Abstract
Introduction
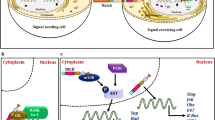
Hedgehog Signaling, a basic cancer stem cell pathway, plays a major role during the embryonic development, is known to play a quiescent role in adults. However, aberrant activation of Hedgehog signaling in adults is known to play a role in cancer development. Hence, the aim of the study was to identify the role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in the Oral cancers.
Materials and Methods
The expression of Hedgehog signaling pathway was evaluated in 124 patients through the quantitative real-time PCR. The association between the gene expression and clinico-pathological parameters were analyzed using the Pearson chi-square test and survival analysis was carried out using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Results
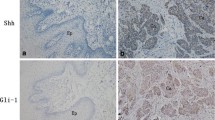
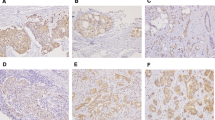
SHH and GLI1 was found to be significantly associated with the Lymph Node Status and SUFU was significantly associated with the Age. SMO and SUFU were found to have a worse prognosis in oral cancer patients. According to our findings, IHH plays a critical role in the activation of the HH signaling pathway in oral cancer.
Conclusion
These findings back up the use of the Hedgehog signaling pathway as a biomarker for early disease prediction in oral cancer, as well as its role in tumor aggressiveness and invasiveness.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request and with the prior permission from the institute.
References
Abati S, Bramati C, Bondi S, Lissoni A, Trimarchi M (2020) Oral cancer and precancer: a narrative review on the relevance of early diagnosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:9160
Athar M, Tang X, Lee JL, Kopelovich L, Kim AL (2006) Hedgehog signalling in skin development and cancer. Exp Dermatol 15:667–677
Avery JT, Zhang R, Boohaker RJ (2021) GLI1: a therapeutic target for cancer. Front Oncol 11:673154
Bakry OA, Samaka RM, Shoeib MA, Megahed DM (2015) Immunolocalization of glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 in non melanoma skin cancer. Ultrastruct Pathol 39:135–146
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, De Oca RM, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K et al (2003) Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature 425:846–851
Bugshan A, Farooq IJF (2020) Oral squamous cell carcinoma: metastasis, potentially associated malignant disorders, etiology and recent advancements in diagnosis. F1000Res 9:229
Cavicchioli Buim ME, Gurgel CA, Goncalves Ramos EA, Lourenco SV, Soares FA (2011) Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling in oral squamous cell carcinomas: a preliminary study. Hum Pathol 42:1484–1490
Chang JH, Wu CC, Yuan KS, Wu ATH, Wu SY (2017) Locoregionally recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: incidence, survival, prognostic factors, and treatment outcomes. Oncotarget 8:55600–55612
Choudhry Z, Rikani AA, Choudhry AM, Tariq S, Zakaria F, Asghar MW et al (2014) Sonic Hedgehog signalling pathway: a complex network. Ann Neurosci 21:28–31
Chung CH, Dignam JJ, Hammond ME, Klimowicz AC, Petrillo SK, Magliocco A et al (2011) Glioma-associated oncogene family zinc finger 1 expression and metastasis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with radiation therapy (RTOG 9003). J Clin Oncol 29:1326–1334
da Silva SD, Ferlito A, Takes RP, Brakenhoff RH, Valentin MD, Woolgar JA et al (2011) Advances and applications of oral cancer basic research. Oral Oncol 47:783–791
Dahmane N, Lee J, Robins P, Heller P, Altaba AR (1997) Activation of the transcription factor Gli1 and the Sonic Hedgehog signalling pathway in skin tumours. Nature 389:876–881
Dimitrova K, Stoehr M, Dehghani F, Dietz A, Wichmann G, Bertolini J et al (2013) Overexpression of the Hedgehog signalling pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Onkologie 36:279–286
Ding YL, Zhou Y, Xiang L, Ji ZP, Luo ZH (2012) Expression of glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 is associated with invasion and postoperative liver metastasis in colon cancer. Int J Med Sci 9:334–338
Dong W, Cui J, Tian X, He L, Wang Z, Zhang P et al (2014) Aberrant sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway and STAT3 activation in papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:1786–1793
D’Souza S, Addepalli V (2018) Preventive measures in oral cancer: an overview. Biomed Pharmacother 107:72–80
