Abstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to explore the effect of using the clinical nursing pathway (CNP) to provide high-quality nursing care to patients undergoing head and neck cancer surgery and provide a theoretical basis for clinical practice.
Methods
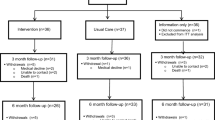
In this study, 303 surgical patients with head and neck cancers were recruited. Participants were divided into 2 groups, based on 2 different nursing methods, i.e.., the control group (152 cases) and the intervention group (151 cases). The control group was given routine nursing care, and the intervention group was assigned high-quality nursing care following the CNP. The knowledge mastery, treatment, psychological status, quality of life, and nursing satisfaction of the two groups were compared.
Results
The knowledge mastery score of the intervention group was higher compared with the control group (p < 0.05); the psychological state score of the intervention group was less than the control group’s score (p < 0.05); the quality-of-life score of the intervention group was higher than the control group’s score (p < 0.05), and the nursing satisfaction score was higher for the intervention group compared with the control group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
High-quality nursing using the CNP for patients undergoing head and neck cancer surgery helps to improve patients’ knowledge mastery, mental state, quality of life, and nursing satisfaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- CNP:
-
The clinical nursing pathway
- HAMA:
-
The Hamilton Anxiety Scale
- HAMD:
-
The Hamilton Depression Scale
- SF-36:
-
The Medical Outcomes Study Short-Form 36
- PF:
-
Physical
- RP:
-
Role physical
- BP:
-
Body pain
- GH:
-
General health
- VT:
-
Vitality
- SF:
-
Social
- MH:
-
Mental health
- PPT:
-
PowerPoint
References
Dou X, Zuo N (2021) Application of clinical nursing pathway in nursing teaching of head and neck surgery——Comment on “Head and Neck Tumor Surgery Nursing Manual.” Chin J Exp Formulas 27(10):160
Guo W (2013) Diagnosis and treatment of head and neck tumors. People's Military Medical Press
Huang C, Zhong Y (2017) Application and effect evaluation of health education pathway in an outpatient operating room of cosmetic and plastic surgery. Lab Med Clin 14(10):1485–1487
Josephson L (2004) Management of increased intracranial pressure: a primer for the non-neuro critical care nurse. Dimens Crit Care Nurs 23:194–207
Li J (2019) Effectiveness of high-quality nursing services in the prevention of acute mucosal radiation reactions in patients with head and neck cancer radiotherapy. Shanxi Med J 48(20):2574–2575
Liang J, Li J (2016) Effect evaluation of high-quality nursing intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Naval Med 37(4):359–361
Liu Z, Wu L (2017) Discussion on the effect of TCM clinical pathway on quality nursing for patients with spleen and heart pain. J Nurses’further Educ 32(4):371–374
Liu L, Yang L (2016) Evaluation and analysis of the effect of clinical nursing pathway applied in patients undergoing thyroidectomy. Chin J Pract Nurs 32(z1):32–32
Luck L, Wilkes L, O’Baugh J (2015) Treading the clinical pathway: a qualitative study of advanced practice nurses in a local health district in Australia. BMC Nurs 14:52
Minier D, Milan C, Woimant F, Bematru I, Fournier O, Osseby GV, Saillard B, Giroud M (2004) Evaluation of care given by nurses during the acute stage of stroke. Rev Neurol (paris) 160:1040–1047 (in French)
Ozasa Y (2002) A study on first-time stroke patients in community use of home visiting assessment by public health nurses (PHNS). Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 49:1076–1086 (in Japan)
Presciutti M (2006) Nursing priorities in caring for patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosci Nurs 38(296–299):315
Sun W, Hou X (2015) Clinical evaluation of clinical nursing pathway in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Int J Nurs 34(17):2419–2422
Waguchi H, Hidaka K, Shinoki K, Matsuoka M, Mito S, Doi S, Hata A, Ibata T, Komuro R, Iijima S (2013) Coordination to assist with hospital-to-home discharge after cerebral hemorrhage-perspectives of a patient’s family and nurse. Gan to Kagaku Ryoho 40:216–218 (in Japanese)
Wang X, Hu Y (2017) Evaluation of a clinical nursing pathway’s application effect based on evidence-based nursing in inpatient chemotherapy patients with lung cancer. J Hebei Med Univ 38(4):474–478
Zhang Y, Wei J, Wang X (2016) Application of information technology in day ward management. China Digit Med 11(8):113–115
Zhu F (2016) Application and effect evaluation of detail nursing in high-quality nursing in the operating room. Chin Med Clin 16(4):601–603
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of the research: YL. Acquisition of data: YL. Analysis and interpretation of the data: YL. Statistical analysis: YL. Writing of the manuscript: YL. Critical revision of the manuscript for intellectual content: YL. All authors read and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, L. The application value of the clinical nursing pathway for patients with head and neck cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 9629–9634 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04679-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04679-1