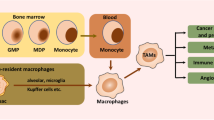
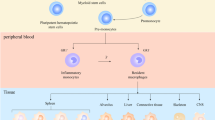
Abstract
The search for therapeutic options for lung cancer continues to advance, with rapid advances in the search for therapies to improve patient prognosis. At present, systemic chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, antiangiogenic therapy, and targeted therapy for driver gene positivity are available in the clinic. Common clinical treatments fail to achieve desired outcomes due to immunosuppression of the tumor microenvironment (TME). Tumor immune evasion is mediated by cytokines, chemokines, immune cells, and other cells such as vascular endothelial cells within the tumor immune microenvironment. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are important immune cells in the TME, inducing tumor angiogenesis, encouraging tumor cell proliferation and migration, and suppressing antitumor immune responses. Thus, TAM targeting becomes the key to lung cancer immunotherapy. This review focuses on macrophage phenotype, polarization mechanism, role in lung cancer, and advances in macrophage centric immunotherapies.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death protein
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death ligand 1
- CSF-1:
-
Colony-stimulating factor 1
- CLL:
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- ICB:
-
Immune checkpoint blockade
- TAMs:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- TDF:
-
Tumor-derived factor
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
References
Anfray C, Ummarino A, Andon FT, Allavena P (2019) Current strategies to target tumor-associated-macrophages to improve anti-tumor immune responses. Cells 9(1):46
Baghdadi M, Wada H, Nakanishi S, Abe H, Han N, Putra WE et al (2016) Chemotherapy-induced IL34 enhances immunosuppression by tumor-associated macrophages and mediates survival of chemoresistant lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 76(20):6030–6042
Barclay AN, Van den Berg TK (2014) The interaction between signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) and CD47: structure, function, and therapeutic target. Annu Rev Immunol 32:25–50
Bonde AK, Tischler V, Kumar S, Soltermann A, Schwendener RA (2012) Intratumoral macrophages contribute to epithelial–mesenchymal transition in solid tumors. BMC Cancer 12:35
Bremnes RM, Donnem T, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Andersen S, Sirera R et al (2011) The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6(1):209–217
Cai H, Zhang Y, Wang J, Gu J (2021) Defects in macrophage reprogramming in cancer therapy: the negative impact of PD-L1/PD-1. Front Immunol 12:690869
Chen J, Zhang K, Zhi Y, Wu Y, Chen B, Bai J et al (2021) Tumor-derived exosomal miR-19b-3p facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and exosomal LINC00273 secretion to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via Hippo pathway. Clin Transl Med 11(9):e478
Cheng C, Hu Z, Cao L, Peng C, He Y (2019) The scavenger receptor SCARA1 (CD204) recognizes dead cells through spectrin. J Biol Chem 294(49):18881–18897
Cotechini T, Atallah A, Grossman A (2021) Tissue-resident and recruited macrophages in primary tumor and metastatic microenvironments: potential targets in cancer therapy. Cells 10(4):960
Cruz-Bermudez A, Laza-Briviesca R, Vicente-Blanco RJ, Garcia-Grande A, Coronado MJ, Laine-Menendez S et al (2019) Cancer-associated fibroblasts modify lung cancer metabolism involving ROS and TGF-beta signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 130:163–173
Dai X, Lu L, Deng S, Meng J, Wan C, Huang J et al (2020) USP7 targeting modulates anti-tumor immune response by reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer. Theranostics 10(20):9332–9347
da Silva MC, Breckwoldt MO, Vinchi F, Correia MP, Stojanovic A, Thielmann CM et al (2017) Iron induces anti-tumor activity in tumor-associated macrophages. Front Immunol 8:1479
DeNardo DG, Ruffell B (2019) Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 19(6):369–382
Deng P, Zhou R, Zhang J, Cao L (2021) Increased expression of KNSTRN in lung adenocarcinoma predicts poor prognosis: a bioinformatics analysis based on TCGA data. J Cancer 12(11):3239–3248
Deng L, Jian Z, Xu T, Li F, Deng H, Zhou Y et al (2023) Macrophage polarization: an important candidate regulator for lung diseases. Molecules 28(5):2379
Devalaraja S, To TKJ, Folkert IW, Natesan R, Alam MZ, Li M et al (2020) Tumor-derived retinoic acid regulates intratumoral monocyte differentiation to promote immune suppression. Cell 180(6):1098–114.e16
Dhawan D, Ramos-Vara JA, Naughton JF, Cheng L, Low PS, Rothenbuhler R et al (2013) Targeting folate receptors to treat invasive urinary bladder cancer. Cancer Res 73(2):875–884
Doedens AL, Stockmann C, Rubinstein MP, Liao D, Zhang N, DeNardo DG et al (2010) Macrophage expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha suppresses T-cell function and promotes tumor progression. Cancer Res 70(19):7465–7475
