Abstract
Background
Although targeted therapies and immunotherapy have achieved significant clinical benefits in patients with certain pathological types of lung cancer. However, prognosis for patients with lung adenocarcinoma still remains unsatisfactory. It is of extremely importance to find ideal prognostic indicators to predict the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients, especially for patients with early and locally advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma. The purpose of this study is to elucidate the significance of Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR1) and Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) expression in predicting progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients with early and locally advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma.
Methods
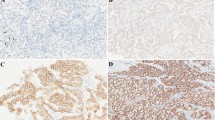
In this study, IGFR1 and VEGF-A expression on 119 specimens of patients early and locally advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma were analyzed by immunohistochemistry with an H-score system.
Results
Both high IGFR1 expression and VEGF-A expression patients were resulted in 59 (49.6%) separately. The numbers and proportions of IGFR1−&VEGF-A− subgroup, IGFR1−&VEGF-A+ subgroup, IGFR1+&VEGF-A− subgroup and IGFR1+&VEGF-A+ subgroup are 23 (19.3%), 37 (31.1%), 37 (31.1%) and 22 (18.5%) respectively. High IGFR1 expression was significantly associated with both poor PFS and OS of all patients in a univariate analysis. Multivariable analysis showed that patients with IGFR1+&VEGF-A+ expression exhibited a worst PFS and OS in the subgroup of lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR mutation.
Conclusions
These results suggest that IGFR1+&VEGF-A+ is expected to be a disadvantageous factor for prognosis in the subgroup of EGFR mutation in patients with early and locally advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma. What’s more, this study may provide the theoretical possibility to screen optimal population for a combination therapy with anti-VEGF and anti-IGFR1 in patients with early and locally advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated or analysed during current study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Ahlen J, Wejde J, Brosjo O et al (2005) Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor expression correlates to good prognosis in highly malignant soft tissue sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:206–216
Alyoussef A (2021) The therapeutic effects of blocking IGF-R1 on mice model of skin cancer. J Dermatolog Treat 32:803–811. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2019.1708243
Cappuzzo F, Toschi L, Tallini G et al (2006) Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR-1) is significantly associated with longer survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. Ann Oncol 17:1120–1127. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdl077
Chen J, Liu BX, Shen Q et al (2020) Limonin inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis of human breast cancer cells by suppressing the VEGFR2/IGFR1-mediated STAT3 signaling pathway. Transl Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr-20-1992
Claesson-Welsh L, Welsh M (2013) VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J Intern Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12019
Dufourny B, Alblas J, Van Teeffelen HA et al (1997) Mitogenic signaling of insulin-like growth factor I in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and is independent of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 272:31163–31171. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.49.31163
Gariboldi MB, Ravizza R, Monti E (2010) The IGFR1 inhibitor NVP-AEW541 disrupts a pro-survival and pro-angiogenic IGF-STAT3-HIF1 pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 80:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2010.05.011
Golestan S, Soltani BM, Jafarzadeh M et al (2023) LINC02381 suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via attenuating IGF1R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in breast cancer. Funct Integr Genomics 23:40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00965-w
Jenkins R, Walker J, Roy UB (2023) 2022 cancer statistics: Focus on lung cancer. Future Oncol. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2022-1214
Joehlin-Price AS, Stephens JA, Zhang J et al (2016) Endometrial cancer insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expression increases with body mass index and is associated with pathologic extent and prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 25:438–445. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-1145
Khandwala HM, Mccutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A et al (2000) The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev 21:215–244. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.21.3.0399
Liu S, Qin T, Jia Y et al (2019) PD-L1 expression Is associated With VEGFA and LADC patients’ survival. Front Oncol 9:189. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00189
Ludovini V, Bellezza G, Pistola L et al (2009) High coexpression of both insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGFR-1) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated with shorter disease-free survival in resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 20:842–849. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdn727
Mathur RS, Mathur SP (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) up-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in cervical cancer in vitro: this action is mediated through HPV-E6 in HPV-positive cancers. Gynecol Oncol 97:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.12.011
Mehta S, Fiorelli R, Bao X et al (2022) A phase 0 trial of Ceritinib in patients with brain metastases and recurrent glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 28:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1096
Micke P, JS Mattsson, D Djureinovic, et al (2016) The Impact of the Fourth Edition of the WHO Classification of Lung Tumours on Histological Classification of Resected Pulmonary NSCCs. J Thorac Oncol https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.01.020.
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E et al (2018) Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol 52:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019
Park E, Park SY, Kim H et al (2015) Membranous Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) expression Is predictive of poor prognosis in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J Pathol Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.10
Qin T, Xia J, Liu S et al (2020) Clinical importance of VEGFC and PD-L1 co-expression in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Thorac Cancer 11:1139–1148. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13354
Ramanathan R, Olex AL, Dozmorov M et al (2017) Angiopoietin pathway gene expression associated with poor breast cancer survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat 162:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4102-2
Reinmuth N, Jauch A, Xu EC et al (2008) Correlation of EGFR mutations with chromosomal alterations and expression of EGFR, ErbB3 and VEGF in tumor samples of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.03.011
Rocha RL, Hilsenbeck SG, Jackson JG et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and insulin receptor substrate-1 in breast cancer: correlation with clinical parameters and disease-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 3:103–109
Da Cunha Santos G, Shepherd FA, Tsao MS (2011) EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 6:49–69. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130206
Sharma R (2022) Mapping of global, regional and national incidence, mortality and mortality-to-incidence ratio of lung cancer in 2020 and 2050. Int J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-021-02108-2
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS et al (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21763
Takahashi N, Iwasa S, Taniguchi H et al (2016) Prognostic role of ERBB2, MET and VEGFA expression in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with anti-EGFR antibodies. Br J Cancer 114:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.74
Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res 57:3079–3083
Wang X, Chen L, Zhao X et al (2020) A cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide suppresses cardiac hypertrophy induced by pressure overload by regulating IGFR1/PI3K/AKT and TLR9/AMPKalpha. Cell Death Dis 11:96. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2296-4
Wang P, Mak VC, Cheung LW (2023) Drugging IGF-1R in cancer: new insights and emerging opportunities. Genes Dis 10:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2022.03.002
Funding
This work was supported in part by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.82272686, Tingting Qin and Grant No.82203628, Jingya Wang), Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (Grant No.21JCYBJC01000, Tingting Qin), Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project (Grant No.TJYXZDXK-010A). This work was supported by Cancer Biobank of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TWL and TTQ analyzed and interpreted the patient data. TWL and LJX performed IHC. WQD, TM and YJW evaluated the data. TTQ and TWL were the major contributors in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital (Tianjin, China) and it conforms to the provisions of in accordance with the Helsinki Declarations revised in 2013, approved the use of human tissues for this study (EK2018039). The study outcomes will not affect the future management of the patients.
Informed consent
All cancer patients signed an informed consent form for participation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Xia, J., Du, Q. et al. Clinico-pathological characteristics of IGFR1 and VEGF-A co-expression in early and locally advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 16365–16376 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05371-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05371-0