Abstract
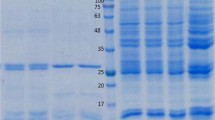
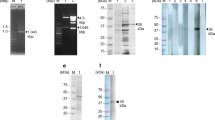
Clonorchis sinensis is a Chinese liver fluke that chronically resides in the biliary tract. The fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) is known to play an important role in the intracellular transport of long-chain fatty acids that are obtained by the fluke from the host. Although FABP has stimulated considerable interest as a vaccine target candidate, the nature of FABP from C. sinensis (CsFABP) remains unclear. In this paper, we describe the cloning and expression of recombinant FABP and immune cross-reaction by Western blot analysis. Sequence analysis revealed that the CsFABP cDNA contained a single open reading frame (ORF) coding for 134 amino acids with an estimated molecular mass of a 15.2 kDa. The DNA sequence of CsFABP cDNA showed significant homology to schistosome cytosolic FABPs, with a 49% amino acid sequence identity and 89% similarity to Schistosoma japonicum. This DNA also showed a high sequence similarity at the amino acid level to S. mansoni (Sm14; 83%) and Fasciola hepatica (80%). The CsFABP cDNA was cloned into expression vector pET28a, expressed in Escherichia coli and the recombinant protein purified by affinity chromatography. The recombinant CsFABP was cross-reacted with sera obtained from patients with fascioliasis and paragonimiasis. These results suggest that CsFABP may be useful as a vaccine for clonorchiasis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpers DH, Strauss AW, Ockner RK, Bass NM, Gordon JI (1984) Cloning of a cDNA encoding rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:313–317
Bassuk JA, Tsichlis PN, Sorof S (1987) Liver fatty acid binding protein is the mitosis-associated polypeptide target of a carcinogen in rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7547–7551
Baxa CA, Sha RS, Buelt MK, Smith AJ, Matarese V, Chinander LL, Boundy KL, Bernlohr DA (1989) Human adipocyte lipid-binding protein: purification of the protein and cloning of its complementary DNA. Biochemistry 28:8683–8690
Becker MM, Kalinna BH, Waine GJ, McManus DP (1994) Gene cloning, overproduction and purification of a functionally active cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding protein (Sj-FABPC) from the human blood fluke Schistosoma japonicum. Gene 148:321–325
Bozas SE, Spithill TW (1996) Identification of 3-hydroxyproline residues in several proteins of Fasciola hepatica. Exp Parasitol 82:69–72
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chapman RW (1999) Risk factors for biliary tract carcinogenesis. Ann Oncol [Suppl 4]:10:308–311
Crompton DWT (1999) How much human helminthiasis is there in the world? J Parasitol 85:397–403
Eads J, Sacchettini JC, Kromminga A, Gordon JI (1993) Escherichia coli-derived rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein with bound myristate at 1.5 A resolution and I-FABPArg106→Gln with bound oleate at 1.74 A resolution. J Biol Chem 268:26375–26385
Estuningsih E, Smooker PM, Wiedosari E, Widjajanti S, Vaiano S, Partoutomo S, Spithill TW (1997) Evaluation of antigens of Fasciola gigantica as vaccines against tropical fasciolosis in cattle. Int J Parasitol 27:1419–1428
Gong YZ, Everett ET, Schwartz DA, Norris JS, Wilson FA (1994) Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and expression of a 14-kDa bile acid-binding protein from rat ileal cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4741–4745
Hillyer GV, Rosa MI, Alicea H, Hernandez A (1987) Acquired resistance to Faciola hepatica in cattle using a purified adult worm antigen. Am J Trop Med Hyg 37:363–369
Hillyer GV, De Galanes M, Rosa MI, Montealegre F (1988) Acquired immunity in schistosomiasis with purified Fasciola hepatica cross-reactive antigens. Vet Parasitol 29:265–280
Kennedy MW, Scott JC, Lo S, Beauchamp J, McManus DP (2000) Sj-FABPc fatty-acid-binding protein of the human blood fluke Schistosoma japonicum: structural and functional characterization and unusual solvent exposure of a portal-proximal tryptophan residue. Biochem J 349:377–384
Kim YI, Rim HJ, Park UB (1993) Effect of Clonorchis sinensis infection and dimethylnitrosamine administration on the induction of cholangiocarcinoma in Syrian golden hamster. Korean J Pathol 31:21–30
Lee JS, Lee J, Park SJ, Yong TS (2003) Analysis of the genes expressed in Clonorchis sinensis adults using the expressed sequence tag approach. Parasitol Res 91:283–289
McManus DP, Bryant C (1986) Biochemistry and physiology of Echinococcus. In: Thompson RCA (ed) The biology of Echinococcus and hydatid disease. Allen & Unwin, London
Moser D, Tendler M, Griffiths G, Klinkert MQ (1991) A 14-kDa Schistosoma mansoni polypeptide is homologous to a gene family of fatty acid binding proteins. J Biol Chem 266:8447–8454
Murphy EJ (1998) L-FABP and I-FABP expression increase NBD-stearate uptake and cytoplasmic diffusion in L cells. Am J Physiol 275:G244–G249
Rodriguez-Perez J, Rodriguez-Medina JR, Garcia-Blanco MA, Hillyer GV (1992) Fasciola hepatica: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression of a gene encoding a polypeptide homologous to a Schistosoma mansoni fatty acid binding protein. Exp Parasitol 74:400–407
Sedzik J, Bergfors T, Jones TA, Weise M (1988) Bovine P2 myelin basic protein crystallizes in three different forms. J Neurochem 50:1908–1911
Smooker PM, Hickford DE, Vaiano SA, Spithill TW (1997) Isolation, cloning, and expression of fatty-acid binding proteins from Fasciola gigantica. Exp Parasitol 85:86–91
Tendler M, Brito CA, Vilar MM, Serra-Freire N, Diogo CM, Almeida MS, Delbem AC, Da Silva JF, Savino W, Garratt RC, Katz N, Simpson AJ (1996) A Schistosoma mansoni fatty acid-binding protein, Sm 14, is the potential basis of a dual-purpose anti-helminth vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:269–273
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1992) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Biotechnology 24:145–149
Veerkamp JH (1995) Fatty acid transport and fatty acid-binding proteins. Proc Nutr Soc 54:23–37
Veerkamp JH, Moerkerk HTB van, Prinsen CF, Kuppevelt TH van (1999) Structural and functional studies on different human FABP types. Mol Cell Biochem 192:137–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JS., Yong, TS. Expression and cross-species reactivity of fatty acid-binding protein of Clonorchis sinensis . Parasitol Res 93, 339–343 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1139-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1139-z