Abstract
Purpose
Surgical resection is cornerstone treatment for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and offers a chance for cure. This study was conducted to determine current surgical treatment patterns and outcomes of Chinese patients with NSCLC.
Methods
Data of patients with histologically confirmed NSCLC of stages IA–IIIA and who underwent surgery between July 2014 and July 2020 were retrospectively collected from 9 tertiary hospitals in China. Cox model was used for multivariate analyses.
Results
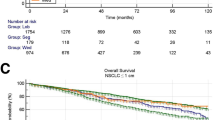
This study included 11,958 patients, among whom 59.1%, 19.2%, and 21.7% were in stages I, II, and IIIA, respectively. Lobectomy was the most common operation method (78.4%), followed by wedge resection (8.2%), segmentectomy (5.4%), pneumonectomy (5.2%), and bronchial sleeve lobectomy (2.8%). Among patients who underwent wedge resection and segmentectomy, majority had stage I NSCLC (87.2% and 93.3%, respectively), and sublobectomy accounted for 20.7% of stage I operations. With a median follow-up time of 30.2 months, disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) rates of entire population were 88.9% and 96.1% at 1 year, 75.2% and 85.1% at 3 years, and 65.3% and 77.0% at 5 years, respectively. The 5-year OS rates for stages IA, IB, IIA, IIB, and IIIA disease were 93.2%, 82.7%, 70.3%, 67.0%, and 52.1%, respectively.
Conclusion
This is the largest real-world cohort study of patients with NSCLC who underwent surgery in China, where we described characteristics of surgical treatment and survival outcomes. The results of our study provide insights into real-world surgical treatment status for surgeons and clinicians.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Ameri M, Bergman P, Franco-Cereceda A, Sartipy U (2018) Video-assisted thoracoscopic versus open thoracotomy lobectomy: a Swedish nationwide cohort study. J Thorac Dis 10:3499–3506. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2018.05.177
Altorki NK, Wang X, Wigle D et al (2018) Perioperative mortality and morbidity after sublobar versus lobar resection for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: post-hoc analysis of an international, randomised, phase 3 trial (CALGB/Alliance 140503). Lancet Respir Med 6:915–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30411-9
Cao M, Chen W (2019) Epidemiology of lung cancer in China: epidemiology of lung cancer in China. Thorac Cancer 10:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12916
Caso R, Watson TJ, Khaitan PG, Marshall MB (2018) Outcomes of minimally invasive sleeve resection. J Thorac Dis 10:6653–6659. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2018.10.97
Dziedzic R, Marjanski T, Binczyk F et al (2018) Favourable outcomes in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer operated on by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: a propensity score-matched analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 54:547–553. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezy101
Erdogu V, Akin H, Sonmezoglu Y et al (2020) Comparison of the video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy versus open thoracotomy for primary non-small cell lung cancer: single cohort study with 269 cases. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul 54:291–296. https://doi.org/10.14744/SEMB.2020.60963
Ezer N, Kale M, Sigel K et al (2018) Outcomes after video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy versus open lobectomy for early-stage lung cancer in older adults. Ann Am Thorac Soc 15:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201612-980OC
Fan X, Liang Y, Bai Y et al (2020) Conditional survival rate estimates of lobectomy, segmentectomy and wedge resection for stage IA1 non-small cell lung cancer: a population-based study. Oncol Lett 20:1607–1618. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11713
Felip E, Altorki N, Zhou C et al (2021) Adjuvant atezolizumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower010): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 398:1344–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02098-5
Flores RM, Park BJ, Dycoco J et al (2009) Lobectomy by video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) versus thoracotomy for lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 138:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.03.030
He J, Li S, Pan H, He J (2020) Treatment for patients with early stage adenosquamous lung cancer. JTO Clin Res Rep 1:100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtocrr.2020.100021
Hennon MW, Kumar A, Devisetty H et al (2019) Minimally invasive approaches do not compromise outcomes for pneumonectomy: a comparison using the national cancer database. J Thorac Oncol 14:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.09.024
Ilonen IK, Räsänen JV, Sihvo EI et al (2007) Pneumonectomy: post-operative quality of life and lung function. Lung Cancer 58:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.07.008
Jiang L, Liu J, Gonzalez-Rivas D et al (2018) Thoracoscopic surgery for tracheal and carinal resection and reconstruction under spontaneous ventilation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 155:2746–2754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.12.153
Lang-Lazdunski L (2013) Surgery for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir Rev 22:382–404. https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00003913
Liao Hu, Jiandong M, Chengwu L et al (2018) A survey on the current development of thoracic surgery in tertiary hospitals of China. Chin J Surg 56:888–891. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2018.12.003
Ljungqvist O, Scott M, Fearon KC (2017) Enhanced recovery after surgery: a review. JAMA Surg 152:292–298. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2016.4952
Ludbrook JJS, Truong PT, MacNeil MV et al (2003) Do age and comorbidity impact treatment allocation and outcomes in limited stage small-cell lung cancer? A community-based population analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 55:1321–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(02)04576-5
Lung Cancer Fact Sheet | American Lung Association. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/lung-cancer/resource-library/lung-cancer-fact-sheet. Accessed 4 Feb 2022
Mei J, Guo C, Xia L et al (2019) Long-term survival outcomes of video-assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy for stage I-II non-small cell lung cancer are more favorable than thoracotomy: a propensity score-matched analysis from a high-volume center in China. Transl Lung Cancer Res 8:155–166. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2018.12.04
Ng CSH, MacDonald JK, Gilbert S et al (2019) Optimal approach to lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer: systemic review and meta-analysis. Innovations (phila) 14:90–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/1556984519837027
