Abstract.
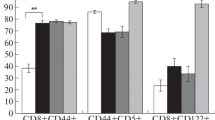
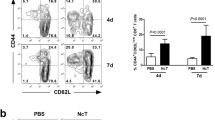
Severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice reconstituted with spleen cells from naive adult BALB/c mice were completely resistant to peroral infection with Encephalitozoon intestinalis (Calli, Kotler and Orenstein, 1993) Canning, Field, Hing and Marriott, 1994, whereas control, non-reconstituted SCID mice succumbed to the infection. The role of T-lymphocyte subpopulations in the protection against peroral E. intestinalis infection was studied in adoptive transfer experiments using SCID mice. SCID mice reconstituted with both CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocyte-depleted splenocytes succumbed to the peroral route of infection. In contrast, SCID mice reconstituted with either CD4+-depleted or CD8+ T-lymphocyte-depleted splenocytes completely resolved the infection. This indicates that CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocyte subpopulations play a substantive role in protection against peroral infection with the microsporidian, E. intestinalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salát, J., Braunfuchsová, P., Kopecký, J. et al. Role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in the protection of mice against Encephalitozoon intestinalis infection. Parasitol Res 88, 603–608 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0620-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0620-9