Abstract
Purpose
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with increasing incidence. Although the burden of disease is high, only limited current real-world data on survival analysis, especially survival time, of German patients with DLBCL are available. This retrospective claims-based analysis was conducted to describe real-world survival evidence and treatment patterns of patients with DLBCL in Germany.
Methods
Using a large claims database of the German statutory health insurance with 6.7 million enrollees, we identified patients between 2010 and 2019 who were newly diagnosed with DLBCL (index date) and had no other cancer co-morbidity. Overall survival (OS) from index date and from the end of each treatment line was plotted by means of the Kaplan–Meier estimator, both for the overall cohort and stratified by treatment regimen. Treatment lines were identified based on a predefined set of medications categorized by established DLBCL treatment recommendations.
Results
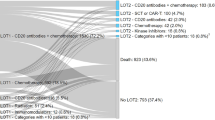
2495 incident DLBCL patients were eligible for the study. After index date, 1991 patients started a first-line, 868 a second-line, and 354 a third-line therapy. In first line, 79.5% of patients received a Rituximab-based therapy. 5.0% of the of the 2495 patients received a stem cell transplantation. Overall, median OS after index was 96.0 months.
Conclusion
DLBCL-associated mortality is still high, especially in relapsed patients and in the elderly. Therefore, there is a high medical need for new effective treatments that can improve survival outcomes in DLBCL patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Due to the sensitivity of the data and data protection regulations, the analysis datasets of the current study cannot not be shared or stored at a public repository.
References
Adzersen K, Friedrich S, Becker N (2016) Are epidemiological data on lymphoma incidence comparable? Results from an application of the coding recommendations of WHO, InterLymph, ENCR and SEER to a cancer registry dataset. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:167–175
Ardeshna KM, Smith P, Norton A et al (2003) British national lymphoma investigation. Long-term effect of a watch and wait policy versus immediate systemic treatment for asymptomatic advanced-stage non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 362(9383):516–522
Armitage J (2007) How I treat patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 110(1):29–36
Blümel M, Spranger A, Achstetter K et al (2020) Germany: health system review. Health Syst Transit 22(6):1–273
Bögemann M, Zagorska A, Akumo D et al (2020) Using data from a sickness fund claims database to assess the treatment patterns and healthcare resource utilization among patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma in Germany. Urol Int 104(11–12):982–993
Borchmann P, Heger J-M, Mahlich J et al (2023) Healthcare resource utilization and associated costs of German patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma—a retrospective health claims data analysis. Oncol Ther 11:65–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40487-022-00211-6
Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U et al (2017) Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood 130(16):1800–1808
Czwikla J, Domhoff D, Giersiepen K (2016) ICD coding quality for outpatient cancer diagnoses in SHI claims data. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundh Wesen 118:48–55
Daneels W, Rosskamp M, Macq G et al (2022) Real-world estimation of first- and second-line treatments for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using health insurance data: a Belgian population-based study. Front Oncol 12:824704
Durmaz M, Visser O, Posthuma E et al (2022) Time trends in primary therapy and relative survival of diffuse large B cell lymphoma by stage: a nationwide, population-based study in the Netherlands, 1989–2018. Blood Cancer J 12(3):38
Ekberg D, Crowther M et al (2022) Patient trajectories after diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma—a multistate modelling approach to estimate the chance of lasting remission. Br J Cancer 127:1642–1649
Epperla N, Vaughn J, Othus M et al (2020) Recent survival trends in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma––have we made any progress beyond rituximab? Cancer Med 9:5519–5525
Fu K, Weisenburger D, Choi W et al (2008) Addition of rituximab to standard chemotherapy improves the survival of both the germinal center B cell-like and non-germinal center B cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 26(28):4587–4594
GBA [Gemeinsamer Bundesauschuss] (2020) Nutzenbewertungsverfahren zum Wirkstoff Polatuzumab Vedotin. Available: https://www.g-ba.de/bewertungsverfahren/nutzenbewertung/518/#dossier. Accessed 30 Aug 2022
Gisselbrecht C, Van Den Neste E (2018) How I manage patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 182:633–643
Jabbour E, Thomas D, Cortes J, Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S (2010) Central nervous system prophylaxis in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: current and emerging therapies. Cancer 116:2290–2300
