Abstract
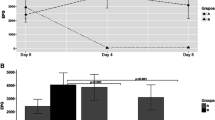
Fasciola hepatica secretes proteolytic enzymes during liver invasion. The present study examined the effects of the cysteine protease inhibitor Ep-475 on sheep considering the following variables: serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, l-lactate dehydrogenase, and γ-glutamyltransferase, liver fluke fecundity, egg viability, parasite burden, and size. Twenty-four male sheep were randomly allocated in four groups of six animals each as follows: group A was infected with F. hepatica metacercariae and treated with 50 mg/kg of Ep-475, group B was infected and untreated, group C was uninfected and treated, and group D was uninfected and untreated. All animals were euthanized 10 weeks after the experimental infection. Serum activities of enzymes in infected animals were significantly lower in Ep-475-treated sheep than in untreated controls, although liver damage was produced. No significant reduction in total worm burden was observed between treated and untreated sheep. However, there was a significant difference on the average size, structure development, ova counts, and egg viability of liver flukes from these two groups. Results showed that Ep-475 reduces liver damage due to fasciolosis and induces an impairment of liver fluke growth and fecundity. These effects pinpoint liver fluke proteases as potential targets for pharmacological intervention.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcala-Canto Y, Ibarra-Velarde F, Sumano-Lopez H, Gracia-Mora J, Alberti-Navarro A (2006) Dose-response inhibition of proteolytic activity by a cysteine protease inhibitor in a murine model of fasciolosis. Parasitol Res 98:438–442
Alvarez LI, Solana HD, Mottier ML, Virkel GL, Fairweather I, Lanusse CE (2005) Altered drug influx/efflux and enhanced metabolic activity in triclabendazole-resistant liver flukes. Parasitology 131:501–510
Bland M (2000) An introduction to medical statistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Bradley RE, Randell WF, Armstrong DA (1981) Anthelmintic efficacy of albendazole in calves with naturally acquired Fasciola hepatica infections. Am J Vet Res 42:1062–1064
Calleja C, Bigot K, Eeckhoutte C, Sibille P, Boulard C, Galtier P (2000) Comparison of hepatic and renal drug-metabolising enzyme activities in sheep given single or two-fold challenge infections with Fasciola hepatica. Int J Parasitol 30:953–958
Dalton JP, Heffernan M (1989) Thiol proteases released in vitro by Fasciola hepatica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 35:161–166
Dalton JP, McGonicle S, Rolph TP, Andrews SJ (1996) Induction of protective immunity in cattle against infection with Fasciola hepatica by vaccination with cathepsin L proteinases and with haemoglobin. Infect Immun 64:5066–5074
Gonzalo-Orden M, Millan L, Alvarez M, Sanchez-Campos S, Jimenez R, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Tunon MJ (2003) Diagnostic imaging in sheep hepatic fascioliasis: ultrasound, computer tomography and magnetic resonance findings. Parasitol Res 90:359–364
Mulcahy G, Dalton JP (2001) Cathepsin L proteinases as vaccines against infection with Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) in ruminants. Res Vet Sci 70:83–86
Perneger TV (1998) What’s wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. Br Med J 316:1236–1238
SAS (1992) Release 6.11. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Smith AM, Dowd AJ, Heffernan M, Robertson CD, Dalton JP (1993) Fasciola hepatica: a secreted cathepsin L-like proteinase cleaves host immunoglobulin. Int J Parasitol 23:977–983
Thienpont D, Rochete F, Vanprijs OF (1979) Diagnosing helminthiasis through coprological examination. Janssen Research Foundation, Beerse, Belgium
Wijffels GL, Salvatore L, Dosen M, Waddington J, Wilson L, Thompson C, Campbell N, Sexton J, Wicker J, Bowen F, Friedel T, Spithill TW (1994) Vaccination of sheep with purified cysteine proteinases of Fasciola hepatica decreases worm fecundity. Exp Parasitol 78:132–148
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to Dr. John P. Dalton of the Institute for the Biotechnology of Infectious Diseases, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, for excellent assistance. This study complies with the current laws of Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alcala-Canto, Y., Ibarra-Velarde, F., Sumano-Lopez, H. et al. Effect of a cysteine protease inhibitor on Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) fecundity, egg viability, parasite burden, and size in experimentally infected sheep. Parasitol Res 100, 461–465 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0308-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0308-7