Abstract
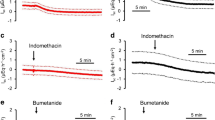
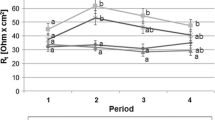
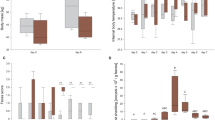
To study the pathophysiology of diarrhoea in coccidial infections, Na+ and Cl− fluxes (J Na, J Cl), short circuit current (I sc) and tissue conductance (g t) were determined in stripped gut epithelia of Eimeria separata infected rats employing the Ussing chamber technique. E. separata invades enterocytes of the caecum and proximal colon. Na+ absorption was generally reduced in infected tissues, Cl− absorption only in the caecum. I sc values were increased in the caecum and reduced in the proximal colon. Tissue conductance was not affected. Values tended to normal with time after infection. Theophylline caused markedly increased I sc and g t values in the caecum epithelia of infected rats. In the epithelia of the distal colon, i.e. the non-infested part of the large intestine, g t values remained unaffected but I sc was fourfold increased. This I sc increase was strongly sensitive to amiloride, suggesting a compensatory activation of Na+ channels in the distal colon of infected rats. Accordingly, serum levels of aldosterone, which activates Na+ channels in the distal colon, were increased to eightfold levels in infected animals. Thus compensatory Na+ absorption was under endocrine control.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen PC (1987) Physiological responses of chicken gut tissue to coccidial infection: comparative effects of Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria mitis on mucosal mass, carotenoid content and brush border enzyme activity. Poult Sci 66:1306–1315
Argenzio RA (1992) Pathophysiology of diarrhea. In: Anderson NV, Sherding RG, Merritt AM, Whitlock RH (eds) Veterinary gastroenterology 2nd edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 163–172
Barker, IK (1993) Pathological processes associated with coccidiosis. In: Barta JR, Fernando MA (eds) Proceedings of the 4th International Coccidiosis Conference, June 21–25, 1993, Guelph/Canada, pp 81–94
Binder HJ, Foster E, Budinger ME, Hayslett JP (1987) Mechanism of electroneutral sodium-chloride absorption in distal colon of the rat. Gastroenterology 93:449–455
Bridges RJ, Nell G, Rummel W (1983) Influence of vasopressin and calcium on electrolyte transport across isolated colonic mucosa of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 338:463–475
Dixon WJ (1993) BMDP statistical software. University of California, Berkeley
Donowitz M, Welsh MJ (1986) Ca2+ and cyclic AMP in regulation of intestinal Na, K, and Cl transport. Annu Rev Physiol 48:135–150
Edmonds CJ, Willis CL (1988) Potassium secretion by rat distal colon during acute potassium loading: effect of sodium, potassium intake and aldosterone. J Physiol (Lond) 401:39–51
Escobar E, Ibarra C, Todisco E, Parisi M (1990) Water and ion handling in the rat caecum. Am J Physiol 259:G786-G791
Fernando MA, McCraw BW (1973) Mucosal morphology and cellular renewal in the intestine of chickens following a single infection of Eimeria acervulina. J Parasitol 59:493–501
Fitzgerald PR (1967) Effect of bovine coccidiosis on blood serum sodium and potassium levels of calves. Am J Vet Res 28:667–670
Foster ES, Zimmerman TW, Hayslett JP, Binder HJ (1983) Corticosteroid alteration of active electrolyte transport in rat distal colon. Am J Physiol 245:G668-G675
Foster ES, Budinger ME, Hayslett JP, Binder HJ (1986) Ion transport in proximal colon of the rat. Sodium depletion stimulates neutral sodium chloride absorption. J Clin Invest 77:228–235
Frizzell RA, Field M, Schultz SG (1979) Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol 236:F1-F8
Halevy JM, Budinger E, Hayslett JP, Binder HJ (1986) Role of aldosterone in the regulation of sodium and chloride transport in the distal colon of sodium-depleted rats. Gastroenterology 91:1227–1233
Heming TA, Copello J, Reuss L (1994) Regulation of cAMP-activated apical membrane chloride conductance in gallbladder epithelium. J Gen Physiol 103:1–18
Holtug K, Hansen MB, Skadhauge E (1996) Experimental studies of intestinal ion and water transport. Scand J Gastroenterol 31 [Suppl] 216:95–110