Kanas G, Ge W, Quek R et al (2022) Epidemiology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL) in the United States and Western Europe: population-level projections for 2020–2025. Leuk Lymphoma 63(1):54–63
Larouche JF, Berger F et al (2010) Lymphoma recurrence 5 years or later following diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: clinical characteristics and outcome. J Clin Oncol 28(12):2094–2100
Mahlich J, Alba A, El Hadad L et al (2019) Drug survival of biological therapies for psoriasis treatment in Germany and associated costs: a retrospective claims database analysis. Adv Ther 36(7):1684–1699
Mahlich J, Olbrich K, Wilk A et al (2021) Time to treatment discontinuation in German patients with Schizophrenia: Long acting injectables versus oral antipsychotics. Clin Drug Investig 41(1):99–113
Moertl B, Dreyling M, Schmidt C et al (2022) Inpatient treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (r/r DLBCL): a health economic perspective. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 22(7):474–482
Morrison VA, Bell JA, Hamilton L et al (2018) Economic burden of patients with diffuse large B cell and follicular lymphoma treated in the USA. Future Oncol 14:2627–2642
NIH [National Institutes of Health] (2022) Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER). Cancer Stat Facts: NHL - Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/dlbcl.html. Accessed 20 Oct 2022
Pavlovsky M, Cubero D, Agreda-Vasquez G et al (2022) Clinical outcomes of patients with B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in real-world settings: findings from the hemato-oncology Latin America observational registry study. JCO Global Oncology 8:e2100265
Pulte D, Jansen L, Gondos A et al (2013) Survival of patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma in Germany in the early 21st century. Leuk Lymphoma 54(5):979–985
Purdum A, Tieu R, Reddy S, Broder M (2019) Direct costs associated with relapsed diffuse large B cell lymphoma therapies. Oncologist 24(9):1229–1236
Scheid C, Kudernatsch R, Eckart M et al (2022) Treatment pathways and health outcomes of German patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a retrospective health claims data analysis. Drugs Real World Outcomes 9:577–588
Scheid C, Kudernatsch R, Eckart M et al (2023) Incidence of graft-versus-host-disease in Germany: evidence from health care claims data. J Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-022-01736-w
Shaw J, Harvey C, Richards C et al (2019) Temporal trends in treatment and survival of older adult diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients in the SEER-Medicare linked database. Leuk Lymphoma 60(13):3235–3243
Tsutsué S, Tobinai K, Yi J et al (2020) Nationwide claims database analysis of treatment patterns, costs and survival of Japanese patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. PLoS ONE 15(8):e0237509
Wolff-Menzler C, Mahlich J, Olbrich K et al (2021) Hospitalisierungen und Behandlungskosten von Schizophreniepatienten nach Umstellung auf Depot-Antispsychotika. Gesundheitsökonomie und Qualitätsmanagement 26(6):302–309
Yamamoto M, Suzuki I, Saitou K et al (2020) Impact of comorbidity and relative dose intensity on outcomes in diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146:2995–3002
Yang X, Laliberté F, Germain G et al (2021) Real-world characteristics, treatment patterns, health care resource use, and costs of patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma in the US. Oncologist 26(5):e817–e826
Zelenetz A, Gordon L, Wierda W et al (2016) Diffuse large B cell lymphoma version 1. J Natl Compr Canc 14(2):196–231
Funding
This study was funded by Miltenyi Biomedicine GmbH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published. PB, JM, MP, SR, and BW designed the study. SR drafted the manuscript, BW did the statistical analysis. PB, J-MH revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JM, SR and MP are employees of Miltenyi Biomedicine GmbH. BW is an employee of Team Gesundheit, a contract research company that received funding from Miltenyi Biomedicine to conduct the study in line with the study protocol. PB and J-MH are employed at the University Hospital Cologne. All authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any other organization or entity with a financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Ethical approval
All individual patient data are anonymized in the research database to comply with German data protection regulations. Institutional review board/ethical approval and informed consent of the individuals were not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Borchmann, P., Heger, JM., Mahlich, J. et al. Survival outcomes of patients newly diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: real-world evidence from a German claims database. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 7091–7101 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04660-y