Abstract
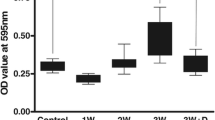
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) is involved in the pathogenesis of parasitic meningitis caused by the nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The present study evaluated the efficacy of albendazole therapy in BALB/c mice infected with the third stage larvae of this nematode. Albendazole showed a pronounced larvicidal activity. Eosinophil numbers significantly increased in infected mice but decreased upon administration of albendazole. Densitometric scanning indicated that albendazole reduced gelatinolytic activity detected by gelatin-substrate zymography. In the cerebrospinal fluid, albendazole reduced the lytic area intensity of the 94 kDa MMP-9 band by 46.5% within 7 days, and by 51.5% by day 14. Examination of brain tissue revealed a similar pattern of decrease (48.6% by day 7, and 53.9% by day 14). Albendazole may thus be an effective compound for the treatment of angiostrongyliasis through its larvicidal activity and facilitation of an improved inflammatory response via the reduction of MMP-9 activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alicata JE (1965) Biology and distribution of the rat lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, and its relationship to eosinophilic meningoencephalitis and other neurological disorders of man and animals. In: Dawes B (ed) Advances in parasitology. Academic, London, pp 223–248
Ash LR (1970) Diagnostic morphology of the third-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus, and Anafilaroides rostratus (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea). J Parasitol 56:249–253
Birkedal-Hansen H (1995) Proteolytic remodeling of extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:728–735
Dorta-Contreras AJ, Reiber H (1998) Intrathecal synthesis of immunoglobulins in eosinophilic meningoencephalitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 5:452–455
Gijbels K, Galardy RE, Steinman L (1994) Reversal of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with a hydroxamate inhibitor of matrix metalloproteases. J Clin Invest 94:2177–2182
Hsu WY, Chen JY, Chien CT, Chi CS, Han NT (1990) Eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 9:443–445
Hwang KP, Chen ER (1988) Larvicidal effect of albendazole against Angiostrongylus cantonensis in mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg 39: 191–195
Hwang KP, Chen ER (1991) Clinical studies on angiostrongyliasis cantonensis among children in Taiwan. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 22:194–199
Ismail Y, Arsura EL (1993) Eosinophilic meningitis. West J Med 159:623
James DM, Gilles HM (1985) Human antiparasitic drugs: pharmacology and usage. Wiley, New York
John DT, Martinez AJ (1975) Animal model of human disease. Central nervous system infection with the nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Animal model: eosinophilic meningoencephalitis in mice infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Am J Pathol 80:345–348
Jung H, Hurtado M, Sánchez M, Medina MT, Sotelo J (1990) Plasma and CSF levels of albendazole and praziquantel in patients with neurocysticercosis. Clin Neuropharmacol 13:559–564
Kaczmarek L, Lapinska-Dzwonek J, Szymczak S (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in the adult brain physiology: a link between c-Fos, AP-1 and remodeling of neuronal connections? EMBO J 21:6643–6648
Lakwo TT, Ishih A, Terada M, Sano M (1998) Effects of albendazole against larval and adult Angiostrongylus cantonensis in rats. Parasitol Int 47: 281–288
Leppert D, Lindberg RL, Kappos L, Leib SL (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases: multifunctional effectors of inflammation in multiple sclerosis and bacterial meningitis. Brain Res Rev 36:249–257
Liuzzi GM, Mastroianni CM, Santacroce MP, Fanelli M, D’Agostino C, Vullo V, Riccio P (2000) Increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated neurological diseases. J Neurovirol 6:156–163
Maki J, Yanagisawa T (1986) Studies on anthelmintic effects of flubendazole and mebendazole on the rat lungworm Angiostrongylus cantonensis in mice and rats. J Parasitol 72:512–516
Maisonneuve H, Rossignol JF, Addo A, Mojon M (1985) Ovicidal effects of albendazole in human ascariasis, ancylostomiasis and trichuriasis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 79:79–82
Matsuura E, Umehara F, Hashiguchi T, Fujimoto N, Okada Y, Osame M (2000) Marked increase of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with fungal or tuberculous meningoencephalitis. J Neurol Sci 173: 45–52
McQuibban GA, Gong JH, Wong JP, Wallace JL, Clark-Lewis I, Overall CM (2002) Matrix metalloproteinase processing of monocyte chemottractant proteins generates CC chemokine receptor antagonists with anti-inflammatory properties in vivo. Blood 100:1160–1167
Muller R (1975) Worms and disease. Heinemann, London
Mun-Bryce S, Rosenberg GA (1998) Gelatinase B modulates selective opening of the blood-brain barrier during inflammation. Am J Physiol 274:1203–1211
Pene P, Mojon M, Garin JP, Coulaud JP, Rossignol JF (1982) Albendazole: a new broad spectrum anthelmintic. Double-blind multicenter clinical trial. Am J Trop Med Hyg 31:263–266
Şenel A, çokluk C, Yildiz L, Ağar E, Ayyildiz M, Önder A (2000) The effects of albendazole solution at scolocidal concentration in the rat brain. Acta Neurochir 142:929–933
Sotelo J, Jung H (1998) Pharmacokinetic optimisation of the treatment of neurocysticercosis. Clin Pharmacokinet 34:503–515
Venkatesan P (1998) Albendazole. J Antimicrob Chemother 41:145–147
Williams PL, Leib SL, Kamberi P, Leppert D, Sobel RA, Bifrare YD, Clemons KV, Stevens DA (2002) Levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 within cerebrospinal fluid in a rabbit model of coccidioidal meningitis and vasculitis. J Infect Dis 186:1692–1695
Woessner JFJr (1994) The family of matrix metalloproteinases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 732:11–21
Yong VW, Krekoski CA, Forsyth PA, Bell R, Edwards DR (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases and diseases of the CNS. Trends Neurosci 21:75–80
Yoshimura K, Sugaya H, Kawamura K, Kumagai M (1988) Ultrastructural and morphometric analyses of eosinophils from the cerebrospinal fluid of the mouse and guinea-pig infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Parasite Immunol 10:411–423
Acknowledgement
This study was supported in part by a grant CSMC-89-OM-B-015 from the Chung Shan Medical University, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, K.P., Wang, C.J., Lai, S.C. et al. The efficacy of therapy with albendazole in mice with parasitic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis . Parasitol Res 93, 311–317 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1105-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1105-9