Abstract
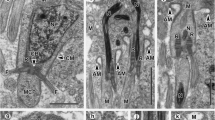
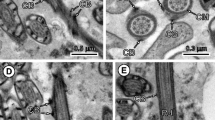
Golden hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) were infected with Taenia solium metacestodes dissected from infected pig meat. Adult worms were collected from hamster intestines of animals killed 5–60 days post-infection (dpi), incubated in RPMI 1640 medium with or without colchicine, fixed and processed for transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Sections for light microscopy from 40 different blocks with scolex, immature and mature proglottids were photographed. Thin sections were cut from 25 selected blocks, examined and photographed with TEM. Metaphase mitosis figures were observed in the subtegument of the germinative tissue and interpreted as germ cell precursors. In immature proglottids (20 dpi), discrete cell clusters of three to four cells surrounded by a thin cytoplasmic envelope were identified along the inner border of the lateral excretory ducts. These were also observed in more mature proglottids (40–60 dpi) as clusters of eight cells enclosed in a cytoplasmic envelope, with nuclei of spermatogonia exhibiting the synaptolems of primary meiotic cells. In mature proglottids from 45 dpi, a large number of spermatocyte lobules were found, exhibiting different stages of spermatogenesis from primary spermatocytes to mature filiform spermatids with a single axoneme, annular nucleus and spiral cortical microtubules, similar to spermatozoa described for type III spermiogenesis of species of the family Taeniidae. All mature spermatocyte lobules were enclosed in a highly organized cellular envelope and surrounded by a basal lamina. The envelopes contained a number of distinct organelles, seen in cross-section as discrete lattices of microtubules located between two layers of plasma membrane, as well as thickened furled cytoplasm with numerous strands of rough endoplasmic reticulum and pockets of microtubules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts B, Bray D, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (1998) Cytoskeleton. In: Essential cell biology. An introduction to the molecular biology of the cell. Garland, New York, pp 513–545
Bâ A, Bâ CT, Marchand B(2000) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and the spermatozoon of Sudarikovina taterae (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea, Anoplocephalidae) intestinal parasite of Tatera gambiana (Rodentia, Gerbillidae). Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 32:137–144
Bâ CT, Marchand B (1998) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and the spermatozoon of Vampirolepis microstoma (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae), intestinal parasite of Rattus rattus. Microsc Res Technol 42:218–225
Bolla RI, Roberts LS (1971) Developmental physiology of cestodes. IX: cytological characteristics of the germinative region of Hymenolepis diminuta. J Parasitol 57:267
Bruñanská M, Nebesárová J, Scholz T, Fagerholm HP (2001) Spermiogenesis in the pseudophyllid cestode Eubothrium crassum (Bloch, 1779). Parasitol Res 87:579–588
Conn DB, Forman L (1993) Morphology and fine structure of the gravid uterus of three hymenolepidid tapeworm species (Platyhelminthes: Cestoda). Invert Reprod Dev 23:95–103
Euzet L, Swiderski Z, Mokhtar-Maamouri F (1981) Ultrastructure comparée du spermatozoïde des cestodes. Relations avec la phylogénèse. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 56:247–259
Gilbert SF (2000) Spermatogenesis. In: Developmental biology, 6th edn. Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass.
