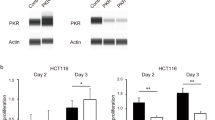
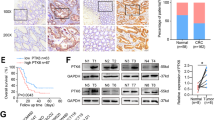
Abstract
Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers. Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1), a member of the serine/threonine kinase PLK family, is the most investigated and essential in the regulation of cell cycle progression, including chromosome segregation, centrosome maturation and cytokinesis. However, the nonmitotic role of PLK1 in CRC is poorly understood. In this study, we explored the tumorigenic effects of PLK1 and its potential as a therapeutic target in CRC.
Methods
GEPIA database and immunohistochemistry analysis were performed to evaluate the abnormal expression of PLK1 in CRC patients. MTT assay, colony formation and transwell assay were performed to assess cell viability, colony formation ability and migration ability after inhibiting PLK1 by RNAi or the small molecule inhibitor BI6727. Cell apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and ROS levels were evaluated by flow cytometry. Bioluminescence imaging was performed to evaluate the impact of PLK1 on CRC cell survival in a preclinical model. Finally, xenograft tumor model was established to study the effect of PLK1 inhibition on tumor growth.
Results
First, immunohistochemistry analysis revealed the significant accumulation of PLK1 in patient-derived CRC tissues compared with adjacent healthy tissues. Furthermore, PLK1 inhibition genetically or pharmacologically significantly reduced cell viability, migration and colony formation, and triggered apoptosis of CRC cells. Additionally, we found that PLK1 inhibition elevated cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and decreased the Bcl2/Bax ratio, which led to mitochondrial dysfunction and the release of Cytochrome c, a key process in initiating cell apoptosis.
Conclusion
These data provide new insights into the pathogenesis of CRC and support the potential value of PLK1 as an appealing target for CRC treatment. Overall, the underlying mechanism of inhibiting PLK1-induced apoptosis indicates that the PLK1 inhibitor BI6727 may be a novel potential therapeutic strategy in the treatment of CRC.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- COAD:
-
Colon adenocarcinoma
- HCT116 and DLD-1:
-
Human colorectal cell lines
- FHC:
-
Normal colon epithelium cell line
- PLK1:
-
Polo-like kinase 1
- Bcl2:
-
B-cell lymphoma-2
- Bax:
-
Bcl2-associated X protein
- Cyt-c:
-
Cytochrome c
- cl-cas3:
-
Cleaved caspase-3
- cl-PARP:
-
Cleaved PARP
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- MTT:
-
Thiazolyl blue
- CCK8:
-
Cholecystokinin-8
- TUNEL:
-
TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
References
Brenner D, Mak TW (2009) Mitochondrial cell death effectors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21(6):871–877
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP (2014) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 383(9927):1490–1502
Cerutti PA (1994) Oxy-radicals and cancer. Lancet 344(8926):862–863
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi B, Varambally S (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19(8):649–658
Chen HY, Villanueva J (2015) Playing Polo-Like Kinase in NRAS-Mutant Melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 135(10):2352–2355
Chen Z, Chai Y, Zhao T, Li P, Zhao L, He F, Lang Y, Qin J, Ju H (2019) Effect of PLK1 inhibition on cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 234(5):5904–5914
Circu ML, Aw TY (2008) Glutathione and apoptosis. Free Radic Res 42(8):689–706
Circu ML, Aw TY (2010) Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 48(6):749–762
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2(9):647–656
de Carcer G, Manning G, Malumbres M (2011) From Plk1 to Plk5: functional evolution of polo-like kinases. Cell Cycle 10(14):2255–2262
Dufies M, Verbiest A, Cooley LS, Ndiaye PD, He X, Nottet N, Souleyreau W, Hagege A, Torrino S, Parola J, Giuliano S, Borchiellini D, Schiappa R, Mograbi B, Zucman-Rossi J, Bensalah K, Ravaud A, Auberger P, Bikfalvi A, Chamorey E, Rioux-Leclercq N, Mazure NM, Beuselinck B, Cao Y, Bernhard JC, Ambrosetti D, Pages G (2021) Plk1, upregulated by HIF-2, mediates metastasis and drug resistance of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Commun Biol 4(1):166
