Abstract
Purpose
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common type of pancreatic malignancies. It is known for its aggressive nature and high mortality rate. This calls for an urgent need of new prognostic and therapeutic markers that can be targeted for personalized treatment of the patient.
Methods
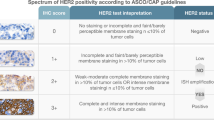
Among 142 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancers at Aga Khan University Hospital, a total of 62 patients were selected based on their confirmed diagnosis of PDAC. Immunohistochemistry was performed on Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) sections using selected antibodies (CD44, CD133, L1CAM, HER2, PD-L1, EGFR, COX2 and cyclin D1). All the slides were scored independently by two pathologists as per the set criteria.
Results
Expression of all cancer stem cell markers was found to be significantly associated with one or more potential therapeutic markers. CD44 expression was significantly associated with HER2 (p = 0.032), COX2 (p = 0.005) and EGFR expression (p = 0.008). CD133 expression also showed significant association with HER2 (p = 0.036), COX2 (p = 0.004) and EGFR expression (p = 0.018). L1CAM expression was found to be associated with expression of COX2 (p = 0.017). None of the proteins markers showed association with overall survival of the patient. On the other hand, among the clinicopathological characteristics, histological differentiation (p = 0.047), lymphovascular invasion (p = 0.021) and perineural invasion (p = 0.014) were found to be significantly associated with patient’s overall survival.
Conclusion
Internationally, this is the first report that assesses the selected panel of cancer stem cell markers and potential therapeutic targets in a single study and evaluates its combined expression. The study clearly demonstrates association between expression of cancer stem cell markers and therapeutic targets hence paves a way for precision medicine for pancreatic cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not Applicable.
References
Al-Aynati MM, Radulovich N, Ho J, Tsao MS (2004) Overexpression of G1-S cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases during multistage human pancreatic duct cell carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 10:6598–6605
Ali SA, Naeem S, Mirza Y, Zahid N, Awan MS (2018) Significance of immunohistochemical overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in overall and disease-free survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Laryngol Otol 132:1102–1109
American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Guidelines (2018) www.asco.org. Accessed 21 Feb 2022
Arnason T, Sapp HL, Barnes PJ, Drewniak M, Abdolell M, Rayson D (2011) Immunohistochemical expression and prognostic value of ER, PR and HER2/neu in pancreatic and small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology 93:249–258
Assenat E, Mineur L, Mollevi C, Lopez-Crapez E, Lombard-Bohas C, Samalin E, Portales F, Walter T, de Forges H, Dupuy M, Boissière-Michot F (2021) Phase II study evaluating the association of gemcitabine, trastuzumab and erlotinib as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma (GATE 1). Int J Cancer 148:682–691
Bachmann K, Neumann A, Hinsch A, Nentwich MF, El Gammal AT, Vashist Y, Perez D, Bockhorn M, Izbicki JR, Mann O (2015) Cyclin D1 is a strong prognostic factor for survival in pancreatic cancer: analysis of CD G870A polymorphism, FISH and immunohistochemistry. J Surg Oncol 111:316–323
Ben QW, Wang JC, Liu J, Zhu Y, Yuan F, Yao WY, Yuan YZ (2010) Positive expression of L1-CAM is associated with perineural invasion and poor outcome in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 17:2213–2221
Bergmann F, Wandschneider F, Sipos B, Moldenhauer G, Schniewind B, Welsch T, Schirrmacher P, Klöppel G, Altevogt P, Schäfer H, SebensMüerköster S (2010) Elevated L1CAM expression in precursor lesions and primary and metastastic tissues of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 24:909–915
Berlin JD, Feng Y, Catalano P, Abbruzzese JL, Philip PA, McWilliams RR et al (2018) An intergroup randomized phase II study of bevacizumab or Ccetuximab in combination with gemcitabine and in combination with chemoradiation in patients with resected pancreatic carcinoma: a trial of the ECOG-ACRIN cancer research group (E2204). Oncology 94:39