Gustafsson MK (1976) Studies on the cytodifferentiation in the neck region of Diphyllobothrium dendriticum Nitzsch, 1824 (Cestoda, Pseudophyllidea). Z Parasitenkd 50:323–329
Hidalgo C, Miquel J, Torres J, Marchand B (2000) Ultrastructural study of spermiogenesis and the spermatozoon in Catenotaenia pusilla, an intestinal parasite of Mus musculus. J Helminthol 74:73–81
Justine JL (1998) Spermatozoa as phylogenetic characters for the Eucestoda. J Parasitol 84:385–408
Karnovsky MJ (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron-microscopy. J Cell Biol 27:137A
Kelsoe GH, Ubelaker JE, Allison VF (1977) The fine structure of spermatogenesis in Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda) with a description of the mature spermatozoon. Z Parasitenkd 54:175–187
Maravilla P, Avila G, Cabrera V, Aguilar L, Flisser A (1998) Comparative development of Taenia solium in experimental models. J Parasitol 84:882–806
Marchand B (1998) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and the spermatozoon of Anoplocephaloides dentata (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea, Anoplocephalidae), an intestinal parasite of Arvicolidae rodents. J Parasitol 84:1128–1136
Mead RW (1982) Changes in the germinative cell frequencies in the germinative region of Hymenolepis diminuta. J Parasitol 68:95
Merchant MT, Corella C, Willms K (1997) Autoradiographic analysis of the germinative tissue in evaginated Taenia solium metacestodes. J Parasitol 83:363–367
Miquel J, Bâ CT, Marchand B (1998) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis of Dipylidium caninum (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea, Dipylidiidae), an intestinal parasite of Canis familiaris. Int J Parasitol 28:1453–1458
Ndiaye PI, Miquel J, Marchand B (2002) Ultrastructure of spermiogenseis and spermatozoa of Taenia parva Baer, 1926 (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea, Taeniidae), a parasite of the common genet (Genetta genetta). Parasitol Res 89:34–43
Roberts L (2000) The crowding effect revisited. 1951. J Parasitol 86:209–211
Sene A, Bâ CT, Marchand B (1997) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and the spermatozoon of Nomimoscolex sp. ( Cestoda, Proteocephalidea) intestinal parasite of Clarotes laticeps (Fish; Teleostei) in Senegal. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 29:115–124
Smyth J, McManus D (1989) The biology of the egg. In: The physiology and biochemistry of cestodes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 156–194
Spurr AR (1969) A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31
Stoitsova SR, Goergiev BB, Dacheva RB (1995) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and the mature spermatozoon of Tetrabothrius erostris Loennberg, 1896 (Cestoda, Tetrabothriidae). Int J Parasitol 25:1427–1436
Swiderski Z, Mackiewicz JS (2002) Ultrastructure of spermatogenesis and spermatozoa of the caryophyllidean cestode Glaridacris catostomi Cooper, 1920. Acta Parasitol 47:87–104
Tian X, Yuan L, Li Y, Huo X, Han X, Xu M, Lu M, Dai J, Dong L (1998a) Ultrastructural observation on spermatocytogenesis in taeniid cestodes. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 16:209–212
Tian X, Yuan L, Li Y, Huo X, Han X, Xu M, Lu M, Dai J, Dong L (1998b) Ultrastructural observation on the transformation of the spermatozoon in spermatogenesis of taeniid cestodes. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 16:269–273
Tidiane-Bâ C, Marchand B (1998) Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis and spermatozoon of Vampirolepis microstoma (Cestoda, Hymenolepididae), intestinal parasite of Rattus rattus. Microsc Res Technol 42:218–225
Wang IC, Guo JX, Ma YX, Chung WC, Lu SC, Fan PC (1999) Sexual development of Taenia solium in hamsters from rodent-derived cysticerci. J Helminthol 73:347–350
Wikgren BJP, Knuts GM (1970) Growth of subtegumental tissue in cestodes by cell migration. Acta Acad Aboiensis 30:1–6
Willms K, Merchant MT, Gómez M, Robert L (2001) Taenia solium: germinal cell precursors in tapeworms grown in hamster intestine. Arch Med Res 32:1–7
Willms K, Robert L, Caro JA (2003) Ultrastructure of smooth muscle, gap junctions and glycogen distribution in Taenia solium tapeworms from experimentally infected hamsters. Parasitol Res 89:308–316
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant to K.W. from the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, Mexico (no.. L0026). The authors thank Dr. Ana Flisser for the generous donation of hamster specimens. The experiments described herein comply with the current laws of science and technology in Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willms, K., Caro, J.A. & Robert, L. Ultrastructure of spermatogonia and spermatocyte lobules in Taenia solium strobilae (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea, Taeniidae) from golden hamsters. Parasitol Res 90, 479–488 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0897-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0897-3