Abstract
Purpose
Anoikis resistance is an important inducer of tumor metastasis. The role of anoikis-related genes (ARGs) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear.
Methods
A list of ARGs was obtained and regression analysis was employed to assemble an anoikis-related prognostic signature and risk score formula from mRNA data and clinical prognostic data downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed on clinical samples to validate the selected ARGs expressions. Kaplan‒Meier curves, ROC curves, and Cox regression analyses were used to demonstrated the prognostic value of this signature. Biological functional enrichment analysis and immune infiltration analysis were utilized to analyze the differences in potential biological functions, immune cell infiltration, immune functions, and immunotherapeutic responses.
Results
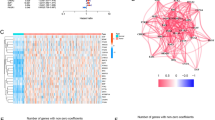
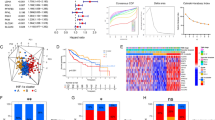
A prognostic signature based on 6 ARGs and corresponding prognostic nomogram were established. Our qRT-PCR results showed a higher expression of 6 ARGs in HCC tissues (p value < 0.05). Kaplan‒Meier curves, ROC curves, and Cox regression analyses demonstrated good prognostic value of the signature in HCC (p value < 0.05). Significant differences between the enriched biological functions and immune landscapes of patients in different risk groups were discovered (p value < 0.05). In addition, patients with higher risk scores possibly had poor therapeutic response to transhepatic arterial chemotherapy and embolization or sorafenib, but their responses to immunotherapy might be more effective.
Conclusion
A successful anoikis-related prognostic signature and corresponding clinical nomogram were established, which might facilitate better predictions of prognosis and therapeutic responses for HCC patients.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All the data analyzed in this research were downloaded from the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/), ICGC (International Cancer Genome Consortium) (https://dcc.icgc.org/projects/LIRI-JP), GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo), and GSEA (gene set enrichment analysis) (https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/index.jsp) databases.
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- ECM:
-
Cell and extracellular matrix
- ARGs:
-
Anoikis-related genes
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- ICGC:
-
International Cancer Genome Consortium
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- GSEA:
-
Gene set enrichment analysis
- TACE:
-
Transhepatic arterial chemotherapy and embolization
- DEARGs:
-
Differentially expressed ARGs
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- K-M:
-
Kaplan–Meier
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- TIDE:
-
Tumor immune dysfunction and exclusion
- CNV:
-
Copy number variation
- TIMER:
-
Tumor Immune Estimation Resource
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression free survival
- TNM:
-
Tumor size/lymph nodes/distant metastasis
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- NK cells:
-
Natural killer cells
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IC50:
-
Half maximal inhibitory concentration
References
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P et al (2013) NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D991-995
Chen Z, Liu X, Zhu Z et al (2022) A novel anoikis-related prognostic signature associated with prognosis and immune infiltration landscape in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front Genet 13:1039465
Chuah S, Lee J, Song Y et al (2022) Uncoupling immune trajectories of response and adverse events from anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 77:683–694
Corpuz AD, Ramos JW, Matter ML (2020) PTRH2: an adhesion regulated molecular switch at the nexus of life, death, and differentiation. Cell Death Discov 6:124
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA et al (2003) DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol 4:P3
Gao R, Kalathur RKR, Coto-Llerena M et al (2021) YAP/TAZ and ATF4 drive resistance to Sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by preventing ferroptosis. EMBO Mol Med 13:e14351
Gilmore AP (2005) Anoikis. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1473–1477
Hausmann M, Leucht K, Ploner C et al (2011) BCL-2 modifying factor (BMF) is a central regulator of anoikis in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 286:26533–26540
Hudson TJ, Anderson W, Artez A et al (2010) International network of cancer genome projects. Nature 464:993–998
Khotskaya YB, Beck BH, Hurst DR et al (2014) Expression of metastasis suppressor BRMS1 in breast cancer cells results in a marked delay in cellular adhesion to matrix. Mol Carcinog 53:1011–1026
Li T, Fan J, Wang B et al (2017) TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Can Res 77:e108–e110
Li K, Zhao G, Ao J et al (2019) ZNF32 induces anoikis resistance through maintaining redox homeostasis and activating Src/FAK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 442:271–278
Lin Z, Niu Y, Wan A et al (2020) RNA m(6) A methylation regulates sorafenib resistance in liver cancer through FOXO3-mediated autophagy. EMBO J 39:e103181
Llovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M et al (2022) Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 19:151–172
Martin SP, Fako V, Dang H et al (2020) PKM2 inhibition may reverse therapeutic resistance to transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 39:99
Mo CF, Li J, Yang SX et al (2020) IQGAP1 promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis through Rac1-dependent ROS accumulation and activation of Src/FAK signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 123:1154–1163
Qi X, Guo J, Chen G et al (2022) Cuproptosis-related signature predicts the prognosis, tumor microenvironment, and drug sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunol Res 2022:3393027
Qiao L, Zhang Q, Sun Z et al (2021) The E2F1/USP11 positive feedback loop promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and inhibits autophagy by activating ERK/mTOR pathway. Cancer Lett 514:63–78
Raoul JL, Forner A, Bolondi L, Cheung TT, Kloeckner R, de Baere T (2019) Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: how and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev 72:28–36
Sangro B, Sarobe P, Hervás-Stubbs S, Melero I (2021) Advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:525–543
Shi Y, Shang J, Li Y et al (2022) ITGA5 and ITGB1 contribute to Sorafenib resistance by promoting vasculogenic mimicry formation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med 12(3):3786–3796
Song J, Liu Y, Liu F et al (2021) The 14-3-3σ protein promotes HCC anoikis resistance by inhibiting EGFR degradation and thereby activating the EGFR-dependent ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Theranostics 11:996–1015
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Chiarugi P (2012) Anoikis: an emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J Pathol 226:380–393
Tang W, Chen Z, Zhang W et al (2020) The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:87
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P, Wiznerowicz M (2015) The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Poznan, Poland) 19:A68-77
Villanueva A (2019) Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380:1450–1462
Wang YN, Zeng ZL, Lu J et al (2018) CPT1A-mediated fatty acid oxidation promotes colorectal cancer cell metastasis by inhibiting anoikis. Oncogene 37:6025–6040
Wei X, Zhao L, Ren R et al (2021) MiR-125b loss activated HIF1α/pAKT loop, leading to transarterial chemoembolization resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology (baltimore, MD) 73:1381–1398
Whelan KA, Caldwell SA, Shahriari KS et al (2010) Hypoxia suppression of Bim and Bmf blocks anoikis and luminal clearing during mammary morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 21:3829–3837
Wu FQ, Fang T, Yu LX et al (2016) ADRB2 signaling promotes HCC progression and sorafenib resistance by inhibiting autophagic degradation of HIF1α. J Hepatol 65:314–324
Xia S, Pan Y, Liang Y, Xu J, Cai X (2020) The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 51:102610
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR (2019) A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:589–604
Yu M, Lu B, Liu Y, Me Y, Wang L, Li H (2017) Interference with Tim-3 protein expression attenuates the invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma and aggravates anoikis. Mol Med Rep 15:1103–1108
Yu Y, Zhao D, Li K et al (2020) E2F1 mediated DDX11 transcriptional activation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis 11:273
Yu Y, Song Y, Cheng L et al (2022) CircCEMIP promotes anoikis-resistance by enhancing protective autophagy in prostate cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 41:188
Zhang YF, Zhang AR, Zhang BC et al (2013) MiR-26a regulates cell cycle and anoikis of human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells through Rb1-E2F1 signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 40:1711–1720
Zhang X, Cheng SL, Bian K et al (2015) MicroRNA-26a promotes anoikis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting alpha5 integrin. Oncotarget 6:2277–2289
Zhang YY, Li XW, Li XD et al (2022a) Comprehensive analysis of anoikis-related long non-coding RNA immune infiltration in patients with bladder cancer and immunotherapy. Front Immunol 13:1055304
Zhang H, Huang Y, Yang E et al (2022b) Identification of a fibroblast-related prognostic model in glioma based on bioinformatics methods. Biomolecules 12:1598
Zhou C, Zhang Z, Zhu X et al (2020) N6-Methyladenosine modification of the TRIM7 positively regulates tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in osteosarcoma through ubiquitination of BRMS1. EBioMedicine 59:102955
Funding
This work was supported by the Shandong Provincial Taishan Scholars Expert Program (Grant No. tstp20221158), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172647, 82073200, 81874178), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Shandong University), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR2021ZD26, ZR2021MH194) and the Jinan University Innovation Team Independent Training Fund (2020GXRC023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CX, GQP and GXM designed the research process of this study. CX, HCW and LJY. downloaded and processed the data from common databases. CX accomplished the experiments in this study. CX, RZL, CCY, YFY and YCY drew the pictures and made all the tables in this research. CX and XZ accomplished and revised the manuscript. ZRD and TL were responsible for the designment and accomplishment of this research. All authors agreed to submit this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics statement
All patient’s samples in this study were approved by the Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

