Abstract
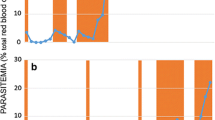
Artemether, a derivative of artemisinin, is effectively used for the treatment of malaria without any clinically relevant resistance to date. Artemether has also been developed as an antischistosomal agent, exhibiting highest activity against immature parasites. Here, we employ a rodent model and investigate whether the proposed artemether treatment schedule to prevent schistosome-attributable morbidity might select for Plasmodium berghei resistance. Mice infected with an ANKA strain of P. berghei were treated with artemether at either 47 mg/kg or 300 mg/kg. Once every 7–10 days, parasitized erythrocytes were passed to the next group of mice, receiving the same doses of artemether, for 50 passages. Resistance development was slow but increased considerably over the final ten passages. At the higher dose of artemether, the indices of resistance were 4.8 and 8.8 after 40 and 50 passages, respectively. Importantly, resistance was unstable, since sensitivity reverted to near-normal after five passages without drug pressure. A moderate index of P. berghei resistance and no apparent reversibility was found in comparative experiments employing pyronaridine. In conclusion, the pace of resistance development in P. berghei to repeated high doses of artemether is slow and reversible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breman JG (2001) The ears of the hippopotamus: manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg 64 [Suppl]:1–11
Chen YD, Lin BY, Zhang JX (2002) Study on introducing an artemisinin-resistant line of Plasmodium berghei. Chin J Parasitol Parasite Dis 20:37–38
Cheng LF, Lu LL, Wu LL (1988) Development of artemether-resistant of line of Plasmodium berghei (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Pharmacol Sin 9:352–355
Dayan AD (1998) Neurotoxicity and artemisinin compounds: do the observations in animals justify limitation of clinical use? Med Trop 58 [Suppl 3]:32–37
Dutta GP, Puri SK, Awasthi A, Mishra M, Tripathi R (2000) Pyronaridine: an effective antimalarial against multidrug-resistant malaria. Life Sci 67:759–763
Genovese RF, Newman DB, Brewer TG (2000) Behavioral and neural toxicity of the artemisinin antimalarial, arteether, but not artesunate and artelinate, in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:37–44
Hastings IM, Bray PG, Ward SA (2002a) A requiem for chloroquine. Science 298:74–75
Hastings IM, Watkins WM, White NJ (2002b) The evolution of drug-resistant malaria: the role of drug elimination half-life. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 357:505–519
Haynes RK (2001) Artemisinin and derivatives: the future for malaria treatment? Curr Opin Infect Dis 14:719–726
Hyde JE (2002) Mechanisms of resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to antimalarial drugs. Microbe Infect 4:165–174
Inselburg J (1985) Induction and isolation of artemisinine-resistant mutants of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg 34:417–418
Ittarat W, Pickard AL, Rattanasinganchan P, Wilairatana P, Looareesuwan S, Emery K, Low J, Udomsangpetch R, Meshnick SR (2003) Recrudescence in artesunate-treated patients with falciparum malaria is dependent on parasite burden not on parasite factors. Am J Trop Med Hyg 68:147–152
Klayman DL (1985) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science 228:1049–1055
Li CS, Du YL, Jiang Q (1986) Development of a qinghaosu-resistant line of Plasmodium berghei ANKA and N strain (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Pharm Sin 21:811–815
Li QG, Mog SR, Si YZ, Kyle DE, Gettayacamin M, Milhous WK (2002) Neurotoxicity and efficacy of arteether related to its exposure times and exposure levels in rodents. Am J Trop Med Hyg 66:516–525
Li Y, Wu YL (2003) An over four millennium story behind qinghaosu (artemisinin)—a fantastic antimalarial drug from a traditional Chinese herb. Curr Med Chem 10:2197–2230
Liu AR, Ren ZH (1987) Development of a line of Plasmodium berghei resistant to sodium artesunate (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Pharmacol Sin 8:149–152
Merkli B, Richle RW (1980) Studies on the resistance to single and combined antimalarials in the Plasmodium berghei mouse model. Acta Trop 37:228–231
Meshnick SR (2002) Artemisinin: mechanisms of action, resistance and toxicity. Int J Parasitol 32:1655–1660
