Abstract
Purpose
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been explored as first-line treatment in various types of previously untreatable malignancies, while limited evidence is available on the management of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in patients undergoing immunotherapy. We systematically reviewed data concerning challenges of hepatic adverse events including HBV reactivation and hepatitis in patients with chronic HBV infection undergoing immunotherapy.
Methods
A systematic search was conducted in Medline, web of science, Embase and Cochrane library up to May 31, 2022. Studies reporting the safety profile of ICIs in patients with HBV infection were eligible. Meta-analyses were conducted to generate odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
A total of 13 studies including 2561 patients were included for meta-analysis. The overall incidence rates of HBV reactivation in patients with chronic HBV infection and past HBV infection were 1.0% (95% CI 0–3%) and 0% (95% CI 0–0%), respectively. Among patients with chronic HBV infection, the incidence rates of HBV reactivation were 1.0% (95% CI 0–2%) and 10.0% (95% CI 4–18%) for patients with and without antiviral prophylaxis, respectively. Patients with chronic HBV infection were at a higher risk of HBV reactivation compared with those with past HBV infection [OR = 8.69, 95% CI (2.16–34.99)]. Antiviral prophylaxis significantly reduced the risk of HBV reactivation [OR = 0.12, 95% CI (0.02–0.67)] and HBV-associated hepatitis [OR = 0.05, 95% CI (0.01–0.28)] in patients with chronic HBV infection.
Conclusions
Prophylactic antiviral therapy should be administered to patients with chronic HBV infection undergoing anticancer immunotherapy. Patients with past HBV infection are at lower risk of HBV reactivation compared with those with chronic HBV infection, they could be initiated with antiviral prophylaxis or monitored with the intent of on-demand antiviral therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH et al (2006) Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439(7077):682–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04444
Byeon S, Cho JH, Jung HA, Sun JM, Lee SH, Ahn JS et al (2020) PD-1 inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer patients with special issues: real-world evidence. Cancer Med 9(7):2352–2362. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2868
Chan GH, Gwee YX, Low JL, Huang Y, Chan ZY, Choo JR et al (2020) Immune checkpoint inhibition for non-small cell lung cancer in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis or Hepatitis B: experience from a single Asian centre. Lung Cancer 146:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.05.020
Choi J, Lim YS (2017) Characteristics, prevention, and management of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in HBV-infected patients who require immunosuppressive therapy. J Infect Dis 216(Suppl_8):S778–S784. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix178
Cohen EEW, Soulières D, Le Tourneau C, Dinis J, Licitr L, Ahn MJ et al (2019) Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 393(10167):156–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31999-8
Day CL, Kaufmann DE, Kiepiela P, Brown JA, Moodley ES, Reddy S et al (2006) PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature 443(7109):350–354. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05115
Duan J, Cui L, Zhao X, Bai H, Cai S, Wang G et al (2020) Use of immunotherapy with programmed cell death 1 vs programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 6(3):375–384. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5367
Feun LG, Li YY, Wu C, Wangpaichitr M, Jones PD, Richman SP et al (2019) Phase 2 study of pembrolizumab and circulating biomarkers to predict anticancer response in advanced, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 125(20):3603–3614. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32339
Godbert B, Petitpain N, Lopez A, Nisse YE, Gillet P (2021) Hepatitis B reactivation and immune check point inhibitors. Dig Liver Dis 53(4):452–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2020.08.041
Gordan JD, Kennedy EB, Abou-Alfa GK, Beg MS, Brower ST, Gade TP et al (2020) Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO guideline. J Clin Oncol 38(36):4317–4345. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.20.02672
Hagiwara S, Nishida N, Ida H, Ueshima K, Minami Y, Takita M et al (2022) Clinical implication of immune checkpoint inhibitor on the chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatol Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.13798
Hanna NH, Schneider BJ, Temin S, Baker S, Brahmer J, Ellis PM et al (2020) Therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer without driver alterations: ASCO and OH (CCO) joint guideline update. J Clin Oncol 38(14):1608–1632. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.19.03022
Havel JJ, Chowell D, Chan TA (2019) The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 19(3):133–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0116-x
He MK, Peng C, Zhao Y, Liang RB, Lai ZC, Kan A et al (2021) Comparison of HBV reactivation between patients with high HBV–DNA and low HBV–DNA loads undergoing PD-1 inhibitor and concurrent antiviral prophylaxis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-02911-w
Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R, Zurawski B, Kim SW, Carcereny Costa E et al (2019) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 381(21):2020–2031. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1910231
Huang YH, Hsiao LT, Hong YC, Chiou TJ, Yu YB, Gau JP et al (2013) Randomized controlled trial of entecavir prophylaxis for rituximab-associated hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with lymphoma and resolved hepatitis B. J Clin Oncol 31(22):2765–2772. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2012.48.5938