Kleyman TR, Cragoe EJ (1988) Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol 105:1–21
Kowalik S, Zahner H (1999) Eimeria separata: method for the excystation of sporozoites. Parasitol Res 85:496–499
Licois D, Mongin P (1980) Hypothèse sur la pathogénie de la diarrhée chez le lapin à partir de l’ étude des contenus intestinaux. Reprod Nutr Dev 20:1209–1216
Long PL (1993) Avian coccidiosis. In: Kreier JP (ed) Parasitic protozoa, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1–88
Lübcke R, Haag K, Berger E, Knauf H, Gerok W (1986) Ion transport in rat proximal colon in vivo. Am J Physiol 251:G132-G139
Marquardt WC, Pafume BA, Bush D (1987) Immunity to Eimeria separata (Apicomplexa: Eimeria): expose and challenge studies in rats. J Parasitol 73:342–344
Mazurkiewicz M, Madej JA, Nicpon J, Sobiech KA, Gawel A (1986) The dynamics of changes in selected parameters of metabolism in chickens infected with Eimeria acervulina and E. tenella. In: McDougald LR, Joyner LP, Long PL (eds) Research in avian coccidiosis. Proceedings of the Georgia Coccidiosis Conference 1985, University of Georgia, Athens, pp 186–193
Powell DW (1974) Intestinal conductance and permselectivity changes with theophylline and choleragen. Am J Physiol 227:1436–1443
Rajendran VM, Binder HJ (1993) Ion transport in rat colon. In: Clauss W (ed) Advances in comparative and environmental physiology, vol 16, Ion transport in vertebrate colon. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 113–137
Rajendran VM, Kashgarian M, Binder HJ (1989) Aldosterone induction of electrogenic sodium transport in the apical membrane vesicles of rat distal colon. J Biol Chem 264:18638–18644
Richer JK, Mayberry LF, Bristol JR, Ellzey JT (1991) Comparative ultrastructural alterations induced in rat intestinal mucosa by Eimeria separata and E. nieschulzi (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Trans Am Microsc Soc 110:262–268
Roudabush RL (1937) The endogenous phases of the life cycles of Eimeria nieschulzi, Eimeria separata and Eimeria miyairii coccidian parasites of rat. J Sci 11:135–163
Ruff MD (1986) Reasons for inadequate nutrient utilization during avian coccidiosis: a review. In: McDougald LR, Joyner LP, Long PL (eds) Research in avian coccidiosis. Proceedings of the Georgia Coccidiosis Conference 1985, University of Georgia, Athens, pp 169–185
Ruff MD, Allen PC (1990) Pathophysiology. In: Long PL (ed) Coccidiosis of man and domestic animals. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 263–280
Ruff MD, Wilkins GC (1980) Total intestinal absorption of glucose and L-methionin in broilers infected with Eimeria acervulina, E. mivati, E. maxima or E. brunetti. Parasitology 80:555–569
Ruff MD, Augustine PC, Madden PA (1981) Eimeria meleagrimitis, E. adenoeides and E. dispersa: Severity of infection and changes in the intestinal mucosa of the turkey. Exp Parasitol 51:87–94
Shi MQ, Huther S, Burkhardt E, Zahner H (2000) Immunity in rats against Eimeria separata: oocyst excretion, effects on endogenous stages and local tissue response after primary and challenge infections. Parasitol Res 86:891–898
Turk DE (1986) Macroelements in the circulation of coccidiosis-infected chicks. Poult Sci 65:462–468
Turnamian SG, Binder HJ (1989) Regulation of active sodium and potassium transport in the distal colon of the rat. Role of the aldosterone and glucocorticoid receptors. Clin Invest 84:1924–1929
Whang EM (1993) Untersuchungen zur intestinalen Resorption von Vitamin A-Alkohol (Retinol) bei einer Eimeria separata-Infektion der Ratte. Inaugural Dissertation, Justus-Liebig-Universität, Giessen
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Failing and Mr. Heiter for help in the statistical analyses as well as to Dr. Seibold for technical assistance during the use of the γ- and β-counter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirak, V.Y., Kowalik, S., Bürger, HJ. et al. Effects of Eimeria separata infections on Na+ and Cl− transport in the rat large intestine. Parasitol Res 92, 490–495 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1077-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1077-9