Fan HX, Wang S, Zhao H, Liu N, Chen D, Sun M et al (2014) Sonic Hedgehog signaling may promote invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by activating MMP-9 and E-cadherin expression. Med Oncol 31:41
Fei DL, Sanchez-Mejias A, Wang Z, Flaveny C, Long J, Singh S et al (2012) Hedgehog signaling regulates bladder cancer growth and tumorigenicity. Cancer Res 72:4449–4458
Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP (1997) Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 277:1109–1113
Gu D, Xie J (2015) Non-canonical Hh signaling in cancer-current understanding and future directions. Cancers (basel) 7:1684–1698
Hanagiri T, Shinohara S, Takenaka M, Shigematsu Y, Yasuda M, Shimokawa H et al (2012) Effects of hyaluronic acid and CD44 interaction on the proliferation and invasiveness of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Tumour Biol 33:2135–2141
Hong Z, Bi A, Chen D, Gao L, Yin Z, Luo L (2014) Activation of Hedgehog signaling pathway in human non-small cell lung cancers. Pathol Oncol Res 20:917–922
Huang S, He J, Zhang X, Bian Y, Yang L, Xie G et al (2006) Activation of the Hedgehog pathway in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 27:1334–1340
Im S, Choi HJ, Yoo C, Jung JH, Jeon YW, Suh YJ et al (2013) Hedgehog related protein expression in breast cancer: gli-2 is associated with poor overall survival. Korean J Pathol 47:116–123
Jakob M, Sharaf K, Schirmer M, Leu M, Kuffer S, Bertlich M et al (2021) Role of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1, BCL11B, BMI-1, and CD44 in the prognosis of advanced HNSCC. Strahlenther Onkol 197:231–245
Jiang J (2022) Hedgehog signaling mechanism and role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 85:107–122
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM et al (1996) Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272:1668–1671
Joshi J, Patel H, Bhavnagari H, Tarapara B, Pandit A, Shah F (2022) Eliminating cancer stem-like cells in oral cancer by targeting elementary signaling pathways. Crit Rev Oncog 27(4):65–82
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A et al (2004) Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature 431:707–712
Ke B, Wang XN, Liu N, Li B, Wang XJ, Zhang RP et al (2020) Sonic Hedgehog/Gli1 signaling pathway regulates cell migration and invasion via induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. J Cancer 11:3932–3943
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Tsakmaki V, Danielidis V, Sivridis E (2012) Cancer stem cell phenotype relates to radio-chemotherapy outcome in locally advanced squamous cell head-neck cancer. Br J Cancer 106:846–853
Kumar V, Vashishta M, Kong L, Wu X, Lu JJ, Guha C et al (2021) The role of notch Hedgehog, and Wnt signaling pathways in the resistance of tumors to anticancer therapies. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:650772
Laurendeau I, Ferrer M, Garrido D, D’Haene N, Ciavarelli P, Basso A et al (2010) Gene expression profiling of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in human meningiomas. Mol Med 16:262–270
Leng Z, Xia Q, Chen J, Li Y, Xu J, Zhao E et al (2018) Lgr5+CD44+EpCAM+ strictly defines cancer stem cells in human colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:860–872
Leovic D, Sabol M, Ozretic P, Musani V, Car D, Marjanovic K et al (2012) Hh-Gli signaling pathway activity in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 34:104–112
Liao X, Siu MK, Au CW, Wong ES, Chan HY, Ip PP et al (2009) Aberrant activation of hedgehog signaling pathway in ovarian cancers: effect on prognosis, cell invasion and differentiation. Carcinogenesis 30:131–140
Lim S, Lim SM, Kim MJ, Park SY, Kim JH (2019) Sonic Hedgehog pathway as the prognostic marker in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer. Yonsei Med J 60:898–904
Lu JT, Zhao WD, He W, Wei W (2012) Hedgehog signaling pathway mediates invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ERK pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:691–700
Ma C, Hu K, Ullah I, Zheng Q-K, Zhang N, Sun Z-G (2022) Molecular mechanisms involving the sonic Hedgehog pathway in lung cancer therapy: recent advances. Front Oncol 12:729088
Nedjadi T, Salem N, Khayyat D, Al-Sayyad A, Al-Ammari A, Al-Maghrabi J (2019) Sonic Hedgehog expression is associated with lymph node invasion in urothelial bladder cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 25:1067–1073
