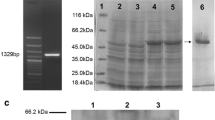
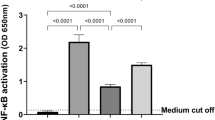
Abstract
In previous studies, cytoplasmic repetitive antigen (CRA) and flagellar repetitive antigen (FRA) proteins induced specific humoral and cellular immune responses in susceptible and resistant mice in the absence of Trypanosoma cruzi infection with a significant induction of the Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) production in those animals. In this follow-up paper, the immunostimulatory and protective effects of these proteins were evaluated by immunizing with CRA or FRA antigens, BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice and challenging with a T. cruzi (Y strain). Both proteins induced humoral response with high levels of IgG isotypes as well as cellular immunity with high levels of IFN-γ when compared to controls. However, the lymphocyte proliferative response was minimal. The survival rate at 30 days post-infection was significant in CRA (60%) or FRA (50%) - immunized BALB/c mice and CRA (83.3%) - immunized C57BL/6 mice. Taken as a whole these findings indicate that CRA and FRA are immunogenic and potentially important for protective immunity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsohn IA, Coffman RL (1995) Cytokine and nitric oxide regulation regulation of the immunosuppression in Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Immunol 155:3955–3963
Abrahamsohn IA, Coffman RL (1996) Trypanosoma cruzi: IL-10, TNF, IFN-γ, and IL-12 regulate innate and acquired immunity to infection. Exp Parasitol 84:231–244
Aliberti JCS, Cardoso MAG, Martins GA, Gazzinelli RT, Vieira LQ, Silva JS (1996) Interleukin-12 mediates resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi in mice and is produced by murine macrophages in response to live trypomastigotes. Infect Immunol 64(6):1961–1967
Andrade V, Barral-Neto M, Andrade SG, Magalhães JB (1985) Aspectos imunológicos da infecção de seis linhagens isogênicas de camundongos por três diferentes cepas do Trypanosoma cruzi. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 80(2):203–211
Araújo FG, Helman B, Tighe L (1984) Antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi detected by different classses and subclasses of antibodies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 78:672–677
Brener Z (1962) Therapeutic activity and criterion of cure in mice experimentally infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo 4:389–396
Brenner Z, Krettli AU (1990) Immunology of Chagas disease. In: Wyler DJ (eds) Modern parasite biology-celullar, immunological, and molecular aspects. Freeman Company, New York, pp 247–261
Brodskyn CI, Silva AMM, Takehara HA, Mota I (1989) IgG subclasses responsible for immune clearance in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Immunol Cell Biol 67:343–348
Cardillo F, Voltarelli JC, Reed SG, Silva JS (1996) Regulation of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice by gamma interferon and interleukin 10: role of NK cells. Infect Immunol 64(1):128–134
Curotto de Lafaille MA, Barbosa de Oliveira LC, Lima GCA, Abrahamsohn IA (1990) Trypanosoma cruzi: maintenance of parasite-specific T cell reponses in lymph nodes during the acute phase of the infection. Exp Parasitol 70:164–174
Franco da Silveira J (1992) Trypanosoma cruzi recombinant antigens for serodiagnosis. In: Wendel S, Brener B, Camargo ME, Rasser A (eds) Chagas disease (American Trypanosomiasis): its impact on transfusion and clinical medicine. International Society of Blood Transfusion, SP, pp 207–217
Frasch ACC, Cazzullo JJ, Aslund L, Petterson U (1991) Comparison of genes encoding Trypanosoma cruzi antigens. Parasitol Today 7:148 –151
Gazzinelli RT, Oswald IP, James SL, Sher A (1992) IL-10 inhibits parasite killing and nitrogen oxide production by IFN-γ-activated macrophages. J Immunol 148(6):1792–1796
Gomes YM (1997) PCR and sero-diagnosis of chronic Chagas’ disease. Biotecnological advances. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 66:107119
