein. Immunogenicity of the recombinant protein was studied in chickens by subcutaneous injection of 50, 100, or 150 μg of the protein with or without Freund’s adjuvant. Immunization with 150 μg α-tubulin-GST protein in combination with Freund’s adjuvant conferred partial protection against E. acervulina oocyst challenge, as shown by a 36% reduction in oocyst shedding, a marked decrease in intestinal lesion score and a significant increase in body weight gain in comparison with the nonimmunized controls. The results suggest that α-tubulin protein may be used as an effective vaccine antigen for the control of Eimeria infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Blake DP, Hesketh P, Archer A, Carroll F, Smith AL, Shirley MW (2004) Parasite genetics and the immune host: recombination between antigenic types of Eimeria maxima as an entree to the identification of protective antigens. Mol Biochem Parasitol 138:143–152
Castle MD, Jenkins MC, Danforth HD, Lillehoj HS (1991) Characterization of a recombinant Eimeria acervulina antigen expressed in sporozoite and merozoite developmental stages. J Parasitol 77:384–390
Chapman HD (1997) Biochemistry, genetic and applied aspects of drug resistance in Eimeria parasites of the fowl. Avian Pathol 26:221–244
Dalloul RA, Lillehoj HS (2005) Recent advances in immunomodulation and vaccination strategies against coccidiosis. Avian Dis 49:1–8
Dalloul RA, Lillehoj HS (2006) Poultry coccidiosis: recent advancements in control measures and vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 5:143–163
Ding X, Lillehoj HS, Quiroz MA, Bevensee E, Lillehoj EP (2004) Protective immunity against Eimeria acervulina following in ovo immunization with a recombinant subunit vaccine and cytokine genes. Infect Immun 72:6939–6944
Ding X, Lillehoj HS, Dalloul RA, Min W, Sato T, Yasuda A, Lillehoj EP (2005) In ovo vaccination with the Eimeria tenella EtMIC2 gene induces protective immunity against coccidiosis. Vaccine 23:3733–3740
Du A, Hu S, Wang S (2005) Eimeria tenella: ginsenosides-enhanced immune response to the immunization with recombinant 5401 antigen in chickens. Exp Parasitol 111:191–197
Jenkins MC, Lillehoj HS, Dame JB (1988) Eimeria acervulina: DNA cloning and characterization of recombinant sporozoite and merozoite antigens. Exp Parasitol 66:96–107
Jenkins MC, Lillehoj HS, Barta JR, Danforth HD, Strohlein DA (1990) Eimeria acervulina: cloning of a cDNA encoding an immunogenic region of several related merozoite surface and rhoptry proteins. Exp Parasitol 70:353–362
Johnson J, Reid WM (1970) Anticoccidial drugs: lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens. Exp Parasitol 28:30–36
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kopko SH, Martin DS, Barta JR (2000) Responses of chickens to a recombinant refractile body antigen of Eimeria tenella administered using various immunizing strategies. Poult Sci 79:336–342
Lillehoj HS (1998) Role of T lymphocytes and cytokines in coccidiosis. Int J Parasitol 28:1071–1081
Lillehoj HS, Lillehoj EP (2000) Avian coccidiosis. A review of acquired intestinal immunity and vaccination strategies. Avian Dis 44:408–425
Lillehoj HS, Choi KD, Jenkins MC, Vakharia VN, Song KD, Han JY, Lillehoj EP (2000) A recombinant Eimeria protein inducing interferon-gamma production: comparison of different gene expression systems and immunization strategies for vaccination against coccidiosis. Avian Dis 44:379–389
Lillehoj HS, Min W, Dalloul RA (2004) Recent progress on the cytokine regulation of intestinal immune responses to Eimeria. Poult Sci 83:611–623
Lillehoj HS, Ding X, Quiroz MA, Bevensee E, Lillehoj EP (2005) Resistance to intestinal coccidiosis following DNA immunization with the cloned 3-1E Eimeria gene plus IL-2, IL-15, and IFN-gamma. Avian Dis 49:112–117
Morrissette NS, Sibley LD (2002) Cytoskeleton of apicomplexan parasites. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:21–38 table of contents
O’Lorcain P, Talebi A, Mulcahy G (1996) B-cell epitope mapping within the MA16 antigenic sequence found in Eimeria acervulina merozoites and sporozoites. Vet Parasitol 66:147–157
Russell DG, Burns RG (1984) The polar ring of coccidian sporozoites: a unique microtubule-organizing centre. J Cell Sci 65:193–207
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Shirley MW, Smith AL, Blake DP (2007) Challenges in the successful control of the avian coccidia. Vaccine 25:5540–5547
Siverajah S, Ryce C, Morrison DA, Ellis JT (2003) Characterization of an alpha tubulin gene sequence from Neospora caninum and Hammondia heydorni, and their comparison to homologous genes from Apicomplexa. Parasitology 126:561–569
Strober W (2001) Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Current Protocols in Immunology. Wiley, New York
Talebi A, Mulcahy G (1995) Correlation between immune responses and oocyst production in chickens monospecifically infected with Eimeria maxima. Avian Pathol 24:485–495
Talebi A, Mulcahy G (2005) Partial protection against Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella induced by synthetic peptide vaccine. Exp Parasitol 110:342–348
Trout JM, Lillehoj HS (1996) T lymphocyte roles during Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 53:163–172
Vermeulen AN (1998) Progress in recombinant vaccine development against coccidiosis. A review and prospects into the next millennium. Int J Parasitol 28:1121–1130
Wallach M, Smith NC, Petracca M, Miller CM, Eckert J, Braun R (1995) Eimeria maxima gametocyte antigens: potential use in a subunit maternal vaccine against coccidiosis in chickens. Vaccine 13:347–354
Wu SQ, Wang M, Liu Q, Zhu YJ, Suo X, Jiang JS (2004) Construction of DNA vaccines and their induced protective immunity against experimental Eimeria tenella infection. Parasitol Res 94:332–336
Xu SZ, Chen T, Wang M (2006) Protective immunity enhanced by chimeric DNA prime-protein booster strategy against Eimeria tenella challenge. Avian Dis 50:579–585
Zhu G, Keithly JS (1996) The beta tubulin gene of Eimeria tenella. Mol Biochem Parasitol 76:315–319
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Prof. Xun Suo for providing experimental instruments and facilities and Ms. Chong Deng and Mr. Jingpeng Han for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, J., Bao, W., Liu, Q. et al. Immunoprotection of chickens against Eimeria acervulina by recombinant α-tubulin protein. Parasitol Res 103, 1133–1140 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1106-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1106-1