Abstract
Purpose
The TMEM196 protein, which comprises four membrane-spanning domains, belongs to the TMEM protein family. TMEM196 was identified as a candidate tumor suppressor gene in lung cancer. However, its role and mechanism in lung cancer metastasis remain unclear. Here, we study the role of TMEM196 in tumor metastasis to further verify the function in lung cancer.
Methods
In this study, we used qRT-PCR, western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry to examine the expression levels of TMEM196 and related proteins in lung cancer tissues and tumor cells. We utilized Transwell assays, xenograft nude mouse models, and TMEM196−/− mouse models to evaluate the effects of TMEM196 on tumor invasion and metastasis. Finally, we used bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter gene assays to explore the molecular mechanism of TMEM196 as a tumor suppressor.
Results
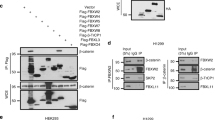
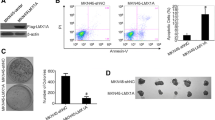
We found that TMEM196 mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly decreased in lung cancer tissues and cells. Low expression of TMEM196 in clinical patients was associated with poor prognosis. TMEM196 strongly inhibited tumor metastasis and progression in vitro and in vivo. The primary lung tumors induced by tail vein-inoculated B16 cells in TMEM196−/− mice were significantly larger than those in TMEM196+/+ mice. Mechanistically, TMEM196 inhibited the Wnt signaling pathway and repressed β-catenin promoter transcription. TMEM196 silencing in lung cancer cells and mice resulted in significant upregulation of the expression of β-catenin and Wnt signaling pathway downstream target genes (MMP2 and MMP7). Decreasing β-catenin expression in TMEM196-silenced cancer cells attenuated the antimetastatic effect of TMEM196.
Conclusions
Our results revealed that TMEM196 acts as a novel lung cancer metastasis suppressor via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TMEM:
-
Transmembrane protein
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- LUSC:
-
Lung squamous cell carcinoma
- TMEM196+/+ :
-
TMEM196 wild type
- TMEM196− / − :
-
TMEM196-null type
- WW:
-
Wild-type mice
- KK:
-
KO mice
References
Berglund E, Akcakaya P, Berglund D et al (2014) Functional role of the Ca2+-activated Cl- channel DOG1/TMEM16A in gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells. Exp Cell Res 326(2):315–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.05.003
Blomme A, Costanza B, De TP et al (2017) Myoferlin regulates cellular lipid metabolism and promotes metastases in triplenegative breast cancer. Oncogene 36(15):2116–2130. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.369
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Cadigan KM, Waterman ML (2012) TCF/LEFs and Wnt signaling in the Nucleus. Csh Perspect Biol 4(11):a007906. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a007906
Duan J, Qian Y, Fu X et al (2021) TMEM106C contributes to the malignant characteristics and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (albany NY) 13(4):5585–5606
Ge YX, Wang CH, Hu FY et al (2018) New advances of TMEM88 in cancer initiation and progression, with special emphasis on Wnt signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 233(1):79–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25853
Guo J, Chen L, Luo N et al (2015) Inhibition of TMEM45A suppresses proliferation, induces cell cycle arrest and reduces cell invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep 33(6):3124–3130. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3902
Han F, Liu WB, Shi XY et al (2018) SOX30 inhibits tumor metastasis through attenuating Wnt-signaling via transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of β-catenin in lung Cancer. EBioMedicine 31:253–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.04.026
Lee JU, Changa HS, Baeka DG et al (2019) Associations between TMEM196 polymorphisms and NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease in asthma. Pharmacogenet Genom 29(4):69–75
Leon MD, Cardenas H, Vieth E et al (2016) Transmembrane protein 88 (TMEM88) promoter hypomethylation is associated with cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 142(3):539–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.06.017
Liu WB, Han F, Jiang X et al (2015) TMEM196 acts as a novel functional tumour suppressor inactivated by DNA methylation and is a potential prognostic biomarker in lung cancer. Oncotarget 6(25):21225–21239
Liu WB, Han F, Huang YS et al (2019) TMEM196 hypermethylation as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for lung cancer. Mol Carcinogen 58(4):474–487
López-Soto A, Gonzalez S, Smyth MJ et al (2017) Control of metastasis by NK cells. Cancer Cell 32(2):135–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.06.009
Lunetta KL, D’Agostino RB Sr, Karasik D et al (2007) Genetic correlates of longevity and selected age-related phenotypes: a genome-wide association study in the Framingham Study. BMC Med Genet 8:S13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S13
Ma R, Feng NN, Yu et al (2017) Promoter methylation of Wnt/β-Catenin signal inhibitor TMEM88 is associated with unfavorable prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Med 14(004):377–386
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X (2009) Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.016
