Abstract
Purpose
To develop and validate a model that incorporates radiomics based on MRI scans and clinical characteristics to predict lymphovascular invasion (LVSI) in endometrial cancer (EC) patients.
Methods
There were 332 patients with EC enrolled retrospectively in this multicenter study. Radiomics score (Radscore) were computed using the valuable radiomics features. The independent predictors of LVSI were identified by univariate logistic analysis. Multivariate logistic regression was used to develop a clinical–radiomics predictive model. Based on the model, a nomogram was developed and validated internally and externally. The nomogram was evaluated with discrimination, calibration, decision curve analysis (DCA), and clinical impact curves (CIC).
Results
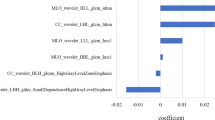
Three predictive models were constructed based on clinicopathological features, radiomic factors and a combination of them, and that the clinic-radiomic model performed best among the three models. Four independent factors comprised the clinical–radiomics model: dynamic contrast enhancement rate of late arterial phase (DCE2), deep myometrium invasion (DMI), lymph node metastasis (LNM), and Radscore. Clinical–radiomics model performance was 0.901 (95% CI 0.84–0.96) in the training cohort, 0.80 (95% CI 0.68–0.92) in the internal validation cohort, and 0.81 (95% CI 0.73–0.9) in the external validation cohort for identifying patients with LVSI, respectively. The model is used to develop a nomogram for clinical use.
Conclusions
The MRI-based radiomics nomogram could serve as a noninvasive tool to predict LVSI in EC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Bosse T et al (2015) Substantial lymph-vascular space invasion (LVSI) is a significant risk factor for recurrence in endometrial cancer—a pooled analysis of PORTEC 1 and 2 trials. Eur J Cancer 51:1742–1750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.05.015
Chen J et al (2021) MRI-based radiomic model for preoperative risk stratification in stage I endometrial cancer. J Cancer 12:726–734. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.50872
Chen J et al (2022) Predicting the risk of active pulmonary tuberculosis in people living with HIV: development and validation of a nomogram. BMC Infect Dis 22:388. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-022-07368-5
Concin N et al (2021) ESGO/ESTRO/ESP guidelines for the management of patients with endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer 31:12–39. https://doi.org/10.1136/ijgc-2020-002230
Crosbie EJ et al (2022) Endometrial cancer. Lancet 399:1412–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00323-3
Dai Y et al (2020) Prognostic significance of lymphovascular space invasion in patients with endometrioid endometrial cancer: a retrospective study from a single center. J Gynecol Oncol 31:e27. https://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e27
Dybvik JA et al (2022) MRI-assessed tumor-free distance to serosa predicts deep myometrial invasion and poor outcome in endometrial cancer. Insights Imaging 13:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-021-01133-z
Jie B et al (2022) Radiomics nomogram improves the prediction of epilepsy in patients with gliomas. Front Oncol 12:856359. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.856359
Jin D, Yuan L, Li F, Wang S, Mao Y (2022) A novel nomogram predicting the risk of postoperative pneumonia for esophageal cancer patients after minimally invasive esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-022-09249-z
Kim SI et al (2021) Prediction of lymphovascular space invasion in patients with endometrial cancer. Int J Med Sci 18:2828–2834. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.60718
Ma X et al (2022) Volumetric ADC histogram analysis for preoperative evaluation of LVSI status in stage I endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Eur Radiol 32:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-07996-6
Mandato VD et al (2020) Accuracy of preoperative endometrial biopsy and intraoperative frozen section in predicting the final pathological diagnosis of endometrial cancer. Surg Oncol 35:229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2020.09.003
Meydanli MM et al (2020) Is it possible to develop a prediction model for lymphovascular space invasion in endometrioid endometrial cancer? Int J Gynecol Pathol 39:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1097/PGP.0000000000000596
Oberndorfer F et al (2021) Risk reclassification of patients with endometrial cancer based on tumor molecular profiling: first real world data. J Pers Med 11:48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010048
Peters EEM et al (2021) Substantial lymphovascular space invasion is an adverse prognostic factor in high-risk endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1097/PGP.0000000000000805
Raffone A et al (2022) Lymphovascular space invasion in endometrial carcinoma: a prognostic factor independent from molecular signature. Gynecol Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2022.01.013
Sahin H et al (2018) Preoperative magnetic resonance volumetry in predicting myometrial invasion, lymphovascular space invasion, and tumor grade: is it valuable in international federation of gynecology and obstetrics stage I endometrial cancer? Int J Gynecol Cancer 28:666–674. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000001208
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Stalberg K et al (2019) Lymphovascular space invasion as a predictive factor for lymph node metastases and survival in endometrioid endometrial cancer—a Swedish Gynecologic Cancer Group (SweGCG) study. Acta Oncol 58:1628–1633. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2019.1643036
Tortorella L et al (2021) Substantial lymph-vascular space invasion (LVSI) as predictor of distant relapse and poor prognosis in low-risk early-stage endometrial cancer. J Gynecol Oncol 32:e11. https://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2021.32.e11
Wang X et al (2022) Development and validation of a novel radiomics-based nomogram with machine learning to preoperatively predict histologic grade in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Front Oncol 12:843376. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.843376
Zhang YF, Ma C, Qian XP (2022) Development and external validation of a novel nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with ascending colon adenocarcinoma after surgery: a population-based study. World J Surg Oncol 20:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-022-02576-4
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate all the patients and their families for participating in this trial. We also express our gratitude to the staffs from our Hospital for their selfless dedication. The authors would like to thank the clinicians in the Department of Radiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine for their professional clinical advice.
Funding
This work is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: 82171925; Developing Program for High-level Academic Talent in Jiangsu Hospital of TCM, Grant/Award Number: y2021rc03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We are so glad to submit our paper to “Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology”. In this research, XW, HL and LS contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; JC, XW, WZ and YT performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; ZW helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions. All the authors reviewed the manuscript, provided feedback, and approved the manuscript in its final form.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they had no financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2023_5044_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 Figure S1 The calibration curves of the clinical-radiomics nomogram in the training, internal validation and external validation cohorts. (TIF 3067 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, X., Lv, H. et al. Development and external validation of a clinical–radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of LVSI status in patients with endometrial carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 13943–13953 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05044-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05044-y