Abstract
Purpose
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder (BUC) and the upper urinary tract (UTUC) are the two most common UCs. The incidence of UTUC in Taiwan is the highest worldwide. Aristolochic acid (AA) was identified as the main cause of UTUC in Taiwan. To explore trends in the incidence of UC in Taiwan after the ban on Chinese herbal preparations containing AA in 2003.
Methods
We used data from the Taiwanese National Health Insurance Research Database–linked Taiwanese National Cancer Registry for 2001–2018. UC was defined in accordance with the International Classification of Disease for Oncology. The age-standardized incidence was calculated on the basis of the World Health Organization standard population. Trends in the incidence were calculated as the annual percent change (APC) by using the Joinpoint regression program.
Results
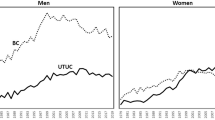
Over the investigated period, the incidence of UC decreased at an average annual percent change (AAPC) of − 1.19% (95% CI − 1.47 ~ − 0.91, P < 0.001). However, the incidence in UTUC significantly increased, with the AAPC being 1.47% (95% CI 1.03 ~ 1.90, P < 0.001). In contrast, the incidence of BUC significantly decreased, with the overall AAPC being − 1.92% (95% CI − 2.3 ~ − 1.54, P < 0. 001). From 2001 to 2018, the overall incidence of UCs and BUC decreased in Taiwan, but the incidence of UTUC significantly increased.
Conclusion
We suggest to apply the same review standards of new drug development process to herbal preparations and incorporate them into the adverse drug reaction or poison surveillance system. Most importantly, raise public awareness of the potential toxicity of phytotherapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary material files. Further enquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Abdullah R, Diaz LN, Wesseling S, Rietjens IM (2016) (2017) Risk assessment of plant food supplements and other herbal products containing aristolochic acids using the margin of exposure (MOE) approach. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 34(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2016.1266098
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M et al (2018) Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 391(10125):1023–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)33326-3
Aly A, Johnson C, Doleh Y, Chirikov V, Botteman M, Shenolikar R et al (2020) The real-world lifetime economic burden of urothelial carcinoma by stage at diagnosis. J Clin Pathw 6(4):51–60
Al-Zoughool M, Bird M, Rice J, Baan RA, Billard M, Birkett N et al (2019) Development of a database on key characteristics of human carcinogens. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 22(7–8):264–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2019.1642593
Bree KK, Shan Y, Hensley PJ, Lobo N, Hu C, Tyler DS et al (2022) Management, surveillance patterns, and costs associated with low-grade papillary stage ta non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer among older adults, 2004–2013. JAMA Netw Open 5(3):e223050. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.3050
Chen CJ, Chuang YC, You SL, Lin TM, Wu HY (1986) A retrospective study on malignant neoplasms of bladder, lung and liver in blackfoot disease endemic area in Taiwan. Br J Cancer 53(3):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1986.65
Chen CH, Dickman KG, Moriya M, Zavadil J, Sidorenko VS, Edwards KL et al (2012) Aristolochic acid-associated urothelial cancer in Taiwan. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(21):8241–8246. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1119920109
Chiang CJ, Wang YW, Lee WC (2019) Taiwan’s nationwide cancer registry system of 40 years: past, present, and future. J Formos Med Assoc 118(5):856–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2019.01.012
Colin P, Koenig P, Ouzzane A, Berthon N, Villers A, Biserte J et al (2009) Environmental factors involved in carcinogenesis of urothelial cell carcinomas of the upper urinary tract. BJU Int 104(10):1436–1440. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08838.x
Dooley EE (2011) The beat. Environ Health Perspect 119(7):a288. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.119-a288b
Freedman ND, Silverman DT, Hollenbeck AR, Schatzkin A, Abnet CC (2011) Association between smoking and risk of bladder cancer among men and women. JAMA 306(7):737–745. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.1142
Fung JW, Lim SB, Zheng H, Ho WY, Lee BG, Chow KY et al (2016) Data quality at the Singapore cancer registry: an overview of comparability, completeness, validity and timeliness. Cancer Epidemiol 43:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2016.06.006
Genkinger JM, De Vivo I, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Michaud DS (2007) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use and risk of bladder cancer in the health professionals follow-up study. Int J Cancer 120(10):2221–2225. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22546
Grollman AP (2013) Aristolochic acid nephropathy: harbinger of a global iatrogenic disease. Environ Mol Mutagen 54(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.21756
Health promotion administration. Adult smoking behavior survey (ASBS). (2023) https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1718&pid=9913 Accessed 5 March.