Marx S, Maso TD, Chen JW et al (2020) Transmembrane (TMEM) protein family members: poorly characterized even if essential for the metastatic process. Semin Cancer Biol 60:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.018
Mo PL, Yang SY (2018) The store-operated calcium channels in cancer metastasis from cell migration invasion to metastatic colonization. Front Mol Biosci 23:1241–1256. https://doi.org/10.2741/4641
Molenaar M, van de Wetering M, Oosterwegel M et al (1996) XTcf-3 transcription factor mediates β-catenin-induced axis formation in xenopus embryos. Cell 86(3):391–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80112-9
Nasim F, Sabath BF, Eapen GA (2019) Lung cancer. Med Clin North Am 103(3):463–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2018.12.006
Ng TP, Lo CM, Guo DY et al (2014) Identification of transmembrane protein 98 as a novel chemoresistance-conferring gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 13(5):1285–1297. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0806
Nusse R, Clevers H (2017) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cel 169(5):985–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016
Paul P (2007) The many ways of Wnt in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2006.12.007
Phillips BT, Kimble J (2009) A new look at TCF and β-catenin through the lens of a divergent C. elegans Wnt pathway. Dev Cell 17(1):27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2009.07.002
Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling and cancer. Gene Dev 14(15):1837–1851. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.14.15.1837
Polakis P (2012) Wnt signaling in cancer. Csh Perspect Biol 4(5):a008052. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008052
Qiu GZ, Sun W, Zou YX et al (2015) RNA interference against TMEM97 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioma cells. Tumour Biol 36(10):8231–8238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3552-6
Russell JO, Monga SP (2019) Wnt/β-catenin signaling in liver development, homeostasis, and pathobiology. Annu Rev Pathol 13:351–378. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-044010
Schmit K, Michiels C (2018) TMEM proteins in cancer: a review. Front Pharmacol 9:1345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01345
Siegel RL (2020) Kimberly DM and Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics. CA-Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Sun YN, Kolligs FT, Hottiger MO (2000) Regulation of β-catenin transformation by the p300 transcriptional coactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 23:12613–12618. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.220158597
Takeuchi T, Adachi Y, Nagayama T (2012) A WWOX-binding molecule, transmembrane protein 207, is related to the invasiveness of gastric signet-ring cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 33(3):548–554. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs001
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA (2011) Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms the invasion-metastasis cascade. Cell 147(2):275–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
Wang H, Zou L, Ma K et al (2017) Cell-specifc mechanisms of TMEM16A Ca2+-activated chloride channel in cancer. Mol Cancer 16(1):152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0720-x
Wilk JB, Walter RE, Laramie JM et al (2007) Framingham heart Study genome-wide association: results for pulmonary function measures. BMC Med Genet 8:S8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S8
Wrzesiński T, Szelag M, Cieslikowski WA et al (2015) Expression of pre-selected TMEMs with predicted ER localization as potential classifiers of ccRCC tumors. BMC Cancer 15(1):518. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1530-4
Yu XM, Zhang XP, Zhang Y et al (2015) Cytosolic TMEM88 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by interacting with Dvl. Oncotarget 6:25034–25045. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4379
Zeeshan R, Mutahir Z (2017) Cancer metastasis tricks of the trade. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 17(3):172–182
Zhang XP, Yu XM, Jiang GY et al (2015) Cytosolic TMEM88 promotes invasion and metastasis in lung cancer cells by binding DVLS. Cancer Res 75(21):4527–4537. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3828
Zhao F, Wang M, Li S et al (2015) DACH1 inhibits SNAI1- mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition and represses breast carcinoma metastasis. Oncogenesis 4:e143. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2015.3
Funding
This work was supported by Youth Foundation of the Army Medical University (No. 2019XQN03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by JC, DW, and HC. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JC and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All mouse experiments were carried out with the permission of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Army Medical University, China.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, D., Chen, H. et al. TMEM196 inhibits lung cancer metastasis by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 653–667 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04363-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04363-w