Bünger S, Barow M, Thorns C, Freitag-Wolf S, Danner S, Tiede S, Pries R, Gorg S, Bruch H-P, Roblick UJ, Kruse C, Habermann JK (2012) Pancreatic carcinoma cell lines reflect frequency and variability of cancer stem cell markers in clinical tissue. Eur Surg Res 49:88–98
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JK, Gourgou- Bourgade S, de la Fouchardière C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Péré-Vergé D, Dalbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux, M (2011) FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 364:1817–1825
Ding Qiang SM, Shinchi H, Kurahara H, Mataki Y, Maemura K, Natsugoe S, Takao S (2009) CD44 and CD133 expressions in primary tumor cells correlate to survival of pancreatic cancer patients. Open Surg Oncol J 1:1–7
Durko L, Wlodarski W, Stasikowska-Kanicka O, Wagrowska-Danilewicz M, Danilewicz M, Hogendorf P, Strzelczyk J, Malecka-Panas E (2017) Expression and clinical significance of cancer stem cell markers CD24, CD44, and CD133 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. Dis Markers 2017:3276806
Dzobo K, Ganz C, Thomford NE, Senthebane DA (2021) Cancer stem cell markers in relation to patient survival outcomes: lessons for integrative diagnostics and next-generation anticancer drug development. OMICS 25:81–92
Fagman JB, Ljungman D, Falk P, Iresjö BM, Engström C, Naredi P, Lundholm K (2019) EGFR, but not COX-2, protein in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is associated with poor survival. Oncol Lett 17:5361–5368
Food and Drugs Administration (FDA), USA (2021) www.fda.gov. Accessed 21 Feb 2022
Guo JA, Hoffman HI, Shroff SG, Chen P, Hwang PG, Kim DY, Kim DW, Cheng SW, Zhao D, Mahal BA, Alshalalfa M (2021) Pan-cancer transcriptomic predictors of perineural invasion improve occult histopathologic detection. Clin Cancer Res 27:2807–2815
Han SH, Ryu KH, Kwon AY (2021) The prognostic impact of HER2 genetic and protein expression in pancreatic carcinoma—HER2 protein and gene in pancreatic cancer. Diagnostics 11:653
Iwatate Y, Hoshino I, Yokota H, Ishige F, Itami M, Mori Y, Chiba S, Arimitsu H, Yanagibashi H, Nagase H, Takayama W (2020) Radiogenomics for predicting p53 status, PD-L1 expression, and prognosis with machine learning in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 123:1253–1261
Kaifi JT, Heidtmann S, Schurr PG, Reichelt U, Mann O, Yekebas EF, Wachowiak R, Strate T, Schachner M, Izbicki JR (2006) Absence of L1 in pancreatic masses distinguishes adenocarcinomas from poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas. Anticancer Res 26:1167–1170
Komoto M, Nakata B, Amano R, Yamada N, Yashiro M, Ohira M, Wakasa K, Hirakawa K (2009) HER2 overexpression correlates with survival after curative resection of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci 100:1243–1247
Kure S, Matsuda Y, Hagio M, Ueda J, Naito Z, Ishiwata T (2012) Expression of cancer stem cell markers in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Int J Oncol 41:1314–1324
Lathia J, Liu H, Matei D (2020) The clinical impact of cancer stem cells. Oncologist 25:123–131
Lee SM, Sung CO (2021) PD-L1 expression and surgical outcomes of adenosquamous carcinoma of the pancreas in a single-centre study of 56 lesions. Pancreatology 21:920–927
Lee SJ, Sung YN, Kim SJ, Shin S, Cho H, Hruban RH, Hong SM (2020) Comprehensive histological evaluation with clinical analysis of venous invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: From histology to clinical implications. Pancreatology 20:1486–1494
Liang X, Sun J, Wu H, Luo Y, Wang L, Lu J, Zhang Z, Guo J, Liang Z, Liu T (2018) PD-L1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 373 Chinese patients using an in vitro diagnostic assay. Diagn Pathol 13:1–8
Lozano-Leon A, Perez-Quintela BV, Iglesias-García J, Lariño-Noia J, Varo E, Forteza J, Domínguez-Muñoz JE (2011) Ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: expression of growth factor receptors, oncogenes and suppressor genes, and their relationship to pathological features, staging and survival. Oncol Lett 2:161–166
Matsubayashi H, Infante JR, Winter JM, Klein AP, Schulick R, Hruban R, Visvanathan K, Visvanathan K, Goggins M (2007) Tumor COX-2 expression and prognosis of patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 6:1569–1575
Mirza Y, Ali SA, Awan MS, Idress R, Naeem S, Zahid N, Qadeer U (2018) Overexpression of EGFR in oral premalignant lesions and OSCC and its impact on survival and recurrence. Oncomedicine 3:28
