Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether induction of temporary threshold shift (TTS) with aspirin prior to cisplatin exposure can prevent or minimize cisplatin detrimental effects on hearing.
Methods
We randomly divided BALB mice into three groups: (1) cisplatin only, (2) aspirin only, and (3) combined aspirin/cisplatin. Cisplatin was administered as a single intraperitoneal injection of 14 mg/kg. Aspirin was administered for three weeks via intraperitoneal injection of 200 mg/kg sodium salicylate, twice daily. Air conduction thresholds were recorded using Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR). Cochleae were harvested and cochlear hair cells were counted using a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results
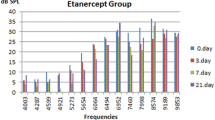
Aspirin-induced TTS have reached an average of 30.05±16.9 dB after 2 weeks. At 60 days, cisplatin-only treated mice experienced an average threshold shifts of 50.7 dB at 4 kHz, 35.16 dB at 8 kHz, 70 dB at 16 kHz, 53.1 dB at 32 kHz. All threshold shifts were significantly worse than for cisplatin/aspirin treated mice with TTS of 11.85 dB at 4 kHz, 3.58 dB at 8 kHz, 16.58 dB at 16 kHz, 20.41 dB at 32 kHz (p < 0.01). Cochlear cell count with SEM has shown reduction in the number of both inner and outer hair cells in the mid-turn in cisplatin treated mice.
Conclusion
Aspirin induced TTS can protect from cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. This beneficial effect was demonstrated by auditory thresholds as well as SEM. Larger pre-clinical and clinical studies are still needed to confirm these findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data and materials availability
The data generated in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem responses
- TTS:
-
Temporary threshold shift
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- IHC:
-
Inner hair cells
- OHC:
-
Outer hair cells
- DPOAEs:
-
Distortion product otoacoustic emissions
- SGCs:
-
Spiral ganglion cells
- BID:
-
Twice a day
- TID:
-
Three times a day
References
Aamdal S, Fodstad O, Pihl A (1988) Sodium thiosulfate fails to increase the therapeutic index of intravenously administered cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) in mice bearing murine and human tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 21(2):129–133
Bader W, Gottfried T, Degenhart G, Johnson Chacko L, Sieber D, Riechelmann H, Fischer N, Hoermann R, Glueckert R, Schrott-Fischer A, Schmutzhard J (2021) Measurement of the intracochlear hypothermia distribution utilizing tympanic cavity hypothermic rinsing technique in a cochlea hypothermia model. Front Neurol 11(11):620691
Balkany TJ, Eshraghi AA, Jiao H, Polak M, Mou C, Dietrich DW et al (2005) Mild hypothermia protects auditory function during cochlear implant surgery. Laryngoscope 115:1543–1547
Boheim K, Bichler E (1985) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: audiometric findings and experimental cochlear pathology. Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 242(1):1–6
Cardinaal RM, de Groot JCMJ, Huizing EH, Veldman JE, Smoorenburg GF (2000) Dose-dependent effect of 8-day cisplatin administration upon the morphology of the albino Guinea pig cochlea. Hear Res 144(1–2):135–146
Cardinaal RM, Groot JCMJ, Huizing EH, Veldman JE, Smoorenburg GF (2000) Dose-dependent effect of 8-day cisplatin administration upon the morphology of the albino guinea pig cochlea. Hearing Res 144:135–146
Crabb SJ, Martin K, Abab J, Ratcliffe I, Thornton R, Lineton B, Ellis M, Moody R, Stanton L, Galanopoulou A, Maishman T, Geldart T, Bayne M, Davies J, Lamb C, Popat S, Joffe JK, Nutting C, Chester J, Hartley A, Thomas G, Ottensmeier C, Huddart R, King E (2017) COAST (Cisplatin ototoxicity attenuated by aspirin trial): A phase II double-blind, randomised controlled trial to establish if aspirin reduces cisplatin induced hearing-loss. Eur J Cancer 87:75–83
Crifò S (1975) Aspirin ototoxicity in the guinea pig. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 37(1):27–34
DeBacker JR, Harrison RT, Bielefeld EC (2020) Cisplatin-induced threshold shift in the CBA/CaJ, C57BL/6J, BALB/Cj mouse models of hearing loss. Hear Res 1(387):107878
Engelman R, Baker RA, Likosky DS, Grigore A, Dickinson TA, Shore-Lesserson L, Hammon JW (2015) The society of thoracic surgeons, the society of cardiovascular anesthesiologists, and the american society of extracorporeal technology: clinical practice guidelines for cardiopulmonary bypass-temperature management during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Extra Corpor Technol 47(3):145–154
Henry KR (1980) Effects of noise, hypothermia and barbiturate on cochlear electrical activity. Audiology 19(1):44–56
Henry KR (2003) Hyperthermia exacerbates and hypothermia protects from noise-induced threshold elevation of the cochlear nerve envelope response in the C57BL/6J mouse. Hear Res 179(1–2):88–96
Henry KR (2003) Hyperthermia exacerbates and hypothermia protects from noise-induced threshold elevation of the cochlear nerve envelope response in the C57BL/6J mouse. Hear Res 179:88–96
Hildesheimer M, Henkin Y, Muchnik C, Anafi R, Sahartov E, Rubinstein M (1991) Sedation effect on temporary threshold shift induced by acoustic overstimulation. Hear Res 51(1):161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5955(91)90014-z
Hill GW, Morest DK, Parham K (2008) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: effect of intratympanic dexamethasone injections. Otol Neurotol 29(7):1005–1011
Hill GW, Morest DK, Parham K (2008) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: effect of intratympanic dexamethasone injections. Otol Neurotol 29:1005–1011
Hong JM, Lee JS, Song HJ, Jeong HS, Choi HA, Lee K (2014) Therapeutic hypothermia after recanalization in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 45(1):134–140