Duan Z, Luo Y (2021) Targeting macrophages in cancer immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):127
Fenalti G, Villanueva N, Griffith M, Pagarigan B, Lakkaraju SK, Huang RY et al (2021) Structure of the human marker of self 5-transmembrane receptor CD47. Nat Commun 12(1):5218
Forssell J, Oberg A, Henriksson ML, Stenling R, Jung A, Palmqvist R (2007) High macrophage infiltration along the tumor front correlates with improved survival in colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(5):1472–1479
Gudgeon J, Marin-Rubio JL, Trost M (2022) The role of macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1) in inflammatory disorders and cancer. Front Immunol 13:1012002
Gurtner A, Manni I, Piaggio G (2017) NF-Y in cancer: impact on cell transformation of a gene essential for proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1860(5):604–616
Harney AS, Arwert EN, Entenberg D, Wang Y, Guo P, Qian BZ et al (2015) Real-time imaging reveals local, transient vascular permeability, and tumor cell intravasation stimulated by TIE2hi macrophage-derived VEGFA. Cancer Discov 5(9):932–943
Kalbasi A, Komar C, Tooker GM, Liu M, Lee JW, Gladney WL et al (2017) Tumor-derived CCL2 mediates resistance to radiotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 23(1):137–148
Kalos M, Levine BL, Porter DL, Katz S, Grupp SA, Bagg A et al (2011) T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. Sci Transl Med 3(95):9573
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11(5):373–384
Kelley JL, Ozment TR, Li C, Schweitzer JB, Williams DL (2014) Scavenger receptor-A (CD204): a two-edged sword in health and disease. Crit Rev Immunol 34(3):241–261
Koukourakis MI, Kalamida D, Mitrakas AG, Liousia M, Pouliliou S, Sivridis E et al (2017) Metabolic cooperation between co-cultured lung cancer cells and lung fibroblasts. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol 97(11):1321–1331
Lan C, Huang X, Lin S, Huang H, Cai Q, Wan T et al (2013) Expression of M2-polarized macrophages is associated with poor prognosis for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat 12(3):259–267
Li Y, Cao F, Li M, Li P, Yu Y, Xiang L et al (2018) Hydroxychloroquine induced lung cancer suppression by enhancing chemo-sensitization and promoting the transition of M2-TAMs to M1-like macrophages. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):259
Li M, Li M, Yang Y, Liu Y, Xie H, Yu Q et al (2020) Remodeling tumor immune microenvironment via targeted blockade of PI3K-gamma and CSF-1/CSF-1R pathways in tumor associated macrophages for pancreatic cancer therapy. J Control Release 321:23–35
Liu J, Xavy S, Mihardja S, Chen S, Sompalli K, Feng D et al (2020) Targeting macrophage checkpoint inhibitor SIRPalpha for anticancer therapy. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.134728
Ma S, Li X, Wang X, Cheng L, Li Z, Zhang C et al (2019) Current progress in CAR-T Cell therapy for solid tumors. Int J Biol Sci 15(12):2548–2560
Ma YF, Chen Y, Fang D, Huang Q, Luo Z, Qin Q et al (2021) The immune-related gene CD52 is a favorable biomarker for breast cancer prognosis. Gland Surg 10(2):780–798
Mantovani A, Allavena P (2015) The interaction of anticancer therapies with tumor-associated macrophages. J Exp Med 212(4):435–445
Nazareth MR, Broderick L, Simpson-Abelson MR, Kelleher RJ Jr, Yokota SJ, Bankert RB (2007) Characterization of human lung tumor-associated fibroblasts and their ability to modulate the activation of tumor-associated T cells. J Immunol 178(9):5552–5562
Ngambenjawong C, Gustafson HH, Pun SH (2017) Progress in tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-targeted therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 114:206–221
Ovais M, Guo M, Chen C (2019) Tailoring nanomaterials for targeting tumor-associated macrophages. Adv Mater 31(19):e1808303
Ramesh A, Kumar S, Brouillard A, Nandi D, Kulkarni A (2020) A Nitric Oxide (NO) nanoreporter for noninvasive real-time imaging of macrophage immunotherapy. Adv Mater 32(24):e2000648
Ravi J, Elbaz M, Wani NA, Nasser MW, Ganju RK (2016) Cannabinoid receptor-2 agonist inhibits macrophage induced EMT in non-small cell lung cancer by downregulation of EGFR pathway. Mol Carcinog 55(12):2063–2076
Reyes NJ, O’Koren EG, Saban DR (2017) New insights into mononuclear phagocyte biology from the visual system. Nat Rev Immunol 17(5):322–332
Richards DM, Hettinger J, Feuerer M (2013) Monocytes and macrophages in cancer: development and functions. Cancer Microenviron 6(2):179–191
Rigo A, Gottardi M, Zamo A, Mauri P, Bonifacio M, Krampera M et al (2010) Macrophages may promote cancer growth via a GM-CSF/HB-EGF paracrine loop that is enhanced by CXCL12. Mol Cancer 9:273
Ruffell B, Coussens LM (2015) Macrophages and therapeutic resistance in cancer. Cancer Cell 27(4):462–472
Ryder M, Ghossein RA, Ricarte-Filho JC, Knauf JA, Fagin JA (2008) Increased density of tumor-associated macrophages is associated with decreased survival in advanced thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 15(4):1069–1074