Niewiadomski P, Niedziolka SM, Markiewicz L, Uspienski T, Baran B, Chojnowska K (2019) Gli proteins: regulation in development and cancer. Cells 8(2):147
Nishimaki H, Kasai K, Kozaki K, Takeo T, Ikeda H, Saga S et al (2004) A role of activated sonic Hedgehog signaling for the cellular proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:313–320
Oliveira LR, Castilho-Fernandes A, Oliveira-Costa JP, Soares FA, Zucoloto S, Ribeiro-Silva A (2014) CD44+/CD133+ immunophenotype and matrix metalloproteinase-9: influence on prognosis in early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 36:1718–1726
Padma R, Kalaivani A, Sundaresan S, Sathish P (2017) The relationship between histological differentiation and disease recurrence of primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 21:461
Patel H, Joshi J, Raval A, Shah F (2022) Identification of natural compounds to inhibit sonic Hedgehog pathway in oral cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 22:905–913
Peacock CD, Wang Q, Gesell GS, Corcoran-Schwartz IM, Jones E, Kim J et al (2007) Hedgehog signaling maintains a tumor stem cell compartment in multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:4048–4053
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Po A, Silvano M, Miele E, Capalbo C, Eramo A, Salvati V et al (2017) Noncanonical GLI1 signaling promotes stemness features and in vivo growth in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 36:4641–4652
Ponta H, Sherman L, Herrlich PA (2003) CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:33–45
Prince ME, Sivanandan R, Kaczorowski A, Wolf GT, Kaplan MJ, Dalerba P et al (2007) Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:973–978
Qi Y, Zhao W, Wang Z, Meng XJIJCEP (2016) Expression of Shh signaling pathway factors in gastrointestinal stromal tumor tissues and their associations with clinical pathological factors. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 9:2841–2848
Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, Hebrink D, Alderete B, Fults DW et al (1997) Sporadic medulloblastomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res 57:842–845
Rather TB, Parveiz I, Bhat GA, Rashid G, Akhtar K, Haque R et al (2023) Colorectal Cancer (CRC): investigating the expression of the suppressor of fused (SuFu) gene and its relationship with several inflammatory blood-based biomarkers. Biomedicines 11(2):540
Rimkus TK, Carpenter RL, Qasem S, Chan M, Lo HW (2016) Targeting the sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway: review of smoothened and GLI inhibitors. Cancers (basel) 8(2):22
Riobo-Del Galdo NA, Lara Montero A, Wertheimer EV (2019) Role of Hedgehog signaling in breast cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutics. Cells 8(4):375
Rivera C (2015) Essentials of oral cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:11884–11894
Robbins DJ, Fei DL, Riobo NA (2012) The Hedgehog signal transduction network. Sci Signal 5:re6
Rodrigues M, Miguita L, De Andrade NP, Heguedusch D, Rodini CO, Moyses RA et al (2018) GLI3 knockdown decreases stemness, cell proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 53:2458–2472
Ruiz i Altaba A, Sanchez P, Dahmane N (2002) Gli and Hedgehog in cancer: tumours, embryos and stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2:361–372
Sabol M, Trnski D, Musani V, Ozretic P, Levanat S (2018) Role of GLI transcription factors in pathogenesis and their potential as new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci 19(9):2562
Saghravanian N, Anvari K, Ghazi N, Memar B, Shahsavari M, Aghaee MA (2017) Expression of p63 and CD44 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and correlation with clinicopathological parameters. Arch Oral Biol 82:160–165
Santini R, Vinci MC, Pandolfi S, Penachioni JY, Montagnani V, Olivito B et al (2012) Hedgehog-GLI signaling drives self-renewal and tumorigenicity of human melanoma-initiating cells. Stem Cells 30:1808–1818
Sarode G, Maniyar N, Sarode SC, Jafer M, Patil S, Awan KH (2020) Epidemiologic aspects of oral cancer. Dis Mon 66:100988
Sawant S, Gokulan R, Dongre H, Vaidya M, Chaukar D, Prabhash K et al (2016) Prognostic role of Oct4, CD44 and c-Myc in radio-chemo-resistant oral cancer patients and their tumourigenic potential in immunodeficient mice. Clin Oral Investig 20:43–56
Sims-Mourtada J, Izzo JG, Apisarnthanarax S, Wu TT, Malhotra U, Luthra R et al (2006) Hedgehog: an attribute to tumor regrowth after chemoradiotherapy and a target to improve radiation response. Clin Cancer Res 12:6565–6572
