Abstract
Purpose
Early diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) is critical to patient prognosis; however, there is lack of non-invasive biomarkers that are extremely sensitive and specific for early screening and diagnosis. Exosomes are a novel tool applied to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Changes in plasma exosomal proteins have a certain relationship with the development of various diseases including tumors. Here, we aimed to find exosomal biomarkers for early diagnosis of CRC.
Methods
Exosomes obtained by ultracentrifugation from CRC patients and healthy donors were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), qNano and western blotting. Proteomic and functional enrichment analyses confirmed differences in the specific expression of exosomal proteins in plasma between CRC patients and healthy donors. Western blotting with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to verify the difference proteins. Statistical methods were used to analyze the relationship between protein levels and CRC.
Results
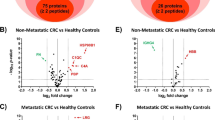
The expression levels of serpin peptidase inhibitor clade A member 1 (SERPINA1) and fibrinogen (PLG) in CRC patients were significantly higher than those in healthy groups. Receptor operating characteristic (ROC) curves analysis was superior to CEA and CA19-9 for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer and early-stage colorectal cancer. The two were related to TNM staging and coagulation, and the difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion
The results of this study have potential value in advancing the clinical diagnosis of colorectal cancer.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Berger DH (2002) Plasmin/plasminogen system in colorectal cancer. World J Surg 26(7):767–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-002-4050-8
Boccaccio C, Medico E (2006) Cancer and blood coagulation. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(9):1024–1027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5570-9
Boccellino M, Pinto F, Ieluzzi V, Giovane A, Quagliuolo L, Fariello C et al (2019) Proteomics analysis of human serum of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer reveals proteins as diagnostic biomarker candidates. J Cell Physiol 234(12):23798–23806. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28948
Chen H, Davids JA, Zheng D et al (2013) The serpin solution; targeting thrombotic and thrombolytic serine proteases in inflammation. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets 13(2):99–110. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871529x11313020003
Cho WC, Cheng CH (2007) Oncoproteomics: current trends and future perspectives. Expert Rev Proteom 4(3):401–410. https://doi.org/10.1586/14789450.4.3.401
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Vignoli A (2013) Coagulation and cancer: biological and clinical aspects. J Thromb Haemost 11(2):223–233. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12075
Grover SP, Mackman N (2022) Anticoagulant SERPINs: endogenous regulators of hemostasis and thrombosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9:878199. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.878199
Heissig B, Salama Y, Osada T, Okumura K, Hattori K (2021) The multifaceted role of plasminogen in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052304
Hsu MT, Wang YK, Tseng YJ (2022) Exosomal proteins and lipids as potential biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030732
Jimenez CR, Verheul HM (2014) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics: from cancer biology to protein biomarkers, drug targets, and clinical applications. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. https://doi.org/10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.e504
Kolch W, Mischak H, Pitt AR (2005) The molecular make-up of a tumour: proteomics in cancer research. Clin Sci 108(5):369–383. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20050006
Kwon CH, Park HJ, Lee JR, Kim HK, Jeon TY, Jo HJ et al (2014) Serpin peptidase inhibitor clade A member 1 is a biomarker of poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 111(10):1993–2002. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.12141
Lakemeyer L, Sander S, Wittau M, Henne-Bruns D, Kornmann M, Lemke J (2021) Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA and CA19–9 in colorectal cancer. Diseases. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases9010021
Li A, Zhang T, Zheng M, Liu Y, Chen Z (2017) Exosomal proteins as potential markers of tumor diagnosis. J Hematol Oncol 10(1):175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0542-8
Li N, Lin G, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Zhang H (2022) Exosome-related protein CRABP2 is upregulated in ovarian carcinoma and enhances cell proliferation. Discov Oncol 13(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-022-00492-3
