Abstract
Purpose
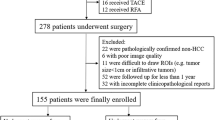
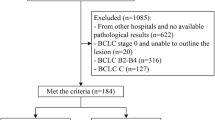
The prognosis of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after radical resection has received widespread attention, but reliable prediction methods are lacking. Radiomics derived from enhanced computed tomography (CT) imaging offers a potential avenue for practical prognostication in HCC patients.
Methods
We recruited early-stage HCC patients undergoing radical resection. Statistical analyses were performed to identify clinicopathological and radiomic features linked to recurrence. Clinical, radiomic, and combined models (incorporating clinicopathological and radiomic features) were built using four algorithms. The performance of these models was scrutinized via fivefold cross-validation, with evaluation metrics including the area under the curve (AUC), accuracy (ACC), sensitivity (SEN), and specificity (SPE) being calculated and compared. Ultimately, an integrated nomogram was devised by combining independent clinicopathological predictors with the Radscore.
Results
From January 2016 through December 2020, HCC recurrence was observed in 167 cases (64.5%), with a median time to recurrence of 26.7 months following initial resection. Combined models outperformed those solely relying on clinicopathological or radiomic features. Notably, among the combined models, those employing support vector machine (SVM) algorithms exhibited the most promising predictive outcomes (AUC: 0.840 (95% Confidence interval (CI): [0.696, 0.984]), ACC: 0.805, SEN: 0.849, SPE: 0.733). Hepatitis B infection, tumour size > 5 cm, and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) > 400 ng/mL were identified as independent recurrence predictors and were subsequently amalgamated with the Radscore to create a visually intuitive nomogram, delivering robust and reliable predictive performance.
Conclusion
Machine learning models amalgamating clinicopathological and radiomic features provide a valuable tool for clinicians to predict postoperative HCC recurrence, thereby informing early preventative strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbasian Ardakani A, Bureau NJ, Ciaccio EJ, Acharya UR (2022) Interpretation of radiomics features—a pictorial review. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 215:106609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106609
Aerts HJ (2016) The potential of radiomic-based phenotyping in precision medicine: a review. JAMA Oncol 2(12):1636–1642. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.2631
Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RT, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, Lambin P (2014) Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 5:4006. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006
Ataei A, Deng J, Muhammad W (2023) Liver cancer risk quantification through an artificial neural network based on personal health data. Acta Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186x.2023.2213445
Bi WL, Hosny A, Schabath MB, Giger ML, Birkbak NJ, Mehrtash A, Aerts H (2019) Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J Clin 69(2):127–157. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21552
Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M (2016) Evidence-Based Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 150(4):835–853. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2015.12.041
D’Souza S, Lau KC, Coffin CS, Patel TR (2020) Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 26(38):5759–5783. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5759
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines (2018) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 69(1):182–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J (2018) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 391(10127):1301–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30010-2
Galle PR, Foerster F, Kudo M, Chan SL, Llovet JM, Qin S, Zhu AX (2019) Biology and significance of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 39(12):2214–2229. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14223
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures. They are Data Radiology 278(2):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Hanif H, Ali MJ, Susheela AT, Khan IW, Luna-Cuadros MA, Khan MM, Lau DT (2022) Update on the applications and limitations of alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 28(2):216–229. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i2.216
Hemming AW, Berumen J, Mekeel K (2016) hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 20(4):703–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2016.06.007
Hu X, Chen R, Wei Q, Xu X (2022) The landscape of alpha fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: where are we? Int J Biol Sci 18(2):536–551. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.64537
Iannacone M, Guidotti LG (2022) Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Nat Rev Immunol 22(1):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-021-00549-4
Jin P, Yang L, Qiao X, Hu C, Hu C, Wang X, Bao J (2022) Utility of clinical-radiomic model to identify clinically significant prostate cancer in biparametric MRI PI-RADS V2.1 category 3 lesions. Front Oncol 12:840786. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.840786
Kamel H, Abdulah D, Al-Tuwaijari JM (2019). Cancer Classification Using Gaussian Naive Bayes Algorithm. In: Paper Presented at the 2019 International Engineering Conference (IEC).
Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM, Peerlings J, de Jong EEC, van Timmeren J, Walsh S (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(12):749–762. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.141
Li J, Xia F, Wang X, Jin Y, Yan J, Wei X, Zhao Q (2023) Multiclassifier radiomics analysis of ultrasound for prediction of extrathyroidal extension in papillary thyroid carcinoma in children. Int J Med Sci 20(2):278–286. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.79758
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Finn RS (2021) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3
Lubner MG, Smith AD, Sandrasegaran K, Sahani DV, Pickhardt PJ (2017) CT texture analysis: definitions, applications, biologic correlates, and challenges. Radiographics 37(5):1483–1503. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2017170056
Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, Heimbach JK (2018) Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the american association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 68(2):723–750. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29913
Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, Häggström I, Szczypiński P, Gibbs P, Cook G (2020) Introduction to radiomics. J Nucl Med 61(4):488–495. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.118.222893
Noble WS (2006) What is a support vector machine? Nat Biotechnol 24(12):1565–1567. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1206-1565
O’Connor JP, Aboagye EO, Adams JE, Aerts HJ, Barrington SF, Beer AJ, Waterton JC (2017) Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(3):169–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.162
O’Leary C, Mahler M, Soulen MC (2020) Curative-Intent Therapies in Localized Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol 21(4):31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-020-0725-3
Park HJ, Park B, Lee SS (2020) Radiomics and deep learning: hepatic applications. Korean J Radiol 21(4):387–401. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2019.0752
Poldrack RA, Huckins G, Varoquaux G (2020) Establishment of best practices for evidence for prediction: a review. JAMA Psychiat 77(5):534–540. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3671
Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Bruix J (2022) BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: the 2022 update. J Hepatol 76(3):681–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
Sapisochin G, Bruix J (2017) Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: outcomes and novel surgical approaches. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(4):203–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.193
Sasaki Y, Yamada T, Tanaka H, Ohigashi H, Eguchi H, Yano M, Maoka S (2006) Risk of recurrence in a long-term follow-up after surgery in 417 patients with hepatitis B- or hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 244(5):771–780. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000225126.56483.b3
Toth R, Schiffmann H, Hube-Magg C, Büscheck F, Höflmayer D, Weidemann S, Gerhäuser C (2019) Random forest-based modelling to detect biomarkers for prostate cancer progression. Clin Epigenetics 11(1):148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0736-8
Traverso A, Wee L, Dekker A, Gillies R (2018) Repeatability and reproducibility of radiomic features: a systematic review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 102(4):1143–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.05.053
Tung-Ping Poon R, Fan ST, Wong J (2000) Risk factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 232(1):10–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-200007000-00003
Ueno M, Hayami S, Shigekawa Y, Kawai M, Hirono S, Okada KH (2015) Prognostic impact of surgery and radiofrequency ablation on single nodular HCC ⩽5 cm: Cohort study based on serum HCC markers. J Hepatol 63(6):1352–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.013
Wei H, Yang T, Chen J, Duan T, Jiang H, Song B (2022) Prognostic implications of CT/MRI LI-RADS in hepatocellular carcinoma: state of the art and future directions. Liver Int 42(10):2131–2144. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.15362
Yang JD, Heimbach JK (2020) New advances in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ 371:m3544. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3544
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR (2019) A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(10):589–604. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y
Zhang W, Zhang B, Chen XP (2021) Adjuvant treatment strategy after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Med 15(2):155–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-021-0848-3
Zheng T, Yang L, Du J, Dong Y, Wu S, Shi Q, Liu L (2021) Combination analysis of a radiomics-based predictive model with clinical indicators for the preoperative assessment of histological grade in endometrial carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:582495. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.582495
Zheng JR, Wang ZL, Feng B (2022) Hepatitis B functional cure and immune response. Front Immunol 13:1075916. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1075916
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Fund, Category B (Grant 20212B037) and Zhejiang Basic Public Welfare Research Program (Grant LGF22H160084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QX, ZZ, and CL contributed conception and design of the study; QX and YY organized the database; QX, ZZ, and DL performed the statistical analysis; QX, ZZ, YY, DL, CL wrote sections of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Cancer Hospital (approval number IRB-2022–503). Since this is a retrospective study, the study was conducted with the exception of informed consent.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Zhao, Z., Yang, Y. et al. Radiomics-guided prognostic assessment of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence post-radical resection. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 14983–14996 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05291-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05291-z