Song L, Chen X, Gao S, Zhang C, Qu C, Wang P et al (2016) Ski modulate the characteristics of pancreatic cancer stem cells via regulating sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway. Tumour Biol 37:16115–16125
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY et al (2003) Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 425:851–856
Thorne RF, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Jing X, Zhang XD, de Bock CE et al (2020) Evaluating nuclear translocation of surface receptors: recommendations arising from analysis of CD44. Histochem Cell Biol 153:77–87
Tostar U, Malm CJ, Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG, Toftgard R, Unden AB (2006) Deregulation of the hedgehog signalling pathway: a possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Pathol 208:17–25
Wang YF, Chang CJ, Lin CP, Chang SY, Chu PY, Tai SK et al (2012) Expression of hedgehog signaling molecules as a prognostic indicator of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 34:1556–1561
Xie J, Murone M, Luoh SM, Ryan A, Gu Q, Zhang C et al (1998) Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature 391:90–92
Xu H, Tian Y, Yuan X, Wu H, Liu Q, Pestell RG et al (2015) The role of CD44 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer development. Onco Targets Ther 8:3783–3792
Xu Y, Song S, Wang Z, Ajani JA (2019) The role of hedgehog signaling in gastric cancer: molecular mechanisms, clinical potential, and perspective. Cell Commun Signal 17:157
Yanai K, Nagai S, Wada J, Yamanaka N, Nakamura M, Torata N et al (2007) Hedgehog signaling pathway is a possible therapeutic target for gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol 95:55–62
Yanamoto S, Yamada S, Takahashi H, Naruse T, Matsushita Y, Ikeda H et al (2014) Expression of the cancer stem cell markers CD44v6 and ABCG2 in tongue cancer: effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on local recurrence. Int J Oncol 44:1153–1162
Yang L, Xie G, Fan Q, Xie J (2010) Activation of the hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene 29:469–481
Yang Q, Shen SS, Zhou S, Ni J, Chen D, Wang G et al (2012) STAT3 activation and aberrant ligand-dependent sonic hedgehog signaling in human pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol 93:227–236
Yao Y, Zhou D, Shi D, Zhang H, Zhan S, Shao X et al (2019) GLI1 overexpression promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration and induces drug resistance by combining with the AKT-mTOR pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 111:993–1004
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden TL (2012) Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinformatics 13:134
Zhang D, Cao L, Li Y, Lu H, Yang X, Xue P (2013) Expression of glioma-associated oncogene 2 (Gli 2) is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatectomy. World J Surg Oncol 11:25
Zhang Z, Zou Y, Liang M, Chen Y, Luo Y, Yang B et al (2017) Suppressor of fused (Sufu) promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:114226–114238
Zhao C, Chen A, Jamieson CH, Fereshteh M, Abrahamsson A, Blum J et al (2009) Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature 458:776–779
Acknowledgements
Hitarth Patel is PhD student of Life science (Faculty of Science), Gujarat University working at The Gujarat Cancer & Research Institute. Dr Franky D. Shah is a recognized PhD Supervisor of Life Science (Faculty of Science), Gujarat University working at The Gujarat Cancer & Research Institute.
Funding
N/A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study Concept - FDS; Study Design - FDS; Data Acquisition - HVP; Data Analysis and Interpretation - HVP, JSJ; Statistical Analysis: HVP, JSJ; Manuscript Preparation: HVP; Manuscript Editing: FDS; Manuscript Review: FDS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest in the paper.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study has been approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (EC/06/2019).
Human and animal rights
N/A.
Consent for publication
The consent for publication has been taken from the Institutional Review Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, H.V., Joshi, J.S. & Shah, F.D. A clinicopathological exploration of Hedgehog signaling: implications in oral carcinogenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 16525–16535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05383-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05383-w