Liu P, Kong L, Jin H, Wu Y, Tan X, Song B (2019) Differential secretome of pancreatic cancer cells in serum-containing conditioned medium reveals CCT8 as a new biomarker of pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Cell Int 19:262. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0980-1
McKiernan J, Donovan MJ, Margolis E, Partin A, Carter B, Brown G et al (2018) A prospective adaptive utility trial to validate performance of a novel urine exosome gene expression assay to predict high-grade prostate cancer in patients with prostate-specific antigen 2–10ng/ml at initial biopsy. Eur Urol 74(6):731–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.019
Nicholl SM, Roztocil E, Davies MG (2006) Plasminogen activator system and vascular disease. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 4(2):101–116. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016106776359880
Novikova SE, Soloveva NA, Farafonova TE, Tikhonova OV, Liao PC, Zgoda VG (2021) Proteomic signature of extracellular vesicles for lung cancer recognition. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206145
Panigrahi GK, Praharaj PP, Kittaka H, Mridha AR, Black OM, Singh R et al (2019) Exosome proteomic analyses identify inflammatory phenotype and novel biomarkers in African American prostate cancer patients. Cancer Med 8(3):1110–1123. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1885
Patel SG, Karlitz JJ, Yen T, Lieu CH, Boland CR (2022) The rising tide of early-onset colorectal cancer: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, clinical features, biology, risk factors, prevention, and early detection. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(3):262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00426-X
Pegtel DM, Gould SJ (2019) Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem 88:487–514. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111902
Rao H, Wu H, Huang Q, Yu Z, Zhong Z (2021) Clinical value of serum CEA, CA24–2 and CA19–9 in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Lab. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.200828
Rau JC, Beaulieu LM, Huntington JA, Church FC (2007) Serpins in thrombosis, hemostasis and fibrinolysis. J Thromb Haemost 1(Suppl1):102–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02516.x
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A (2006) Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Chapter 3: Unit 3.22.1-3.22.29. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471143030.cb0322s30
Tomiyama E, Matsuzaki K, Fujita K, Shiromizu T, Narumi R, Jingushi K et al (2021) Proteomic analysis of urinary and tissue-exudative extracellular vesicles to discover novel bladder cancer biomarkers. Cancer Sci 112(5):2033–2045. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14881
Wang X, Zhong W, Bu J, Li Y, Li R, Nie R et al (2019) Exosomal protein CD82 as a diagnostic biomarker for precision medicine for breast cancer. Mol Carcinog 58(5):674–685. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22960
Wojtukiewicz MZ, Sierko E, Kisiel W (2007) The role of hemostatic system inhibitors in malignancy. Semin Thromb Hemost 33(7):621–642. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-991530
Wong SC, Chan CM, Ma BB et al (2009) Advanced proteomic technologies for cancer biomarker discovery. Expert Rev Proteom 6(2):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1586/epr.09.1
Yoon JH, Ashktorab H, Smoot DT, Nam SW, Hur H, Park WS (2020) Uptake and tumor-suppressive pathways of exosome-associated GKN1 protein in gastric epithelial cells. Gastric Cancer 23(5):848–862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-020-01068-2
Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, Chakrabortty SK, Enderle D, Noerholm M et al (2021) Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol 32(4):466–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.074
Zhang W, Ou X, Wu X (2019) Proteomics profiling of plasma exosomes in epithelial ovarian cancer: a potential role in the coagulation cascade, diagnosis and prognosis. Int J Oncol 54(5):1719–1733. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4742
Funding
This work was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020LZL017, ZR2019PH023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiment was designed and supervision by LX and XGS. LL and GXC written the first draft as well as data analysis. Material preparation and samples collection were performed by ZZ, BBZ, QRZ and SW. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute (No. 20171008). The patients/participants provided written informed consent for the participant's reference.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Song, X., Chen, G. et al. Plasma exosomal protein PLG and SERPINA1 in colorectal cancer diagnosis and coagulation abnormalities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8507–8519 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04776-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04776-1