Hsieh SC, Lin IH, Tseng WL, Lee CH, Wang JD (2008) Prescription profile of potentially aristolochic acid containing Chinese herbal products: an analysis of national health insurance data in Taiwan between 1997 and 2003. Chin Med 3:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8546-3-13
Humphrey PA, Moch H, Cubilla AL, Ulbright TM, Reuter VE (2016) The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part B: prostate and bladder tumours. Eur Urol 70(1):106–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.028
International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. 82
Jhuang JR, Chiang CJ, Su SY, Yang YW, Lee WC (2019) Reduction in the incidence of urological cancers after the ban on chinese herbal products containing aristolochic acid: an interrupted time-series analysis. Sci Rep 9(1):19860. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56394-y
Johnson C, Peace S, Adamo P, Fritz A, Percy-Laurry A, Edwards B (2007) The 2007 multiple primary and histology coding rules. National Cancer Institute, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program Bethesda, MD.
Joinpoint help system (2021). Number of joinpoints. Accessed 15 Jan. https://surveillance.cancer.gov/help/joinpoint/setting-parameters/method-and-parameters-tab/number-of-joinpoints
Kao WH, Hong JH, See LC, Yu HP, Hsu JT, Chou IJ et al (2018) Validity of cancer diagnosis in the national health insurance database compared with the linked national cancer registry in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 27(10):1060–1066. https://doi.org/10.1002/pds.4267
Kao CW, Chiang CJ, Lin LJ, Huang CW, Lee WC, Lee MY (2021) Accuracy of long-form data in the Taiwan cancer registry. J Formos Med Assoc 120(11):2037–2041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2021.04.022041
Kessler DA (2000) Cancer and herbs. N Engl J Med 342(23):1742–1743. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200006083422309
Lai MN, Lai JN, Chen PC, Hsieh SC, Hu FC, Wang JD (2010a) Risks of kidney failure associated with consumption of herbal products containing Mu Tong or Fangchi: a population-based case-control study. Am J Kidney Dis 55(3):507–518. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.10.055
Lai MN, Wang SM, Chen PC, Chen YY, Wang JD (2010b) Population-based case-control study of Chinese herbal products containing aristolochic acid and urinary tract cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(3):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djp467
Lai TS, Hsu CC, Lin MH, Wu VC, Chen YM (2022) Trends in the incidence and prevalence of end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis in Taiwan: 2010–2018. J Formos Med Assoc 121(Suppl 1):S5–S11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2021.12.013
Larsen IK, Småstuen M, Johannesen TB, Langmark F, Parkin DM, Bray F et al (2009) Data quality at the cancer registry of Norway: an overview of comparability, completeness, validity and timeliness. Eur J Cancer 45(7):1218–1231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.037
Lord GM, Cook T, Arlt VM, Schmeiser HH, Williams G, Pusey CD (2001) Urothelial malignant disease and Chinese herbal nephropathy. Lancet 358(9292):1515–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(01)06576-x
Marshall G, Ferreccio C, Yuan Y, Bates MN, Steinmaus C, Selvin S et al (2007) Fifty-year study of lung and bladder cancer mortality in Chile related to arsenic in drinking water. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(12):920–928. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djm004
Milojevic B, Dzamic Z, Kajmakovic B, Milenkovic Petronic D, Sipetic Grujicic S (2015) Urothelial carcinoma: Recurrence and risk factors. J Buon 20(2):391–398
Miyazaki J, Nishiyama H (2017) Epidemiology of urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol 24(10):730–734. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.13376
Nortier JL, Martinez MC, Schmeiser HH, Arlt VM, Bieler CA, Petein M et al (2000) Urothelial carcinoma associated with the use of a Chinese herb (Aristolochia fangchi). N Engl J Med 342(23):1686–1692. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200006083422301
Saginala K, Barsouk A, Aluru JS, Rawla P, Padala SA, Barsouk A (2020) Epidemiology of bladder cancer. Med Sci (basel) 8(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci8010015
Sanderson KM, Cai J, Miranda G, Skinner DG, Stein JP (2007) Upper tract urothelial recurrence following radical cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: an analysis of 1069 patients with 10-year followup. J Urol 177(6):2088–2094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.01.133
Schwetz BA (2001) Safety of aristolochic acid. JAMA 285(21):2705. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.21.2705
Shen CH, Chiou HY, Tung MC, Wu CC, Kao WT, Wang YH et al (2017) Clinical and demographic characteristics among patients with urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract and bladder in Taiwan. J Chin Med Assoc 80(9):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2017.03.008
Sigurdardottir LG, Jonasson JG, Stefansdottir S, Jonsdottir A, Olafsdottir GH, Olafsdottir EJ et al (2012) Data quality at the Icelandic Cancer Registry: comparability, validity, timeliness and completeness. Acta Oncol 51(7):880–889. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186x.2012.698751