N’Goran EK, Utzinger J, Gnaka HN, Yapi A, N’Guessan NA, Kigbafori SD, Lengeler C, Chollet J, Xiao SH, Tanner M (2003) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oral artemether for the prevention of patent Schistosoma haematobium infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg 68:24–32
Noedl H, Wernsdorfer WH, Krudsood S, Wilairatana P, Viriyavejakul P, Kollaritsch H, Wiedermann G, Looareesuwan S (2001) In vivo–in vitro model for the assessment of clinically relevant antimalarial cross-resistance. Am J Trop Med Hyg 65:696–699
Nosten F, Brasseur P (2002) Combination therapy for malaria: the way forward? Drugs 62:1315–1329
Peters W, Robinson BL (1999) The chemotherapy of rodent malaria. LVI. Studies on the development of resistance to natural and synthetic endoperoxides. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 93:325–329
Peters W, Portus JH, Robinson BL (1975) The chemotherapy of rodent malaria, XXII. The value of drug-resistant strains of P. berghei in screening for blood schizontocidal activity. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 69:155–171
Price RN (2000) Artemisinin drugs: novel antimalarial agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9:1815–1827
Ridley RG (2002) Medical need, scientific opportunity and the drive for antimalarial drugs. Nature 415:686–693
Utzinger J, Xiao SH, N’Goran EK, Bergquist R, Tanner M (2001) The potential of artemether for the control of schistosomiasis. Int J Parasitol 31:1549–1562
Utzinger J, Bergquist R, Xiao SH, Singer BH, Tanner M (2003a) Sustainable schistosomiasis control—the way forward. Lancet 362:1932–1934
Utzinger J, Keiser J, Xiao SH, Tanner M, Singer BH (2003b) Combination chemotherapy of schistosomiasis in laboratory studies and clinical trials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:1487–1495
Walker DJ, Pitsch JL, Peng MM, Robinson BL, Peters W, Bhisutthibhan J, Meshnick SR (2000) Mechanisms of artemisinin resistance in the rodent malaria pathogen Plasmodium yoelii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:344–347
Wellems TE, Plowe CV (2001) Chloroquine-resistant malaria. J Infect Dis 184:770–776
White N (1999) Antimalarial drug resistance and combination chemotherapy. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 354:739–749
White NJ, Pongtavornpinyo W (2003) The de novo selection of drug-resistant malaria parasites. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 270:545–554
Wongsrichanalai C, Pickard AL, Wernsdorfer WH, Meshnick SR (2002) Epidemiology of drug-resistant malaria. Lancet Infect Dis 2:209–218
Xiao SH, Hotez PJ, Tanner M (2000) Artemether, an effective new agent for chemoprophylaxis against schistosomiasis in China: its in vivo effect on the biochemical metabolism of the Asian schistosome. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 31:724–732
Xiao SH, Chollet J, Utzinger J, Matile H, Mei JY, Tanner M (2001) Artemether administered together with haemin damages schistosomes in vitro. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 95:67–71
Xiao SH, Tanner M, N’Goran EK, Utzinger J, Chollet J, Bergquist R, Chen MG, Zheng J (2002a) Recent investigations of artemether, a novel agent for the prevention of schistosomiasis japonica, mansoni and haematobia. Acta Trop 82:175–181
Xiao SH, Yang YQ, You QQ, Utzinger J, Guo HF, Jiao PY, Mei JY, Guo J, Bergquist R, Tanner M (2002b) Potential long-term toxicity of repeated orally administered doses of artemether in rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg 66:30–34
Xiao SH, You JQ, Gao HF, Mei JY, Jiao PY, Chollet J, Tanner M, Utzinger J (2002c) Schistosoma japonicum: effect of artemether on glutathione S-transferase and superoxide dismutase. Exp Parasitol 102:38–45
Xiao SH, Wu YL, Tanner M, Wu WM, Utzinger J, Mei JY, Scorneaux B, Chollet J, Zhai Z (2003) Schistosoma japonicum: in vitro effects of artemether combined with haemin depend on cultivation media and appraisal of artemether products appearing in the media. Parasitol Res 89:459–466
Acknowledgements
This investigation received financial support from the Ninth Five-Year Key Research Program of China. J.U. is grateful to the Center for Health and Wellbeing at Princeton University and the Swiss Tropical Institute for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, SH., Yao, JM., Utzinger, J. et al. Selection and reversal of Plasmodium berghei resistance in the mouse model following repeated high doses of artemether. Parasitol Res 92, 215–219 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-1029-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-1029-9