Sanchez-Martin L, Estecha A, Samaniego R, Sanchez-Ramon S, Vega MA, Sanchez-Mateos P (2011) The chemokine CXCL12 regulates monocyte-macrophage differentiation and RUNX3 expression. Blood 117(1):88–97
Sarode P, Schaefer MB, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Savai R (2020) Macrophage and tumor cell cross-talk is fundamental for lung tumor progression: we need to talk. Front Oncol 10:324
Sawa-Wejksza K, Kandefer-Szerszen M (2018) Tumor-associated macrophages as target for antitumor therapy. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (warsz) 66(2):97–111
Schultze JL, Schmieder A, Goerdt S (2015) Macrophage activation in human diseases. Semin Immunol 27(4):249–256
Shi Y, Lammers T (2019) Combining nanomedicine and immunotherapy. Acc Chem Res 52(6):1543–1554
Sica A, Allavena P, Mantovani A (2008) Cancer related inflammation: the macrophage connection. Cancer Lett 267(2):204–215
Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han G, Nayar T et al (2010) Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 362(10):875–885
Sterner RC, Sterner RM (2021) CAR-T cell therapy: current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J 11(4):69
Stifano G, Christmann RB (2016) Macrophage involvement in systemic sclerosis: do we need more evidence? Curr Rheumatol Rep 18(1):2
Takahashi R, Ijichi H, Sano M, Miyabayashi K, Mohri D, Kim J et al (2020) Soluble VCAM-1 promotes gemcitabine resistance via macrophage infiltration and predicts therapeutic response in pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep 10(1):21194
Timaner M, Bril R, Kaidar-Person O, Rachman-Tzemah C, Alishekevitz D, Kotsofruk R et al (2015) Dequalinium blocks macrophage-induced metastasis following local radiation. Oncotarget 6(29):27537–27554
Trauelsen M, Hiron TK, Lin D, Petersen JE, Breton B, Husted AS et al (2021) Extracellular succinate hyperpolarizes M2 macrophages through SUCNR1/GPR91-mediated Gq signaling. Cell Rep 35(11):109246
Tsai RK, Discher DE (2008) Inhibition of “self” engulfment through deactivation of myosin-II at the phagocytic synapse between human cells. J Cell Biol 180(5):989–1003
Vernon-Wilson EF, Kee WJ, Willis AC, Barclay AN, Simmons DL, Brown MH (2000) CD47 is a ligand for rat macrophage membrane signal regulatory protein SIRP (OX41) and human SIRPalpha 1. Eur J Immunol 30(8):2130–2137
Wang N, Liang H, Zen K (2014) Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1–m2 polarization balance. Front Immunol 5:614
Wang J, Li D, Cang H, Guo B (2019) Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Med 8(10):4709–4721
Weichand B, Popp R, Dziumbla S, Mora J, Strack E, Elwakeel E et al (2017) S1PR1 on tumor-associated macrophages promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis via NLRP3/IL-1beta. J Exp Med 214(9):2695–2713
Welsh TJ, Green RH, Richardson D, Waller DA, O’Byrne KJ, Bradding P (2005) Macrophage and mast-cell invasion of tumor cell islets confers a marked survival advantage in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(35):8959–8967
Wu JY, Huang TW, Hsieh YT, Wang YF, Yen CC, Lee GL et al (2020) Cancer-derived succinate promotes macrophage polarization and cancer metastasis via succinate receptor. Mol Cell 77(2):213–27.e5
Xiao H, Guo Y, Li B, Li X, Wang Y, Han S et al (2020) M2-Like tumor-associated macrophage-targeted codelivery of STAT6 inhibitor and IKKbeta siRNA induces M2-to-M1 repolarization for cancer immunotherapy with low immune side effects. ACS Cent Sci 6(7):1208–1222
Xu J, Escamilla J, Mok S, David J, Priceman S, West B et al (2013) CSF1R signaling blockade stanches tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells and improves the efficacy of radiotherapy in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 73(9):2782–2794
Yang H, Shao R, Huang H, Wang X, Rong Z, Lin Y (2019) Engineering macrophages to phagocytose cancer cells by blocking the CD47/SIRPa axis. Cancer Med 8(9):4245–4253
Zhao H, Song S, Ma J, Yan Z, Xie H, Feng Y et al (2022) CD47 as a promising therapeutic target in oncology. Front Immunol 13:757480
Zhou D, Luan J, Huang C, Li J (2021) Tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma: friend or foe? Gut Liver 15(4):500–516
Zhu L, Jones C, Zhang G (2018) The role of phospholipase C signaling in macrophage-mediated inflammatory response. J Immunol Res 2018:5201759
Zhu Y, Li X, Wang L, Hong X, Yang J (2022) Metabolic reprogramming and crosstalk of cancer-related fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 13:988295
Funding
This work has been funded with support from Nantong Science and Technology Bureau.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QX and YLZ provided the direction and guidance of this manuscript. HM and ZZ wrote the whole manuscript. QH, HC, and GW made significant revisions to the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Zhang, Z., Hu, Q. et al. Shedding light on macrophage immunotherapy in lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8143–8152 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04740-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04740-z