Myoteri D, Dellaportas D, Lykoudis PM, Apostolopoulos A, Marinis A, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A (2017) Prognostic evaluation of vimentin expression in correlation with Ki67 and CD44 in surgically resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Res Prac 2017:2017
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo A, Kanehiro H, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Yagita H, Azuma M, Nakajima Y (2007) Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the programmed death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:2151–2157
Ohnishi Y, Watanabe M, Wato M, Tanaka A, Kakudo K, Nozaki M (2014) Cyclin D1 expression is correlated with cell differentiation and cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol Lett 7:1123–1127
Park SJ, Gu MJ, Lee DS, Yun SS, Kim HJ, Choi JH (2015) EGFR expression in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:8298
Pilleron S, Soerjomataram I, Charvat H, Chokunonga E, Somdyala NI, Wabinga H, Korir A, Bray F, Jemal A, Maxwell Parkin D (2019) Cancer incidence in older adults in selected regions of sub-Saharan Africa, 2008–2012. Int J Cancer 144:1824–1833
Rawla P, Sunkara T, Gaduputi V (2019) Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: global trends, etiology and risk factors. World J Oncol 10:10
Saad AM, Turk T, Al-Husseini MJ, Abdel-Rahman O (2018) Trends in pancreatic adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in the United States in the last four decades; a SEER-based study. BMC Cancer 18:1–1
Si D, Yin F, Peng J, Zhang G (2020) High expression of CD44 predicts a poor prognosis in glioblastomas. Cancer Manag Res 12:769
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Takahashi H, Katsuta E, Yan L, Tokumaru Y, Katz MH, Takabe K (2020) Transcriptomic profile of lymphovascular invasion, a known risk factor of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis. Cancers 12:2033
van der Maten M, Reijnen C, Pijnenborg J, Zegers MM (2019) L1 cell adhesion molecule in cancer, a systematic review on domain-specific functions. Int J Mol Sci 20:4180
Wachowiak R, Krause M, Mayer S, Peukert N, Suttkus A, Müller WC, Lacher M, Meixensberger J, Nestler U (2018) Increased L1CAM (CD171) levels are associated with glioblastoma and metastatic brain tumors. Medicine 97:e12396
Xiaoping L, Xiaowei Z, Leizhen Z, Weijian G (2015) Expression and significance of CD44 and p-AKT in pancreatic head cancer. World J Surg Oncol 13:1–7
Yun G, Kim YH, Lee YJ, Kim B, Hwang JH, Choi DJ (2018) Tumor heterogeneity of pancreas head cancer assessed by CT texture analysis: association with survival outcomes after curative resection. Sci Rep 8:1
Zhang M, Song T, Yang L, Chen R, Wu L, Yang Z, Fang J (2008) Nestin and CD133: valuable stem cell-specific markers for determining clinical outcome of glioma patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:1–7
Zińczuk J, Zaręba K, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Kędra B, Kemona A, Pryczynicz A (2018) Expression of chosen cell cycle and proliferation markers in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Prz Gastroenterol 13:118–126
Funding
The study was funded by University Research Council (Grant ID: 183027SUR), Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Research Idea: S.M Adnan Ali, Project Development and Proposal Writing for Grant—Yumna Adnan, Bench Work—Hasnain Ahmad Farooqui, Bench Work Supervision: S.M Adnan Ali, Review of H&E and Immunohistochemistry Slides—Zubair Ahmad, Patient Recruitment and Data Acquisition—Tabish Chawla, Data Entry—Saleema Mehboob Ali, Data Analysis and Interpretation—S.M Adnan Ali, Saleema Mehboob Ali and Yumna Adnan, Drafting of Manuscript—Saleema Mehboob Ali and S.M Adnan Ali, Critical Review and Manuscript Finalization—S.M Adnan Ali, Approval of Final Version of the Manuscript—All Authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Committee of Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan (2018-0449-1058).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all the participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of their data with anonymous identities.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S.M.A., Adnan, Y., Ali, S.M. et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of a panel of cancer stem cell markers and potential therapeutic markers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 2279–2292 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04315-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04315-4