Abstract
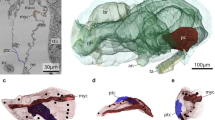
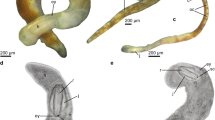
Aplacophora is a small enigmatic group of worm-like molluscs covered by sclerites. The general morphology of the posterior end, including the gonopericardial system, in many species is well studied using light microscopy. However, knowledge of the ultrastructure of this complex is fragmentary and many questions concerning the excretion of metabolites in this group still remain. The gonopericardial system of Chaetoderma nitidulum Lovén, 1844 (Caudofoveata) from the White Sea was studied using light microscopy and 3D reconstruction from a series of semi-thin sections. The ultrastructure of the gonopericardial system was described in detail for the first time. The gonopericardial complex consists of gonads connected to the pericardium by ciliated paired gonopericardioducts. The pair of gonoducts begins at the lateral sides of the pericardium and opens into the mantle cavity. Gonoducts consist of upper and lower parts that are morphologically differentiated. The walls of the upper gonoducts consist of cells that likely participate in the excretion of metabolites and reabsorption of useful substances. Lower gonoducts are bulk bags with a small cell wall, in which there is a ciliary tract, likely for the excretion of metabolites and reproductive products. Spermatozoa were found at different stages of development in different parts of the pericardium and gonoducts. On the basis of previously published and newly obtained data, the process of excretion by C. nitidulum is proposed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba K (1940) The mechanisms of absorption and excretion in a Solenogastre, Epimenia verrucosa (Nierstrasz), studied by means of injection methods. J Dept Agric Kyushu Imperial Univ 6(4):119–166
Bergmeier FS, Brandt A, Schwabe E, Jörger KM (2017) Abyssal Solenogastres (Mollusca, Aplacophora) from the Northwest Pacific: scratching the surface of deep-sea diversity using integrative taxonomy. Front Mar Sci 4:410
Fahrner A, Haszprunar G (2002) Ultrastructure of the renopericardial complex in Hypselodoris tricolor (Gastropoda, Nudibranchia). Zoomorphology 121(3):183–194
García-Álvarez O, Salvini-Plawen LV (2007) Species and diagnosis of the families and genera of Solenogastres (Mollusca). Iberus 25(2):73–143
Handl CH (2002) Imeroherpia laubieri, a new solenogaster from the Bay of Biscay. J Molluscan Stud 68(4):329–335
Haszprunar G (1992) The first molluscs-small animals. Ital J Zool 59(1):1–16
Hoffman S (1949) Uber das Integument der Solenogastren, nebst Bemerkungen uber die Verwandtschaft zwischen den Solenogastren und Placophoren. Zool Bidr Upps 27:293–427
Hyman LH (1967) Class Aplacophora. Invertebrates 6:13–70
Ivanov DL (1996) Origin of Aculifera and problems of monophyly of higher taxa in molluscs. In: Taylor JD (ed) Origin and evolutionary radiation of the Mollusca. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 59–65
Nielsen C, Haszprunar G, Ruthensteiner B, Wanninger A (2007) Early development of the aplacophoran mollusc Chaetoderma. Acta Zool 88(3):231–247
Nierstrasz HF (1903a) Neue Solenogastren. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Anatomie und Ontogenie der Tiere Abteilung für Anatomie und Ontogenie der Tiere 18:359–386
Nierstrasz HF (1903b) Das Herz der Solenogastren. Verh. Akad. Amsterdam 10(2):1–52
Reynolds PD, Morse MP, Norenburg J (1993) Ultrastructure of the heart and pericardium of an aplacophoran mollusc (Neomeniomorpha): evidence for ultrafiltration of blood. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 254:147–152
Ruthensteiner B, Hess M (2008) Embedding 3D models of biological specimens in PDF publications. Microsc Res Tech 71(11):778–786
Salvini-Plawen LV, Bartolomaeus T (1995) Mollusca: mesenchymata with a “coelom”. In: Lanzavecchia G, Valvassori R, Carrnevali MD (eds) Body cavities: function and phylogeny. Mucci Editore, Modena, pp 75–92
Salvini-Plawen LV, Öztürk B (2006) New records of Caudofoveata (Falcidens gutturosus, Prochaetoderma raduliferum) and of Solenogastres (Eleutheromenia carinata, spec. nov.) from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Spixiana 29:217–224
Salvini-Plawen L, Steiner G (2014) The Testaria concept (Polyplacophora + Conchifera) updated. J Nat Hist 48(45–48):2751–2772
Scheltema AH (1973) Heart, pericardium, coelomoduct openings, and juvenile gonad in Chaetoderma nitidulum and Falcidens caudatus (Mollusca, Aplacophora). Z Morphol Tiere 76(1):97–107
Scheltema AH (1988) Ancestors and descendants: relationships of the Aplacophora and Polyplacophora. Am Malacol Bull 6(1):57–68
Scheltema AH (1993) Aplacophora as progenetic aculiferans and the coelomate origin of mollusks as the sister taxon of Sipuncula. Biol Bull 184(1):57–78
Scheltema AH (1996) Phylogenetic position of Sipuncula, Mollusca and the progenetic Aplacophora. Origin and evolutionary radiation of the Mollusca. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 53–58
Scheltema AH, Tscherkassky M, Kuzirian AM (1994) Aplacophora. Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 13–54
Todt C (2013) Aplacophoran mollusks—still obscure and difficult? Am Malacol Bull 31(1):181–188
Todt C, Okusu A, Schander C, Schwabe E (2008) Solenogastres, Caudofoveata, and Polyplacophora. Phylogeny Evol Mollusca 4:71–96
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. A. Tzetlin for useful advice and discussions of the results. We thank our friend Ivan Ponomarev for help with English. We express our gratitude to G. Davidovich and A. Bogdanov and the Electron Microscopy Laboratory of the Shared Facilities Center of Lomonosov Moscow State University sponsored by the RF Ministry of Education and Science and Research. The authors also thank S. Mitelev and G. Bykov (I.D. Papanin Institute for the Biology of Inland Waters Russian Academy of Sciences) for help with electron microscopy. The light microscopy study was conducted using equipment from the Center of Microscopy of White Sea Biological Station.
Funding
The study was funded by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, Grant Nos. 18-05-60158 and 19-04-00501, and Russian Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naduvaeva, E., Vortsepneva, E. General morphology and ultrathin structure of the gonopericardial complex of Chaetoderma nitidulum Lovén, 1844 (Caudofoveata). Zoomorphology 139, 21–35 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-019-00473-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-019-00473-1