Abstract
Background
Acute myeloid leukaemia carries the risk of complications associated with dysfunctions in haemostasis system. The purpose of this study was to investigate the factors associated with the risk of bleeding in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).
Methods
This study involved the methods of immunoenzymatic analysis and classical coagulation studies. The number of biochemical parameters important for establishing coagulative dysfunction in acute myeloid leukaemia was determined, the main ones being the level of von Willebrand factor, the Ristocetin-cofactor activity of von Willebrand factor and factor VIII activity, prothrombin time, platelet count, and fibrinogen concentration.
Results
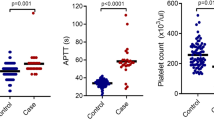
According to the results of the present study, the reduced activity of von Willebrand factor in patients with AML was associated with severe bleeding. The authors observed an increase in the number of platelets count in patients with AML who experienced haemorrhages compared to patients with no bleeding signs. The study also established an increase in the concentration of fibrinogen in cancer patients, compared to the control sample. Symptoms and quantitative indicators for diagnosing the severity of haemorrhagic syndrome were grouped. The authors considered the advantages and disadvantages of many therapeutic preparations and focussed on specific markers of activated haemorrhage-predicting platelets.
Conclusion
Further studies concern the search for effective markers and therapeutic approaches to minimize haemorrhagic syndrome. The results were statistically processed using the functions ANOVA, t test, CORREL, determination of the value of reliability, and mean square deviation.

Source: K. Kolev and C. Longstaff (2016)



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awuah A, Asiedu K, Adanusa M, Ntodie M, Acquah E, Kyei S (2015) A case of leukemic retinopathy mimicking common ishemic retinopathies. Clin Case Rep 4(2):133–137
Bhatt VR (2019) Personalizing therapy for older adults with acute myeloid leukemia: role of geriatric assessment and genetic profiling. Cancer Ther Rev 75:52–61
David S, Mathews V (2018) Mechanisms and management of coagulopathy in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Thromb Res 164(1):82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2018.01.041
Dohner H, Estey E, Grimwade D (2017) Diagnosis and management of AML in adults 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 129(4):424–427. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196
Eisfeld AK, Kohlschmidt J, Mrozek K (2018) Mutation patterns identify adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia aged 60 years or older who respond favorably to standard chemotherapy: an analysis of Alliance studies. Leukemia 32(6):1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-018-0068-2
Estcourt LJ, Birchall J, Allard S, Bassey SJ, Hersey P, Kerr JP, Mumford AD, Stanworth SJ, Tinegate H (2017) Guidelines for the use of platelet transfusions. Br J Haematol 176(3):365–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14423
Falanga A (2017) Predicting APL lethal bleeding in the ATRA era. Blood 129(13):1739–1740. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-02-763490
Frederiksen H, Hvas AM, Sprogoe U, Nielsen C (2017) Measurement of platelet aggregation, independently of patient platelet count: a flow-cytometric approach. J Thromb Haemost 15(6):1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.13675
Goel S, Das D, Saurabh K, Roy R, Das S, Nigam E (2020) Bilateral sub-internal limiting membrane haemorrhage in acute myeloid leukaemia. Clin Exp Optom 104(1):122–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/cxo.13106
Golebiewska EM, Poole AW (2015) Platelet secretion: from haemostasis to wound healing and beyond. Blood Rev 29(3):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2014.10.003
Guo Z, Chen X, Tan Y, Xu Z, Xu L (2020) Coagulopathy in cytogenetically and molecularly distinct acute leukemias at diagnosis: Comprehensive study. Blood Cells Mol Dis 81:102393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2019.102393
Hala HM, Abaza B, Farweez AT, Samaan SF (2016) Platelet-dependent von Willebrand factor activity in acute myeloid leukemia patients: role in hemostatic alterations. Egypt J Haematol 41(1):1–8
Hastings A, Apperley JF, Nadal-Melsio E, Brown L, Bain BJ (2021) Acute myeloid leukemia with a severe coagulopathy and t(8;16)(p11;p13). Am J Hematol 96(1):163–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25903
Kanaya M, Kondo T (2020) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage during induction therapy for acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22). Int J Hematol 112(2):134–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-020-02900-2
Kolev K, Longstaff C (2016) Bleeding related to disturbed fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol 175(1):12–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14255
Legler TJ, Fischer I, Dittmann J, Simson G, Lynen R, Humpe A, Riggert J, Schleyer E, Kern W, Hiddemann W, Kohler M (1997) Frequency and causes of refractoriness in multiply transfused patients. Ann Hematol 74(4):185–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050280
Ley TJ, Miller C, Ding L (2013) Cancer genome atlas research network. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. New Eng J Med. 368(22):2059–2074. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1301689
Loes LC, Caram-Deelder C, Meier RT, Zwaginga JJ, Evers D (2021) Platelet transfusion and tranexamic acid to prevent bleeding in outpatients with a hematological disease: a Dutch nationwide survey. Eur J Haematol 106(3):362–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13555