Soualhi A, Rammant E, George G, Russell B, Enting D, Nair R et al (2021) The incidence and prevalence of upper tract urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review. BMC Urol 21(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-021-00876-7
Tan LB, Chen KT, Guo HR (2008) Clinical and epidemiological features of patients with genitourinary tract tumour in a blackfoot disease endemic area of Taiwan. BJU Int 102(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07565.x
Tsai SM, Wang TN, Ko YC (1998) Cancer mortality trends in a blackfoot disease endemic community of Taiwan following water source replacement. J Toxicol Environ Health A 55(6):389–404. https://doi.org/10.1080/009841098158322
Vaclavik L, Krynitsky AJ, Rader JI (2014) Quantification of aristolochic acids I and II in herbal dietary supplements by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-multistage fragmentation mass spectrometry. Food Addit Contam Part A 31(5):784–791. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2014.892215
Wang SM, Lai MN, Chen PC, Pu YS, Lai MK, Hwang JS et al (2014) Increased upper and lower tract urothelial carcinoma in patients with end-stage renal disease: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan during 1997–2008. Biomed Res Int 2014:149750. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/149750
Williams SB, Howard LE, Foster ML, Klaassen Z, Sieluk J, De Hoedt AM et al (2021) Estimated costs and long-term outcomes of patients with high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin in the veterans affairs health system. JAMA Netw Open 4(3):e213800. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3800
Wong MCS, Fung FDH, Leung C, Cheung WWL, Goggins WB, Ng CF (2018) The global epidemiology of bladder cancer: a joinpoint regression analysis of its incidence and mortality trends and projection. Sci Rep 8(1):1129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19199-z
World Health Organization. 2013. International classification of diseases for oncology (ICD-O), 3rd ed., 1st revision. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/96612
Wu KM, Farrelly JG, Upton R, Chen J (2007) Complexities of the herbal nomenclature system in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): lessons learned from the misuse of Aristolochia-related species and the importance of the pharmaceutical name during botanical drug product development. Phytomedicine 14(4):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2006.05.009
Xu T, Chen W, Zhou J, Dai J, Li Y, Zhao Y (2021) Computational analysis of naturally occurring aristolochic acid analogues and their biological sources. Biomolecules 11(9):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091344
Yang CY, Chiu HF, Chang CC, Ho SC, Wu TN (2005) Bladder cancer mortality reduction after installation of a tap-water supply system in an arsenious-endemic area in southwestern Taiwan. Environ Res 98(1):127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.07.013
Yang HY, Wang JD, Lo TC, Chen PC (2013) Occupational exposure to herbs containing aristolochic acids increases the risk of urothelial carcinoma in Chinese herbalists. J Urol 189(1):48–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.090
Yang HY, Chen PC, Wang JD (2014) Chinese herbs containing aristolochic acid associated with renal failure and urothelial carcinoma: a review from epidemiologic observations to causal inference. Biomed Res Int 2014:569325. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/569325
Yeh YH, Chou YJ, Huang N, Pu C, Chou P (2016) The trends of utilization in traditional Chinese medicine in Taiwan from 2000 to 2010: a population-based study. Medicine (baltimore) 95(27):e4115. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000004115
Zi H, He SH, Leng XY, Xu XF, Huang Q, Weng H et al (2021) Global, regional, and national burden of kidney, bladder, and prostate cancers and their attributable risk factors, 1990–2019. Mil Med Res 8(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-021-00354-z
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Health Insurance Administration and Health and Welfare Data Science Center, Ministry of Health and Welfare, for providing data and the Institute of Population Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, for supporting this study.
Funding
This work was supported by grants (VGHKS111-142 to CIL, VGHKS111-174 to KJC) from Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K-JC and C-IL conceived the study concept and designed the study. C-IL, H-CF, C-TT and K-JC conducted material preparation, data collection, analysis and generated figures and tables. C-IL, H-CF and K-JC wrote the manuscript. P-TL, C-YH, C-LC, C-WH, X-YC, and S-HO provided important intellectual content to the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital Research Ethics Committee (KSVGH20- EM 1-01). Informed consent of the study participants was waived as this study used deidentified administrative data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, CI., Fang, HC., Lee, PT. et al. Trends in the incidence of urothelial carcinoma in Taiwan after the ban on aristolochic acid-containing Chinese herbal preparations, 2001–2018: a national population-based cohort study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8201–8211 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04771-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04771-6