Fu Y, Wang Y, Gao X, Li H, Yuan Y (2020) Dynamic expression of HDAC3 in db/db mouse RGCs and its relationship with apoptosis and autophagy. J Diabetes Res 2020:6086780
Fu Z, Wen D (2017) The Emerging Role of Polo-Like Kinase 1 in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Metastasis, Cancers (Basel) 9(10)
Gavet O, Pines J (2010) Activation of cyclin B1-Cdk1 synchronizes events in the nucleus and the cytoplasm at mitosis. J Cell Biol 189(2):247–259
Huang F, Zhao S, Yu F, Yang Z, Ding G (2017) Protective Effects and Mechanism of Meretrix meretrix Oligopeptides against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Mar Drugs 15(2)
Jang YJ, Lin CY, Ma S, Erikson RL (2002) Functional studies on the role of the C-terminal domain of mammalian polo-like kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(4):1984–1989
Jeong SB, Im JH, Yoon JH, Bui QT, Lim SC, Song JM, Shim Y, Yun J, Hong J, Kang KW (2018) Essential role of polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) oncogene in tumor growth and metastasis of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 17(4):825–837
Jia J, Dai S, Sun X, Sang Y, Xu Z, Zhang J, Cui X, Song J, Guo X (2015) A preliminary study of the effect of ECRG4 overexpression on the proliferation and apoptosis of human laryngeal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms. Mol Med Rep 12(4):5058–5064
Klauck PJ, Bagby SM, Capasso A, Bradshaw-Pierce EL, Selby HM, Spreafico A, Tentler JJ, Tan AC, Kim J, Arcaroli JJ, Purkey A, Messersmith WA, Kuida K, Eckhardt SG, Pitts TM (2018) Antitumor activity of the polo-like kinase inhibitor, TAK-960, against preclinical models of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 18(1):136
Lee KS, Burke TR Jr, Park JE, Bang JK, Lee E (2015) Recent advances and new strategies in targeting Plk1 for anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 36(12):858–877
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91(4):479–489
Li J, Yang Z, Li Y, Xia J, Li D, Li H, Ren M, Liao Y, Yu S, Chen Y, Yang Y, Zhang Y (2016) Cell apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis in osteosarcoma treatment. Oncotarget 7(28):44763–44778
Li CX, Chen J, Xu ZG, Yiu WK, Lin YT (2020) The expression and prognostic value of RNA binding proteins in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res 9(12):7415–7431
Li H, Wang H, Sun Z, Guo Q, Shi H, Jia Y (2017) The clinical and prognostic value of polo-like kinase 1 in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients: immunohistochemical analysis, Biosci Rep 37(4)
Liu X (2015) Targeting polo-like kinases: a promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment. Transl Oncol 8(3):185–195
Liu X, Zhou T, Kuriyama R, Erikson RL (2004) Molecular interactions of Polo-like-kinase 1 with the mitotic kinesin-like protein CHO1/MKLP-1. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 15):3233–3246
Liu XS, Song B, Elzey BD, Ratliff TL, Konieczny SF, Cheng L, Ahmad N, Liu X (2011) Polo-like kinase 1 facilitates loss of Pten tumor suppressor-induced prostate cancer formation. J Biol Chem 286(41):35795–35800
Liu F, Liu S, Ai F, Zhang D, Xiao Z, Nie X, Fu Y (2017a) miR-107 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of colon cancer cells by targeting prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par4). Oncol Res 25(6):967–974
Liu M, Gao L, Zhao L, He J, Yuan Q, Zhang P, Zhao Y, Gao X (2017b) Peptide-Au clusters induced tumor cells apoptosis via targeting glutathione peroxidase-1: the molecular dynamics assisted experimental studies. Sci Rep 7(1):131
Lopez J, Tait SW (2015) Mitochondrial apoptosis: killing cancer using the enemy within. Br J Cancer 112(6):957–962
Ma K, Chen G, Li W, Kepp O, Zhu Y, Chen Q (2020) Mitophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis, and cell fate, front cell. Dev Biol 8:467
Ma X, Wang L, Huang, Li Y, Yang D, Li T, Li F, Sun L, Wei H, He K, Yu F, Zhao D, Hu L, Xing S, Liu Z, Li K, Guo J, Yang Z, Pan X, Li A, Shi Y, Wang J, Gao P, Zhang H (2017) Polo-like kinase 1 coordinates biosynthesis during cell cycle progression by directly activating pentose phosphate pathway, Nat Commun 8(1):1506.
