Abstract
Background
The incidence of lung cancer tends to be younger, and adenocarcinoma is the main histological type. Even patients with the same tumor type may have significant differences in clinical features, tumor microenvironment and genomic background at different ages. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been shown to improve clinical outcomes in patients with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). However, differences in ICI efficacy between older and younger patients are unknown. Our study aimed to explore the relationship between age and immunotherapy in LUAD.
Methods
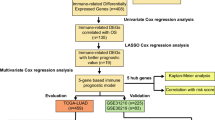
In our study, 1313 resected LUAD patients in our hospital were divided into young (age ≤ 50) and old groups (age > 50), and the clinical characteristic differences between them were analyzed. Of these, next-generation sequencing (NGS) was performed on the 311 cases. In addition, immune-related signatures of 508 LUAD patients were analyzed by TCGA RNA expression data. Then, we validated genomic and clinical information of 270 LUAD samples in the MSKCC cohort.
Results
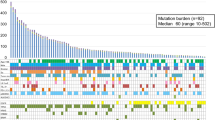
ERBB2 and EGFR gene mutations were significantly different between the two groups, and the gene mutation number in the old group was significantly higher than that in the young group. In addition, immune-related signatures of LUAD patients were analyzed by TCGA RNA expression data, which indicated that the patients in the old group might have a better immune microenvironment. Then, we validated the MSKCC cohort and found that the TMB of the old group was significantly higher than that of the young group, and the OS of immunotherapy was longer in the old group.
Conclusion
Our study was the first to analyze the differences in the genomic landscape and immune-related biomarkers between the young and old groups of LUAD patients and found that the old group had a better efficacy of immunotherapy, providing a reference for the study design and treatment of patients with LUAD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arnold BN, Thomas DC, Rosen JE, Salazar MC, Blasberg JD, Boffa DJ et al (2016) Lung cancer in the very young: treatment and survival in the national cancer data base. J Thorac Oncol 11(7):1121–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.023
Ayers M, Lunceford J, Nebozhyn M, Murphy E, Loboda A, Kaufman DR et al (2017) IFN-γ-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest 27(8):2930–2940. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI91190
Büttner R, Gosney JR, Skov BG et al (2017) Programmed death-ligand 1 immunohistochemistry testing: a review of analytical assays and clinical implementation in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 35(34):3867–3876. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.74.7642
Cai L, Chen Y, Tong X, Wu X, Bao H, Shao Y et al (2021) The genomic landscape of young and old lung cancer patients highlights age-dependent mutation frequencies and clinical actionability in young patients. Int J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33583
Camidge DR, Doebele RC, Kerr KM (2019) Comparing and contrasting predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy and targeted therapy of NSCLC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 16(6):341–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0173-9
Cao J, Li J, Yang X, Li P, Yao Z, Han D et al (2021) Transcriptomics analysis for the identification of potential age-related genes and cells associated with three major urogenital cancers. Sci Rep 11(1):641. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80065-y
Carbone DP, Reck M, Paz-Ares L, Creelan B, Horn L, Steins M, CheckMate 026 Investigators et al (2017) First-line nivolumab in stage iv or recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 376(25):2415–2426. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1613493
Casaluce F, Sgambato A, Maione P, Spagnuolo A, Gridelli C (2018) Lung cancer, elderly and immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Thorac Dis 10(Suppl 13):S1474–S1481. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2018.05.90
Charvat H, Sasazuki S, Shimazu T, Budhathoki S, Inoue M, Iwasaki M, JPHC Study Group et al (2018) Development of a risk prediction model for lung cancer: The Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. Cancer Sci 109(3):854–862. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13509
Chen DS, Mellman I (2013) Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 39(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F et al (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chen J, Yang H, Teo ASM et al (2020) Genomic landscape of lung adenocarcinoma in East Asians. Nat Genet 52(2):177–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0569-6
Danaher P, Warren S, Dennis L, D’Amico L, White A, Disis ML et al (2017) Gene expression markers of Tumor Infiltrating Leukocytes. J Immunother Cancer 5:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-017-0215-8
Davoli T, Uno H, Wooten EC, Elledge SJ (2017) Tumor aneuploidy correlates with markers of immune evasion and with reduced response to immunotherapy. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8399
Elias R, Giobbie-Hurder A, McCleary NJ, Ott P, Hodi FS, Rahma O (2018) Efficacy of PD-1 & PD-L1 inhibitors in older adults: a meta-analysis. J Immunother Cancer 6(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0336-8
Gu Y, Zhang J, Zhou Z, Liu D, Zhu H, Wen J et al (2020) Metastasis patterns and prognosis of octogenarians with NSCLC: a population-based study. Aging Dis 11(1):82–92. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2019.0414
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu WJ, Kefford R et al (2019) Five-year survival outcomes for patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-001. Ann Oncol 30(4):582–588. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz011
Hellmann MD, Ciuleanu TE, Pluzanski A et al (2018) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden. N Engl J Med 378(22):2093–2104. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1801946
Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387(10027):1540–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7
Hwang KB, Lee IH, Li H, Won DG, Hernandez-Ferrer C, Negron JA et al (2019) Comparative analysis of whole-genome sequencing pipelines to minimize false negative findings. Sci Rep 9(1):3219. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39108-2
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, Fu J, Sahu A, Hu X et al (2018) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24(10):1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Kim H, Kwon HJ, Kim ES et al (2021) Comparison of the predictive power of a combination versus individual biomarker testing in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Res Treat. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2021.583.http
Lai Z, Markovets A, Ahdesmaki M, Chapman B, Hofmann O, McEwen R et al (2016) VarDict: a novel and versatile variant caller for next-generation sequencing in cancer research. Nucleic Acids Res 44(11):e108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw227
Li Q, Wang K (2017) InterVar: clinical interpretation of genetic variants by the 2015 ACMG-AMP guidelines. Am J Hum Genet 100(2):267–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.01.004
Liang Y, Hou H, Jiang M, Zhang C, Liu D, Zhang X (2020) Results of randomized, multicenter, double-blind phase III trial of rh-endostatin (YH-16) in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 23(4):239–246. https://doi.org/10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.17
Liu L, Liu J, Shao D, Deng Q, Tang H, Liu Z et al (2017) Comprehensive genomic profiling of lung cancer using a validated panel to explore therapeutic targets in East Asian patients. Cancer Sci 108(12):2487–2494. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13410
Liu B, Quan X, Xu C et al (2019) Lung cancer in young adults aged 35 years or younger: a full-scale analysis and review. J Cancer 10(15):3553–3559. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.27490
Mamdani H, Matosevic S, Khalid AB, Durm G, Jalal SI (2022) Immunotherapy in lung cancer: current landscape and future directions. Front Immunol 13:823618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.823618
Naltet C, Besse B (2021) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in elderly patients treated for a lung cancer: a narrative review. Transl Lung Cancer Res 10(6):3014–3028. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-1239
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, et al (2022) Non-small cell lung cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 20(5):497–530. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2022.0025
Newman AM, Bratman SV, Stehr H, Lee LJ, Liu CL, Diehn M et al (2014) FACTERA: a practical method for the discovery of genomic rearrangements at breakpoint resolution. Bioinformatics 30(23):3390–3393. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu549
Paz-Ares L, Vicente D, Tafreshi A, Robinson A, Soto Parra H, Mazières J et al (2020) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC: protocol-specified final analysis of KEYNOTE-407. J Thorac Oncol 15(10):1657–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2020.06.015
Paz-Ares L, Ciuleanu TE, Cobo M, Schenker M, Zurawski B, Menezes J et al (2021) First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 22(2):198–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30641-0
Petitprez F, de Reyniès A, Keung EZ, Chen TW, Sun CM, Calderaro J et al (2020) B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma. Nature 577(7791):556–560. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1906-8
Prat A, Navarro A, Paré L et al (2017) Immune-related gene expression profiling after PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung carcinoma, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Cancer Res 77(13):3540–3550. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472 (CAN-16-3556)
Qiu B, Guo W, Zhang F, Lv F, Ji Y, Peng Y et al (2021) Dynamic recurrence risk and adjuvant chemotherapy benefit prediction by ctDNA in resected NSCLC. Nat Commun 12(1):6770. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27022-z
Reck M, Mok TSK, Nishio M, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, IMpower150 Study Group et al (2019a) Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med 7(5):387–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30084-0
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A et al (2019b) Updated analysis of KEYNOTE-024: pembrolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score of 50% or greater. J Clin Oncol 37(7):537–546. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.00149
Reck M, Schenker M, Lee KH, Provencio M, Nishio M, Lesniewski-Kmak K et al (2019c) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with high tumour mutational burden: patient-reported outcomes results from the randomised, open-label, phase III CheckMate 227 trial. Eur J Cancer 116:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2019.05.008
Sacher AG, Dahlberg SE, Heng J, Mach S, Jänne PA, Oxnard GR (2016) Association between younger age and targetable genomic alterations and prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol 2(3):313–320. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.4482
Sanmamed MF, Nie X, Desai SS et al (2021) A burned-Out CD8+ T-cell subset expands in the tumor microenvironment and curbs cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Discov 11(7):1700–1715. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0962
Shah Y, Verma A, Marderstein AR, White J, Bhinder B, Garcia Medina JS et al (2021) Pan-cancer analysis reveals molecular patterns associated with age. Cell Rep 37(10):110100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110100
Soh J, Hamada A, Fujino T, Mitsudomi T (2021) Perioperative therapy for non-small cell lung cancer with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancers (basel) 13(16):4035. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164035
