Abstract
Purpose
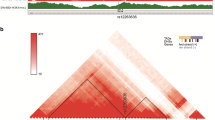
Genome-wide association studies have identified SMAD7 as a colorectal cancer (CRC) susceptibility gene. However, its underlying mechanism has not yet been characterized. This study screened functional SNPs (fSNPs) related to colorectal cancer through Reel-seq and obtained regulatory proteins on functional SNPs.
Methods
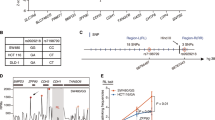
The candidate fSNPs on the SMAD7 locus were screened by Reel-seq method. Eight SNPs such as rs8085824 were identified as functional SNPs by luciferase reporter assay and EMSA, SDCP-MS and AIDP-WB revealed that HNRNPK can specifically bind to the rs8085824-C allele. The knockdown of HNRNPK by RNAi proved that HNRNPK could affect cell function by regulating SMAD7.
Results
Eight functional SNPs was found on the SMAD7 locus in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with R2 > 0.8, i.e., rs12953717, rs7227023, rs34007497, rs58920878, rs8085824, rs4991143, rs4939826, and rs7227023. We also identified allele-imbalanced binding of HNRNPK to rs8085824, H1-3 to rs12953717, THOC6 to rs7227023, and DDX21 to rs58920878. Further functional analysis revealed that these proteins are the regulatory proteins that modulate the expression of SMAD7 in the human colorectal cancer cell line DLD1. In particular, we discovered that siRNA knockdown of HNRNPK inhibits cell proliferation and cell clonal formation by downregulating SMAD7, as the decreased cell proliferation and cell clonal formation in the siRNA HNRNPK knockdown cells was restored by SMAD7 overexpression.
Conclusion
Our findings reveal a mechanism which underlies the contribution of the fSNP rs8085824 on the SMD7 locus to CRC susceptibility.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article are available in the article and in its online supplementary material.
References
Bogaert J, Prenen HJAOG (2014) Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Ann Gastroenterol 27(1):9–14
Boulay JL, Mild G, Lowy A, Reuter J, Lagrange M, Terracciano L et al (2003) SMAD7 is a prognostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 104:446–449
Cheng X, Zhang F, Gong J, Li Y, Zhou D, Wang J et al (2022) Identification of potential functional variants and genes at 18q211 associated with the carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet 18:e1010050
De Simone V, Bevivino G, Sedda S, Izzo R, Laudisi F, Dinallo V et al (2017) Smad7 knockdown activates protein kinase RNA-associated eIF2α pathway leading to colon cancer cell death. Cell Death Dis 8:e2681–e2681
Edlund S, Lee SY, Grimsby S, Zhang S, Aspenström P, Heldin C-H et al (2005) Interaction between Smad7 and β-catenin: importance for transforming growth factor β-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 25:1475–1488
El-Fattah A, Ahmed A, Sadik NAH, Shaker OG, Mohamed Kamal AJMOI (2018) Single nucleotide polymorphism in SMAD7 and CHI3L1 and colorectal cancer risk. 2018:9853192
Fitzpatrick-Lewis D, Ali MU, Warren R, Kenny M, Sherifali D, Raina PJCCC (2016) Screening for colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Colorectal Cancer 15:298–313
Fortini BK, Tring S, Plummer SJ, Edlund CK, Moreno V, Bresalier RS et al (2014) Multiple functional risk variants in a SMAD7 enhancer implicate a colorectal cancer risk haplotype. PLoS ONE 9:e111914
Halder SK, Beauchamp RD, Datta PKJECR (2005) Smad7 induces tumorigenicity by blocking TGF-β-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 307:231–246
Huang Y, Wu W, Nie M, Li C, Wang LJO (2016) SMAD7 polymorphisms and colorectal cancer risk: a meta-analysis of case–control studies. Oncotarget 7:75561
Keum N, Giovannucci EJN, r. G. & hepatology. (2019) Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:713–732
Liu S, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Wu J, Liang J, Yu S et al (2017) Systematic identification of regulatory variants associated with cancer risk. Genome Biol 18:1–14
Nakao AJIOS, Afrakhte M, Moren A, Nakayama T, Christian JL, Heuchel R, Itoh S, Kawabata M, Heldin NE, Heldin CH, Ten Dijke P (1997) A TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta signalling. Nature 389:631–635
Rao H-L, Chen J-W, Li M, Xiao Y-B, Fu J, Zeng Y-X et al (2012) Increased intratumoral neutrophil in colorectal carcinomas correlates closely with malignant phenotype and predicts patients’ adverse prognosis. PLoS ONE 7:e30806
Rich JNJCR (2007) Cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Cancer Res 67:8980–8984
Sanjana NE, Shalem O, Zhang FJNM (2014) Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat Methods 11:783–784
Stolfi C, De Simone V, Colantoni A, Franze E, Ribichini E, Fantini M et al (2014) A functional role for Smad7 in sustaining colon cancer cell growth and survival. Cell Death Dis 5:e1073–e1073
Tong L, Shen S, Huang Q, Fu J, Wang T, Pan L et al (2020) Proteasome-dependent degradation of Smad7 is critical for lung cancer metastasis. Cell Death Differ 27:1795–1806
Venables JP, Koh C-S, Froehlich U, Lapointe E, Couture S, Inkel L et al (2008) Multiple and specific mRNA processing targets for the major human hnRNP proteins. Mol Cell Biol 28:6033–6043
Wang Z, Qiu H, He J, Liu L, Xue W, Fox A et al (2020) The emerging roles of hnRNPK. J Cell Physiol 235:1995–2008
Zhao Y, Zhao M-F, Jiang S, Wu J, Liu J, Yuan X-W et al (2020) Liver governs adipose remodelling via extracellular vesicles in response to lipid overload. Nat Commun 11:719
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Gang Li (University of Pittsburgh, USA) for scientific discussions concerning this work.
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (23141901800, 23141903300) and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (82173099, 32270960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MQ and HR supervised the project. ZL, HS, HM, YW and CT performed the experiments and analyzed the data. MQ, YZ and TF supervised the Reel-seq experiments. BD and JQ provided advice and technical expertise. HR and ZL wrote the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and approved its final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no relevant financial interests and no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2023_5402_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 Supplementary Figure 2. The luciferase reporter gene demonstrated that HNRNPK could regulate luciferase activity through rs8085824-C, through knockdown or overexpression of HNRNPK in DLD1 cells(n>3). RLA relative luciferase activity, P value was calculated using Student’s t test with two tails. Error bars, SD. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (TIF 4403 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Song, H. et al. Identification and characterization of colorectal-cancer-associated SNPs on the SMAD7 locus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 16659–16668 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05402-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05402-w