Gomes YM, Nakazawa MN, Abath FGC, Minoprio P, Vouldoukis I, Monjour L (1999) Partial protection of mice against Trypanosoma cruzi after immunization with TcY antigenic preparation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 94:167–172
Jankovic D, Sher A, Yap G (2001) Th1/Th2 effector choice in parasitic infection: decision making by committe. Curr Opin Immunol 13:403–409
Kierszenbaum F (1981) On evasion of Trypanosoma cruzi from host immune response. Lymphoproliferative responses to trypanosomal antigens during acute and chronic experimental Chagas’ disease. Immunology 44:641–648
Kierszenbaum F, Hayes MM (1980) Evaluation of lymphocyte responsiveness to polyclonal activators during acute and chronic experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg 29(4):708–710
Krieger MA, Almeida E, Oelemann W, Lafaille JJ, Pereira JB, Carvalho MR, Goldenberg S (1992) Use of recombinant antigens for the accurate immunodiagnosis of Chagas’disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg 46(4):427–434
Millar AE, Kahn SJ (2000) The SA85-1.1 protein of the Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase superfamily is a dominant T-cell antigen. Infect Immunol 68(6):3574–3580
Miller MJ, Wrightsman RA, Manning JE (1996) Trypanosoma cruzi: protective immunity in mice immunized with paraflagellar rod proteins is associated with a T-helper type 1 response. Exp Parasitol 84:156–167
Minoprio PM, Eisen H, Forni L, D’Imperio Lima MR, Joskowicz M, Coutinho A (1986) Polyclonal lymphocyte responses to murine T. cruzi infection. I - Quantitation of both T- and B- cell responses. Scand J Immunol 24:661–668
Minoprio P, Burlen O, Pereira P, Guilbert B, Andrade L, Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M, Coutinho A (1988) Most B cells in acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection lack parasite specificity. Scand J Immunol 28:553–561
Motran C, Gruppi A, Vullo CM, Pistoresi-Palencia MC, Serra HM (1996) Involvement of acessory cells in the Trypanosoma cruzi-induced inhibition of the polyclonal response of T lymphocytes. Parasite Immunol 18:43–48
Muñoz-Fernández MA, Fernández MA, Fresno M (1992) Synergism between tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ on macrophage activation for the killing of intracellular Trypanosoma cruzi through a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Eur J Immunol 22:301–307
Nabors GS, Tarleton RL (1991) Differential control of IFN-γ and IL-2 production during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Immunol 146(10):3591–3598
Pereira VRA, Lorena VMB, Nakazawa M, Galvão da Silva AP, Montarroyos U, Correa-Oliveira R, Gomes YM (2003a) Evaluation of immune response in C57Bl/6 mice immunized with CRA and FRA recombinant antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 36(4):435–440
Pereira VRA, Lorena VMB, Verçosa AFA, Galvão da Silva AP, Silva ED, Ferreira AGP, Montarroyos U, Gomes YM (2003b) Antibody isotype responses in BALB/c mice immunized with the cytoplasmic repetitive antigen and flagellar repetitive antigen recombinant antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 98(6):823–825
Pereira VRA, Lorena VMB, Galvão da Silva AP, Coutinho EM, Miranda P, Silva ED, Ferreira AGP, Krieger MA, Goldenberg S, Soares MBP, Correa-Oliveira R, Gomes YM (2004) Immunization with cytoplasmic repetitive antigen and flagellar repetitive antigen of Trypanosoma cruzi stimulates a cellular immune response in mice. Parasitology 129(5):563–570
Pereira-Chioccola VL, Costa F, Ribeirão M, Soares IS, Arena F, Schenkman S, Rodrigues MM (1999). Comparison of antibody and protective immune responses against Trypanosoma cruzi infection elicited by immunization with a parasite antigen delivered as naked DNA or recombinant protein. Parasite Immunol 21:103–110
Powell MR, Wassom DL (1993) Host genetics and resistance to acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. I. Antibody isotype profiles. Parasite Immunol 15:215–221
