Summary.
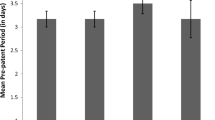
The selenium-deficient mouse-trypanosome system was used to study the effects of selenium deficiency in Swiss Webster mice infected with Trypanosoma musculi. In selenium-deficient mice, a low parasitemia was observed and infection was cleared by day 16 post-inoculation (PI), whereas control mice sustained the parasitemia until day 24 PI. There were no significant differences in size variability of the trypanosomes; however the range of variability in the length of parasites differed significantly between the three groups. In comparison to mice on complete or pair-fed diets, the selenium-deficient mice produced lower concentrations of IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and IgM. The levels of IgG2a and IgA were lower than normal controls. The results of the present study indicated that there was a severe depression in primary and secondary antibody responses to sheep red blood cells in all inoculated mice. However, these responses were significantly less depressed in selenium-deficient mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ongele, E., Ashraf, M., Nesbitt, R. et al. Effects of selenium deficiency in the development of trypanosomes and humoral immune responses in mice infected with Trypanosoma musculi . Parasitol Res 88, 540–545 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0617-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0617-4