Abstract
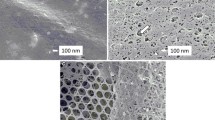
In the present study, morphological observations on the extracellular structures found on the apical surface of the midgut epithelium, known as the peritrophic membrane (PM) or glycocalyx, are described in Haemaphysalis longicornis females and larvae. These structures have been hypothesized to provide protection to the microvilli of epithelial cells of the digestive tract. Our aim was to determine whether the extracellular structures are important in the digestion of the blood meal and/or as a protection against infection or injury. The PM was detectable in the midgut of engorged larvae by electron microscopy, but not in engorged females. However, a PM-like structure, stainable with toluidine blue, was observed in females by light microscopy. From the results of confocal laser scanning and electron microscopic observations with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA lectin) staining for chitin of the PM, however, the structure was clearly recognized. The structure in the female is likely to be PM because staining with WGA lectin in the presence of GlcNAc indicates the presence of chitin and various morphologies of PM have been reported in insects and ticks. These results show morphologically that different types of PM-like structure are formed in larvae and females of H. longicornis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbede RIS, Kemp DH, Hoyfe HMD (1986) Babesia bovis infection of secretory cells in the gut of the vector tick Boophilus microplus. Int J Parasitol 16:109–114
Allen K, Neuberger A, Sharon N (1973) The purification, composition and specificity of wheatgerm agglutinin. Biochem J 131:155–162
Billingsley PF, Rudin W (1992) The role of the mosquito peritrophic membrane in bloodmeal digestion and infectivity of Plasmodium species. J Parasitol 78:430–440
Evans DA, Ellis DS (1983) Recent observations on the behaviour of certain trypanosomes within their insect hosts. Adv Parasitol 22:1–42
Friedhoff KT (1987) Interaction between parasite and vector. Int J Parasitol 17:587–595
Fujisaki K, Kitaoka S, Morii T (1976) Comparative observations of Japanese ixodid ticks under laboratory conditions. Nat Inst Anim Health Q (Jpn) 16:122–128
Fujisaki K, Kamio T, Kawazu S (1991) Theileria sergenti cannot be regarded as the same species as T. bufferi and T. orientalis because of its transmissibility only by Kaiseriana ticks. In: Dusbabeck F, Bukva V (eds) Modern acarology, vol 1. Academia, Prague, pp. 233–237
Fujisaki K, Kamio T, Kawazu S (1993a) Development of Theileria sergenti in vector ticks, Haemaphysalis longicornis, during blood sucking. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 87:95–97
Fujisaki K, Kamio T, Kawazu S (1993b) Theileria sergenti: transformation of zygotes into kinetes in vector ticks, Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis, and H. (K.) mageshimaensis. J Vet Med Sci 55:849–851
Grandjean O (1984) Blood digestion in Ornithodoros moubata Murry sensu stricto Walton (Ixodidea: Argasidae) female. I. Biochemical changes in the midgut lumen and ultrastructure of the midgut cell, related to intracellular digestion. Acarologia 25:147–165
Hardy JL, Houk EJ, Kramer LD, Reeves W (1983) Intrinsic factors affecting vector competence of mosquitoes for arboviruses. Annu Rev Entomol 28:229–262
Higuchi S, Izumitani M, Hoshi H, Kawamura S, Yasuda Y (1999) Development of Babesia gibsoni in the midgut of larval tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus. J Vet Med Sci 61:689–691
Huber M, Cabib E, Miller LH (1991) Malaria parasite chitinase and penetration of the mosquito peritrophic membrane. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 88:2807–2810
Kawazu S, Kamio T, Kakuda T, Terada Y, Sugimoto C, Fujisaki K (1999) Phylogenetic relationships of the benign Theileria species in cattle and Asian buffalo based on the major piroplasm surface protein (p33/34) gene sequences. Int J Parasitol 29:613–618
Keirans JE (1992) Systematics of the Ixodida (Argasidae, Ixodidae, Nuttalliellidae): an overview and some problems. In: Fivaz BH, Petney TN, Horak IG (eds) Tick vector biology: medical and veterinary aspects. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 1–21
Laurence BR (1966) Intake and migration of the microfilariae of Onchocerca volvulus (Leuckart) in Simulium damnosum Theobald. J Helminthol 40:337–342
Lehane MT (1997) Peritrophic membrane structure and function. Annu Rev Entomol 42:525–550
Lehane MT, Allingham PG, Weglicki P (1996) Composition of the peritrophic matrix of the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans morsitans. Cell Tissue Res 283:375–384
Peters W (1992) Zoophysiology, vol 30, Peritrophic membranes. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg.
Peters W, Latka I (1986) Electron microscopic localisation of chitin using colloidal gold labeled with wheat germ agglutinin. Histochemistry 84:155–160
Potgieter FT, Els HJ (1977) Light and electron microscopic observations on the development of Babesia bigemina in larvae, nymphae and non-replete females of Boophilus decoloratus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 44:213–232
Potgieter FT, Els HJ, van Vuuren S (1976) The fine structure of merozoites of Babesia bovis in the gut epithelium of Boophilus microplus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 43:1–10
Rudin W, Hecker H (1989) Lectin-binding sites in the midgut of mosquitoes Anopheles stephensi (Liston) and Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Cullicidae). Parasitol Res 75:268–279
Rudzinska MA, Spielman A, Lewengrub S, Piesman J (1982) Penetration of the peritrophic membrane of the tick by Babesia microti. Cell Tissue Res 221:471–481
Rudzinska MA, Lewengrub S, Spielman A, Piesman J (1983) Invasion of Babesia microti into epithelial cells of the tick gut. J Protozool 30:338–346
Shao L, Devenport M, Iacobs-Lorena M (2001) The peritrophic matrix of hematophagous insects. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 47:119–125
Shen Z, Dimopoulos G, Kafatos FC, Jacobs-Lorena M (1999) A cell surface mucin specifically expressed the midgut of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 96:5610–5615
Tellam RL, Eisemann C (2000) Chitin is only a minor component of the peritrophic matrix from larvae of Lucilia cuprina. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:1189–1201
Terra WR (2001) The origin and functions of the insect peritrophic membrane and peritrophic gel. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 47(2): 47–61
Vinetz JM, Valenzuela JG, Specht CA, Aravind L, Langer RC, Ribeiro JMC, Kaslow DC (2000) Chitinases of the avian malaria parasite Plasmodium gallinaceum, a class of enzymes necessary for parasite invasion of the mosquito midgut. J Biol Chem 275:10331–10341
Yuda M, Sawai T, Chinzei Y (1999) Structure and expression of an adhesive protein-like molecular of mosquito invasive-stage malaria parasite. J Exp Med 189:1947–1952
Zapf F, Schein E (1994) The development of Babesia (Theileria) equi (Laveran, 1901) in the gut and the haemolymph of the vector ticks, Hyalomma species. Parasitol Res 80:297–302
Zhu Z, Gern, L, Aeschlimann A (1991) The peritrophic membrane of Ixodes ricinus. Parasitol Res 77:635–641
Zieler H, Nawrocki JP, Shahabuddin M (1999) Plasmodium gallinaceum ookinetes adhere specifically to the midgut epithelium of Aedes aegypti by interaction with a carbohydrate ligand. J Exp Biol 202:485–495
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. This study was supported by a grant from The 21st Century COE Program (A-1) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Sciences, and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuo, T., Sato, M., Inoue, N. et al. Morphological studies on the extracellular structure of the midgut of a tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 90, 243–248 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0833-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0833-6