Hu SS, Mei L, Chen JY, Huang ZW, Wu H (2014) Effects of salicylate on the inflammatory genes expression and synaptic ultrastructure in the cochlear nucleus of rats. Inflammation 37(2):365–373
Huang ZW, Luo Y, Wu Z, Tao Z, Jones RO, Zhao HB (2005) Paradoxical enhancement of active cochlear mechanics in long-term administration of salicylate. J Neurophysiol 93(4):2053–2061
Hunter-Duvar IM (1978) A technique for preparation of cochlear specimens for assessment with the scanning electron microscope. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 351:3–23
Hyppolito MA, de Oliveira JA, Rossato M (2006) Cisplatin ototoxicity and otoprotection with sodium salicylate. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263(9):798–803
Inoue M, Shimizu C, Shimizu H, Tanizawa O (1991) Neutralizing effect of sodium thiosulfate on antitumor efficacy of cisplatin for human carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Gynecol Oncol 40(1):34–37
Kamimura T, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (1999) Effect of 4-methylthiobenzoic acid on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in the rat. Hear Res 131(1–2):117–127
Komune S, Asakuma S, Snow JB (1981) Pathophysiology of the ototoxicity of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 89(2):275–282
Lanvers-Kaminsky C, Zehnhoff-Dinnesen AAM, Parfitt R, Ciarimboli G (2017) Drug-induced ototoxicity: mechanisms, pharmacogenetics, and protective strategies. Clin Pharmacol Ther 101(4):491–500
Laurell G, Bagger-Sjoback D (1991) Degeneration of the organ of Corti following intravenous administration of cisplatin. Acta Otolaryngol 111(5):891–898
Laurell G, Bagger-Sjoback D (2000) Dose-dependent inner ear changes after i.v. administration of cisplatin. J Otolaryngol 20:158–167
Li G, Sha SH, Zotova E, Arezzo J, Van de Water T, Schacht J (2002) Salicylate protects hearing and kidney function from cisplatin toxicity without compromising its oncolytic action. Lab Invest 82(5):585–596
Mccabe PA, Dey FL (1965) The effect of aspirin upon auditory sensitivity. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 74:312–325
McFadden D, Plattsmier HS (1983) Aspirin can potentiate the temporary hearing loss induced by intense sounds. Hear Res 9(3):295–316
Minami SB, Sha SH, Schacht J (2004) Antioxidant protection in a new animal model of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Hear Res 198(1–2):137–143
Moroso MJ, Blair RL (1983) A review of cis-platinum ototoxicity. J Otolaryngol 12:365–369
Myers EN, Bernstein JM (1965) Salicylate ototoxicity: a clinical and experimental study. Arch Otolaryngol 82(5):483–493
Reser D, Rho M, Dewan D, Herbst L, Li G, Stupak H, Zur K, Romaine J, Frenz D, Goldbloom L, Kopke R, Arezzo J, Van De Water T (1999) L- and D- methionine provide equivalent long term protection against CDDP-induced ototoxicity in vivo, with partial in vitro and in vivo retention of antineoplastic activity. Neurotoxicology 20(5):731–748
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D, Ramkumar V (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear Res 226:157–167
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V (2009) Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp Med 219:177–186
Sheppard A, Hayes SH, Chen GD, Ralli M, Salvi R (2014) Review of salicylate-induced hearing loss, neurotoxicity, tinnitus and neuropathophysiology. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 34(2):79–93
Spankovich C, Lobarinas E, Ding D, Salvi R, Le Prell CG (2016) Assessment of thermal treatment via irrigation of external ear to reduce cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Hear Res 332:55–60
Surnar B, Kolishetti N, Basu U, Ahmad A, Goka E, Marples B, Kolb D, Lippman ME, Dhar S (2018) Reduction of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity without compromising its antitumor activity. Biochemistry 57(46):6500–6513
Szepesy J, Humli V, Farkas J, Miklya I, Tímár J, Tábi T, Gáborján A, Polony G, Szirmai Á, Tamás L, Köles L, Vizi ES, Zelles T (2021) Chronic oral selegiline treatment mitigates age-related hearing loss in balb/c mice. Int J Mol Sci 22(6):2853
Tamames I, King C, Bas E, Dietrich WD, Telischi F, Rajguru SM (2016) A cool approach to reducing electrode-induced trauma: localized therapeutic hypothermia conserves residual hearing in cochlear implantation. Hear Res 339:32–39
Willott JF, Turner JG, Carlson S, Ding D, Seegers Bross L, Falls WA (1998) The BALB/c mouse as an animal model for progressive sensorineural hearing loss. Hear Res 115(1–2):162–174
Yu N, Zhu M-L, Johnson B, Liu Y-P, Jones RO, Zhao H-B (2008) Prestin up-regulation in chronic salicylate (aspirin) administration: an implication of functional dependence of prestin expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(15):2407–2418
Acknowledgements
We thank Advanced Bionics for their technical support and guidance and Dr. Ofir Zavdy for illustration assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by a research grant provided by Rabin Medical Center, Israel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST performed the majority of the experimental work and wrote the manuscript, AM conceptualized the research, reviewed, and edited the manuscript, NB performed the experimental work, SS performed the histological analysis, EY performed the experimental work, YA conceptualized the research, reviewed, and edited the manuscript and OH conceptualized the research, reviewed, and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All housing and experimental procedures were reviewed and approved by Rabin Medical Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (020502).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzelnick, S., Mizrachi, A., Barkan, N. et al. The protective effect of aspirin-induced temporary threshold shift in an animal model of cisplatin-related ototoxicity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 2009–2016 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04144-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04144-5