Marmol I, Sanchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ (2017) Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer, Int J Mol Sci 18(1)
Murphy KM, Ranganathan V, Farnsworth ML, Kavallaris M, Lock RB (2000) Bcl-2 inhibits Bax translocation from cytosol to mitochondria during drug-induced apoptosis of human tumor cells. Cell Death Differ 7(1):102–111
Narita M, Shimizu S, Ito T, Chittenden T, Lutz RJ, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y (1998) Bax interacts with the permeability transition pore to induce permeability transition and cytochrome c release in isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(25):14681–14686
Nasseri Y, Langenfeld SJ (2017) Imaging for colorectal cancer. Surg Clin North Am 97(3):503–513
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C, Garufi A, D’Orazi G (2016) Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging (albany NY) 8(4):603–619
Quan R, Wei L, Hou L, Wang J, Zhu S, Li Z, Lv M, Liu J (2020) Proteome Analysis in a Mammalian Cell line Reveals that PLK2 is Involved in Avian Metapneumovirus Type C (aMPV/C)-Induced Apoptosis, Viruses 12(4)
Raab CA, Raab M, Becker S, Strebhardt K (2021) Non-mitotic functions of polo-like kinases in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1875(1):188467
Ran Z, Chen W, Shang J, Li X, Nie Z, Yang J, Li N (2019) Clinicopathological and prognostic implications of polo-like kinase 1 expression in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene 721:144097
Ruf S, Heberle AM, Langelaar-Makkinje M, Gelino S, Wilkinson D, Gerbeth C, Schwarz JJ, Holzwarth B, Warscheid B, Meisinger C, van Vugt MA, Baumeister R, Hansen M, Thedieck K (2017) PLK1 (polo like kinase 1) inhibits MTOR complex 1 and promotes autophagy. Autophagy 13(3):486–505
Seki A, Coppinger JA, Jang CY, Yates JR, Fang G (2008) Bora and the kinase Aurora a cooperatively activate the kinase Plk1 and control mitotic entry. Science 320(5883):1655–1658
Shalaby R, Flores-Romero H, Garcia-Saez AJ (2020) The Mysteries around the BCL-2 Family Member BOK, Biomolecules 10(12)
Shieh PC, Chen YO, Kuo DH, Chen FA, Tsai ML, Chang IS, Wu H, Sang S, Ho CT, Pan MH (2010) Induction of apoptosis by [8]-shogaol via reactive oxygen species generation, glutathione depletion, and caspase activation in human leukemia cells. J Agric Food Chem 58(6):3847–3854
Tait SW, Green DR (2010) Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(9):621–632
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2007) Role of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition in cell death. Apoptosis 12(5):835–840
van de Weerdt BC, Medema RH (2006) Polo-like kinases: a team in control of the division. Cell Cycle 5(8):853–864
Weichert W, Kristiansen G, Winzer KJ, Schmidt M, Gekeler V, Noske A, Muller BM, Niesporek S, Dietel M, Denkert C (2005) Polo-like kinase isoforms in breast cancer: expression patterns and prognostic implications. Virchows Arch 446(4):442–450
Wong RS (2011) Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:87
Yim H, Erikson RL (2009) Polo-like kinase 1 depletion induces DNA damage in early S prior to caspase activation. Mol Cell Biol 29(10):2609–2621
Yu C, Gong Y, Zhou H, Wang M, Kong L, Liu J, An T, Zhu H, Li Y (2017) Star-PAP, a poly(A) polymerase, functions as a tumor suppressor in an orthotopic human breast cancer model. Cell Death Dis 8(2):e2582
Yu Z, Deng P, Chen Y, Liu S, Chen J, Yang Z, Chen J, Fan X, Wang P, Cai Z, Wang Y, Hu P, Lin D, Xiao R, Zou Y, Huang Y, Yu Q, Lan P, Tan J, Wu X (2021) Inhibition of the PLK1-Coupled Cell Cycle Machinery Overcomes Resistance to Oxaliplatin in Colorectal Cancer, Adv Sci (Weinh) 8(23): e2100759.
Zhao C, Wang M, Cheng A, Yang Q, Wu Y, Jia R, Zhu D, Chen S, Liu M, Zhao X, Zhang S, Liu Y, Yu Y, Zhang L, Tian B, Rehman MU, Pan L, Chen X (2019) Duck Plague Virus Promotes DEF Cell Apoptosis by Activating Caspases, Increasing Intracellular ROS Levels and Inducing Cell Cycle S-Phase Arrest, Viruses 11(2)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Xinying Wu (Animal Center of Nankai University) for technical support of imaging in vivo. This work was supported by the “The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nankai University, #ZB19100128)” to C.L, “Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau of China (#cstc2019jcyj-msxm1819)” and “National Natural Science Foundation of China (#81901427)” to D.S.
Funding
“The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nankai University, #ZB19100128)” to C.L., “Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau of China (#cstc2019jcyj-msxm1819)” and “National Natural Science Foundation of China (#81901427)” to D.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YF and TL designed, performed, and analyzed in vitro and in vivo experiments. ZL, YL and XH performed PLK1 knockdown experiments in vitro and a xenograft tumor model establish in vivo. XP and ZF performed xenograft tumor collection. QW provided CRC patient-derived tissues. CL, YF, and TL contributed to the study design, implementation, and supervision of the study. YF and CL wrote the manuscript. DS and CL contributed to review the manuscript and supported funding. All authors had full access to the data and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Animal experiments were performed according to the Guidelines on Laboratory Animals of Nankai University and were approved by the Institute Research Ethics Committee at Nankai University (No: 2021-SYDWLL-000462). All relevant human studies were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institute Research Ethics Committee at Nankai University (No. NKUIRB2021107).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Li, T., Lin, Z. et al. Inhibition of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) triggers cell apoptosis via ROS-caused mitochondrial dysfunction in colorectal carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 6883–6899 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04624-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04624-2