432_2023_5428_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file1 Fig. S1: qRT-PCR results showing the expression of 6 ARGs in HCC and paracancerous tissues. (A) E2F1. (B) BRMS1. (C) ITGA5. (D) PTRH2. (E) PTK2. (F) BMF. * p value <0.05; ** p value <0.01 (JPG 1009 KB)

432_2023_5428_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file2 Fig. S2: Verifying the values of the signature to predict HCC patient prognosis via data from the GSE116174 dataset. (A) Kaplan‒Meier curves showing the OS of HCC patients in different risk groups. (B-C) Scatterplots showing the survival conditions and survival times of HCC patients in the GSE116174 dataset. (D) ROC curves showing the AUC values of the prognostic signature at 1, 3, and 5 years in the GSE116174 dataset. (F) A heatmap showing the expression levels of 6 ARGs in tissues of different risk groups in the GSE116174 dataset (JPG 693 KB)

432_2023_5428_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file3 Fig. S3: Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses of the risk score. (A): Univariate Cox regression analysis via data from TCGA database. (B): Multivariate Cox regression analysis via data from the TCGA database. (C): Univariate Cox regression analysis via data from the ICGC database. (D): Multivariate Cox regression analysis via data from the ICGC database (JPG 404 KB)

432_2023_5428_MOESM4_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file4 Fig. S4: Boxplots showing the expression of 6 ARGs in patients with different clinical features. * p value <0.05; ** p value <0.01; *** p value <0.001 (JPG 1028 KB)

432_2023_5428_MOESM5_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file5 Fig. S5: Boxplots showing the different IC50 values of 6 types of common chemotherapeutic drugs between patients with different prognostic risks. (A): Cisplatin. (B): Cyclophosphamide. (C): 5-Fluorouracil. (D): Gemcitabine. (E): Oxaliplatin. (F): Temozolomide (JPG 971 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, C., Pan, G., Wang, H. et al. Construction of an anoikis‒related prognostic signature to predict immunotherapeutic response and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 16869–16884 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05428-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05428-0