Ramos C, Schädtler-Siwon I, Ortiz-Ortiz L (1979) Supressor cells present in the spleens of Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice. J Immunol 122(4):1243–1247
Reed SG (1988) In vivo administration of recombinant IFN-γ induces macrophage activation, and prevents acute disease, immune supression, and death in experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infections. J Immunol 140:4342–4347
Rottenberg ME, Bakhiet M, Olsson T, Kristensson TM, Hans W, Örn A (1993) Differential susceptibilities of mice genomically deleted of CD4 and CD8 to infections with Typanosoma cruzi or Trypanosoma brucei. Infect Immunol 61(12):5129–5133
Santori FR, Paranhos-Bacalla GS, Silveira JF, Yamauchi LM, Araya JE, Yoshida N (1996) A recombinant protein based on the Trypanosoma cruzi metacyclic Trypomastigote 82-kilodalton antigen that induces on effective imune response to acute infection. Infect Immunol 64:1093–1099
Schnapp AR, Eickhoff CS, Sizemore D, Curtis III R, Hoft DF (2002) Cruzipain induces both mucosal and systemic protection against Trypanosoma cruzi in mice. Infect Immun 70(9):5065–5074
Seder R, Gazzinelli R, Sher A, Paul WE (1993) Interleukin 12 acts directly on CD4+ T cells to enhance priming for interferon γ production and diminishes interleukin 4 inhibition of such priming. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10188–10192
Sher A, Coffman RL (1992) Regulation of immunity to parasites by T cells and T cell-derived cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 10:385–409
Silva JS, Morryssey PJ, Grabstein KH, Mohler KM, Anderson D, Reed SG (1992) Interleukin-10 and interferon-γ regulation of experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Exp Med 175:169–174
Silva JS, Vespa GNR, Cardoso MAG, Aliberti JCS, Cunha FQ (1995) Tumor necrosis factor alpha mediates resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice by inducing nitric oxide production in infected gamma-interferon-activated macrophages. Infect Immunol 63(12):4862–4867
Taibi A, Espinoza AG, Ouaissi A (1995) Trypanosoma cruzi analysis of cellular and humoral response against a protective recombinant antigen during experimental Chagas’ disease. Immunol Lett 48:193–200
Takehara HA, Perini A, Silva MH, Mota I (1981) Trypanosoma cruzi: role of different antibody classes in protection against infection in the mouse. Exp Parasitol 52:137–146
Vespa GNR, Cunha FQ, Silva JS (1994) Nitric oxide is involved in control of Trypanosoma cruzi-induced parasitemia and directly kills the parasite in vitro. Infect Immunol 62(11):5177–5182
WHO- World Health Organization (2002) The World Health Report, Geneva
Wrighstsman R, Krassner S, Watson J (1982) Genetic control of responses to Trypanosoma cruzi in mice: multiple genes influencing parasitemia and survival. Infect Immunol 36(2):637–44
Zambrano-Villa S, Rosales-Borjas D, Carrero JC, Ortiz-Ortiz L (2002) How protozoan parasites evade the immune response. Trends Parasitol 18(6):272–278
Zinkernagel RM (2000). Localization dose and time antigens determine immune reactivity. Sem Immunol 12:163–171
Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H (2001) Regulation of the immune response by antigen. Science 293(5528):251–253
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Roni Evencio Araújo for his technical assistance . This investigation was supported by Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Centro de Pesquisas Aggeu Magalhães and Biomanguinhos) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). This research was partially supported by Bio-Manguinhos/FIOCRUZ and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, V.R.A., Lorena, V.M.B., Nakazawa, M. et al. Humoral and cellular immune responses in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice immunized with cytoplasmic (CRA) and flagellar (FRA) recombinant repetitive antigens, in acute experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Parasitol Res 96, 154–161 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-005-1336-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-005-1336-4