Mantha S (2019) Bleeding disorders associated with cancer. Cancer Treat Res 17:191–203
Mevatee P, Tantiworawit A, Traisathit P, Puaninta C, Mevatee U, Angsuchawan S, Bumroongkit K (2017) FLT-ITD NPM1 and DNMTA gene mutations and risk factors in normal karyotype acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome patients in Upper Northern Thailand. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. https://doi.org/10.22034/apjcp.2017.18.11.3031
Murphy T, Yee KW (2017) Cytarabine and daunorubicin for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother 18(16):1765–1780
Newell LF, Cook RJ (2021) Advances in acute myeloid leukemia. BMJ 375:2026
Pabinger I, Fries D, Schochl H, Streif W, Toller W (2017) Tranexamic acid for treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding and hyperfibrinolysis. Wien Klin Woch 129(9–10):303–316
Prada-Arismendy J, Ospina J, Rothlisberger S (2017) Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev 31(1):63–76
Sanz MA, Montesinos P (2020) Advances in the management of coagulopathy in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Thromb Res 191(1):63–67
Satio H, Maruyama I, Shimazaki S, Yamamoto Y, Aikaawa N, Ohno R, Hirayama A, Matsuda T, Asakura H, Nakashima M, Aoki N (2007) Efficacy and safety of recombinant human solublet hrombomodulin (ART-123) in disseminated intravascular coagulation: results of a phase III, randomized, double-blindclinicaltrial. J Thromb Haemost 5(1):31–41
Schiffer CA, Bohlke K, Delaney M, Hume H, Magdalinski AJ, McCullough JJ, Omel JL, Rainey JM, Rebulla P, Rowley SD, Troner MB, Anderson KC (2018) Platelet transfusion for patients with cancer: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 36(3):283–299. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2017.76.1734
Skolskaya OYu, Tarasova LN, Vladimirova SG, Cherepanova VV (2013) Endothelial dysfunction and hemostatic disorders in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia De Novo. Hematol Transfus 58(1):28–31
Slichter SJ, Davis K, Enright H, Braine H, Gernsheimer T, Kao KJ, Kickler T, Lee E, McFarland J, McCullough J, Rodey G, Shiffer CA, Woodson R (2005) Factors affecting posttransfusion platelet increments, platelet refractoriness, and platelet transfusion intervals in thrombocytopenic patients. Blood 105(10):4106–1426. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-08-2724
Slichter SJ, Kaufman RM, Assmann SF (2010) Dose of prophylactic platelet transfusions and prevention of hemorrhage. New Eng J Med 362(7):600–613
Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia – Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). (2019). https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html.
Stupakova ZV (2021) Hemorrhagic syndrome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and the effect of coagulation disorders on the course of the disease. Clin Onc 11(3–4):43–44
Svanberg R, Ostrowski SR, Nasserinejad K, Kersting S, Dobber JA, Mattson M, Tran HTT, Levin MD, Mous R, Kater AP, Niemann CU (2020) Changes in primary and secondary hemostasis with CLL treated with venetoclax and ibrutinib. Leuk Lymphoma 61(14):3422–3431. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2020.1811270
Tallman MS, Mantha S, Devlin SM, Soff GA (2018) Predictive factors of fatal bleeding in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Thromb Res 164(1):98–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2018.01.038
Uhl L, Assmann SF, Hamza TH, Harrison RW, Gernsheimer T, Slichter SJ (2017) Laboratory predictors of bleeding, and effect of platelet and RBC transfusions on bleeding outcomes, in the PLADO trial. Blood 130(10):1247–1258
Vienthira A, Premkumar D, Callum J, Lin Y, Wells RA, Chodirker L, Lenis M, Mamedov A, Buckstein R (2019) The management and outcomes of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome with persistent severe thrombocytopenia: an observational single centre registry study. Leuk Res 7:76–81
Vinholt PJ, Knudsen GH, Sperling S, Frederiksen H, Nielsen C (2019) Platelet function tests predict bleeding in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and thrombocytopenia. Am J Hematol 94(8):891–901. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25512
Vladimirova SG, Tarasova LN, Skolskaya AYu (2012) Hemostasis in acute myeloid leukemia patients during disease manifestation. Oncohematol 7(2):36–41
Voso MT, Ottone T, Lavorgna S, Venditti A, Maurillo L, Lo-Coco F, Buccisano F (2019) MRD in AML: the role of new techniques. Front in Oncol 9:655
Yezefski T, Xie H, Walter R, Pagel J, Becker PS, Hendrie P, Sandhu V, Shannon-Dorcy K, Abkowitz J, Appelbaum FR, Estey E (2015) Value of day 14 marrow exam in newly diagnosed AML. Leukemia 29:247–249
Yoshinobu S, Honda G, Kawano N, Uchiyama T, Kawasugi K, Madoiwa S, Takezako N, Takayuki I, Wada H (2021) Clinical features of disseminated intravascular coagulation according to the French-American-British Classification in patients with acute leukemia and thrombomodulin alfa treatment-a cohort study using a postmarketing surveillance database. Clin Appl Thromb/hemostasis. https://doi.org/10.1177/10760296211054094
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zinaida Stupakova and Iryna Diagil wrote the main manuscript text, Ulyana Melnyk and Anna Sergeieva prepared figures and research, and Oksana Karnabeda provided the research with data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Stupakova, Z., Diagil, I., Melnyk, U. et al. Primary hemostasis dysfunctions and bleeding risk in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8167–8176 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04751-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04751-w