Spigel DR, McCleod M, Jotte RM, Einhorn L, Horn L, Waterhouse DM et al (2019) Safety, efficacy, and patient-reported health-related quality of life and symptom burden with nivolumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer, including patients aged 70 years or older or with poor performance status (CheckMate 153). J Thorac Oncol 14(9):1628–1639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.05.010
Suidan AM, Roisman L, Belilovski Rozenblum A et al (2019) Lung cancer in young patients: higher rate of driver mutations and brain involvement, but better survival. J Glob Oncol 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1200/JGO.18.00216
Talevich E, Shain AH, Botton T, Bastian BC (2016) CNVkit: genome-wide copy number detection and visualization from targeted DNA sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol 12(4):e1004873. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004873
Tanaka K, Hida T, Oya Y et al (2017) Unique prevalence of oncogenic genetic alterations in young patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer 123(10):1731–1740. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30539
Tang S, Qin C, Hu H et al (2022) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: progress, challenges, and prospects. Cells 11(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030320
Thomas A, Chen Y, Yu T, Jakopovic M, Giaccone G (2015) Trends and characteristics of young non-small cell lung cancer patients in the United States. Front Oncol 5:113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2015.00113
Tian P, Liu Y, Zeng H et al (2020) Unique molecular features and clinical outcomes in young patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring ALK fusion genes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146(4):935–944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03116-6
US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, Mangione CM, Barry MJ, Cabana M et al (2021) Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 325(10):962–970. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.1117
Vitiello GA, Bowler TG, Liu M, Medina BD, Zhang JQ, Param NJ et al (2019) Differential immune profiles distinguish the mutational subtypes of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Invest 129(5):1863–1877. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI124108
Wang Y, Chen J, Ding W, Yan B, Gao Q, Zhou J (2015) Clinical features and gene mutations of lung cancer patients 30 years of age or younger. PLoS ONE 10(9):e0136659. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136659
Wu YL, Planchard D, Lu S, Sun H, Yamamoto N, Kim DW et al (2019) Pan-Asian adapted Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a CSCO-ESMO initiative endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS. SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol 30(2):171–210. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy554
Yang B, Li J, Li F et al (2019) Comprehensive analysis of age-related somatic mutation profiles in Chinese young lung adenocarcinoma patients. Cancer Med 8(4):1350–1358. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1839
Ye Y, Jing Y, Li L et al (2020) Sex-associated molecular differences for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 11(1):1779. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15679-x
Zhang C, Zhang J, Xu FP, Wang YG, Xie Z, Su J et al (2019a) Genomic landscape and immune microenvironment features of preinvasive and early invasive lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 14(11):1912–1923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.07.031
Zhang L, Sun L, Yu J, Shan F, Zhang K, Pang X et al (2019b) Comparison of immune checkpoint inhibitors between older and younger patients with advanced or metastatic lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2019:9853701. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9853701
Zhang QJ, Luan JC, Song LB et al (2021) Age-related differences in molecular profiles for immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Front Immunol 12:657575. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.657575
Zhou C, Wang Z, Sun Y, Cao L, Ma Z, Wu R et al (2022) Sugemalimab versus placebo, in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, as first-line treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (GEMSTONE-302): interim and final analyses of a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 clinical trial. Lancet Oncol 23(2):220–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00650-1
Zhuo H, Zhao Y, Cheng X, Xu M, Wang L, Lin L et al (2019) Tumor endothelial cell-derived cadherin-2 promotes angiogenesis and has prognostic significance for lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer 18(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0987-1
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Qin Zhang, Mr. Hao Guo, Mr. Wang-Long Deng, Mr. Guang-Hua Lu, Mr. Ran Ding, Ms. Qin Shuai and Ms. Fei Wang from Simceredx for the kindly assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by following grants: WU JIEPING Medical Foundation (No. 320.6750.2021-01-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YJW, PL, and SYC planed the study. YXQ, NNL, XFZ, and MHG analyzed data and interpreted the results. PL, QJL, YPX, and JLL enrolled the patients, involved in the patients’ treatment and collected the clinical data. YXQ, NNL, XFZ, and MML wrote the manuscript. YJW, TTS, and CQ participated in manuscript revision and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This work was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University (number: QYFY WZLL 26936).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2022_4195_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1. Fig. S1. KEGG and GO enrichment of gene mutations in the different groups. A KEGG enrichment for the genomic alteration results of 311 LUAD patients using a 224-gene panel. B GO enrichment for the genomic alteration results of 311 LUAD patients using a 224-gene panel. (DOCX 408 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Che, S., Qi, Y. et al. Age-dependent genomic characteristics and their impact on immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 2997–3007 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04195-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04195-8