Oda R, Okuda K, Osaga S et al (2019) Long-term outcomes of video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery lobectomy vs. thoracotomy lobectomy for stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. Surg Today 49:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-018-1746-4
Saji H, Okada M, Tsuboi M et al (2022) Segmentectomy versus lobectomy in small-sized peripheral non-small-cell lung cancer (JCOG0802/WJOG4607L): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 399:1607–1617. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02333-3
Scott WJ, Allen MS, Darling G et al (2010) Video-assisted thoracic surgery versus open lobectomy for lung cancer: a secondary analysis of data from the American College of surgeons oncology group Z0030 randomized clinical trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 139:976–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.11.059
Sepesi B, Gold KA, Correa AM et al (2017) The influence of body mass index on overall survival following surgical resection of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 12:1280–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.05.010
Shi Y, Wu S, Ma S et al (2022) Comparison between wedge resection and lobectomy/segmentectomy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: a bayesian meta-analysis and systematic review. Ann Surg Oncol 29:1868–1879. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-021-10857-7
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Sun D, Chen P, Liu L et al (2021) The 5-year survival rate of 11 958 postoperative non-small cell lung cancer patients in stage I-IIIA by two different follow-up patterns: a multi-center, real-world study. Chin J Clin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 28:615–622
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tomita M, Ayabe T, Nakamura K (2017) Low body mass index is an independent predictive factor after surgical resection in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 18:3353–3356. https://doi.org/10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3353
Tsukazan MTR, Vigo Á, da Silva VD et al (2017) Lung cancer: changes in histology, gender, and age over the last 30 years in Brazil. J Bras Pneumol 43:363–367. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1806-37562016000000339
Wang H, Zhang J, Shi F et al (2017) Better cancer specific survival in young small cell lung cancer patients especially with AJCC stage III. Oncotarget 8:34923–34934. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16823
Wu Y-L, Tsuboi M, He J et al (2020) Osimertinib in resected EGFR -mutated non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 383:1711–1723. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2027071
Xu J, Ni H, Wu Y et al (2021) Perioperative comparison of video-assisted thoracic surgery and open lobectomy for pT1-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients in China: a multi-center propensity score-matched analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res 10:402–414. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-1132
Yamashita S-I, Tokuishi K, Moroga T et al (2020) Long-term survival of thoracoscopic surgery compared with open surgery for clinical No adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Dis 12:6523–6532. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd-20-2259
Yang H-X, Woo KM, Sima CS et al (2017) Long-term survival based on the surgical approach to lobectomy for clinical stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer: comparison of robotic, video-assisted thoracic surgery, and thoracotomy lobectomy. Ann Surg 265:431–437. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000001708
Yang C-FJ, Kumar A, Klapper JA et al (2019) A national analysis of long-term survival following thoracoscopic versus open lobectomy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Surg 269:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000002342
Yang X-N, Yan H-H, Wang J et al (2022) Real-world survival outcomes based on egfr mutation status in chinese patients with lung adenocarcinoma after complete resection: results from the ICAN study. JTO Clin Res Rep 3:100257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100257
Yun JK, Jeong JH, Lee GD et al (2022) Predicting postoperative complications and long-term survival after lung cancer surgery using eurolung risk score. J Korean Med Sci 37:e36. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e36
Zhao J, Li W, Wang M et al (2021) Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery lobectomy might be a feasible alternative for surgically resectable pathological N2 non-small cell lung cancer patients. Thorac Cancer 12:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13680
Zheng RS, Sun KX, Zhang SW et al (2019) Report of cancer epidemiology in China, 2015. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 41:19–28. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.01.005
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the study participants and investigators for their participation. Technical support for this work was provided by LinkDoc Inc., and the authors thank Liu Jie, Chen Zijia, and Tang Lang for their support in data curation, statistical analysis, and data interpretation.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. SD, HJ: Writing and experimental design; Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. CP: Statistical guidance. LX: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. HeJianxing: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. XL: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. FX: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. LY: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. LD: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. ZX: Data collection, curation, and putting forward modification opinions. LL: Experimental design conceptualization and finalizing the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Daqiang Sun, Jian Hu, Xiaofei Li, Jianxing He, Lin Xu, Xiangning Fu, Yang Liu, Deruo Liu, Pingyan Chen, Xun Zhang, and Lunxu Liu declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the medical ethics committee of the Tianjin Chest Hospital (institutional review board number, 2021-LW-001) and was conducted in accordance with the Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki and its latest amendments.
Consent to participate
There was no active enrollment or active follow-up of study subjects, and no data were collected directly from individuals. The need for written informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature.
Consent to publish
All authors have consented to publication of the results presented in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Hu, J., Li, X. et al. Real-world surgical treatment patterns and clinical outcomes in patients with stages IA–IIIA non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective multicentric observational study involving 11,958 patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8213–8223 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04729-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04729-8