Huang H, Li X, Zhu J, Ye S, Zhang H, Wang W et al (2014) Entecavir vs lamivudine for prevention of hepatitis B virus reactivation among patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving R-CHOP chemotherapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 312(23):2521–2530. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.15704
Hwang JP, Lok AS, Fisch MJ, Cantor SB, Barbo A, Lin HY et al (2018) Models to predict hepatitis B virus infection among patients with cancer undergoing systemic anticancer therapy: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol 36(10):959–967. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2017.75.6387
Hwang JP, Feld JJ, Hammond SP, Wang SH, Alston-Johnson DE, Cryer DR et al (2020) Hepatitis B virus screening and management for patients with cancer prior to therapy: ASCO provisional clinical opinion update. J Clin Oncol 38(31):3698–3715. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.20.01757
Ingles Garces AH, Au L, Mason R, Thomas J, Larkin J (2019) Building on the anti-PD1/PD-L1 backbone: combination immunotherapy for cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 28(8):695–708. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2019.1649657
Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M, Garrido M, Salman P, Shen L (2021) First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 398(10294):27–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00797-2
Knolle PA, Thimme R (2014) Hepatic immune regulation and its involvement in viral hepatitis infection. Gastroenterology 146(5):1193–1207. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.036
Lau GK, Yiu HH, Fong DY, Cheng HC, Au WY, Lai LS et al (2003) Early is superior to deferred preemptive lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B patients undergoing chemotherapy. Gastroenterology 125(6):1742–1749. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2003.09.026
Lee YH, Bae SC, Song GG (2013) Hepatitis B virus reactivation in HBsAg-positive patients with rheumatic diseases undergoing anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy or DMARDs. Int J Rheum Dis 16(5):527–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185x.12154
Lee PC, Chao Y, Chen MH, Lan KH, Lee IC, Hou MC, Huang YH (2020) Risk of HBV reactivation in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-treated unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-001072
Lemery S, Keegan P, Pazdur R (2017) First FDA approval agnostic of cancer site—when a biomarker defines the indication. N Engl J Med 377(15):1409–1412. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1709968
Lin Z, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Chen C, He LN, Li H et al (2022) Hepatotoxicity associated with PD-1 blockade antibodies in cancer patients co-infected with hepatitis B virus. Cancer Immunol Immunother 71(5):1247–1255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-03082-4
Loomba R, Liang TJ (2017) Hepatitis B reactivation associated with immune suppressive and biological modifier therapies: current concepts, management strategies, and future directions. Gastroenterology 152(6):1297–1309. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.009
Mori S, Fujiyama S (2015) Hepatitis B virus reactivation associated with antirheumatic therapy: risk and prophylaxis recommendations. World J Gastroenterol 21(36):10274–10289. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i36.10274
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S et al (2015) Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 373(19):1803–1813. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1510665
Naghavi M, Abajobir AA, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, Abera SF et al (2017) Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death 1980–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390(10100):1151–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9
Ng KYY, Wong LWJ, Ang AJS, Tan SH, Choo SP, Tai DW, Lee JJX (2020) Real-world efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: experience of a tertiary Asian Center. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.13454
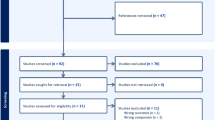
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n160. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n160
Peng G, Li S, Wu W, Tan X, Chen Y, Chen Z (2008) PD-1 upregulation is associated with HBV-specific T cell dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B patients. Mol Immunol 45(4):963–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.07.038
Pertejo-Fernandez A, Ricciuti B, Hammond SP, Marty FM, Recondo G, Rangachari D et al (2020) Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection. Lung Cancer 145:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.02.013
Radziewicz H, Ibegbu CC, Fernandez ML, Workowski KA, Obideen K, Wehbi M et al (2007) Liver-infiltrating lymphocytes in chronic human hepatitis C virus infection display an exhausted phenotype with high levels of PD-1 and low levels of CD127 expression. J Virol 81(6):2545–2553. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02021-06
Ramsey SD, Unger JM, Baker LH, Little RF, Loomba R, Hwang JP et al (2019) Prevalence of hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and HIV infection among patients with newly diagnosed cancer from academic and community oncology practices. JAMA Oncol 5(4):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.6437
Razavi-Shearer D, Gamkrelidze I, Nguyen MH, Chen DS, Damme PV, Abbas Z (2018) Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(6):383–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30056-6
Razavi-Shearer D, Gamkrelidze I, Nguyen MH, Chen DS, Van Damme P, Abbas Z, Abdulla M, Abou Rached A, Adda D, Aho I, Akarca U (2018) Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(6):383–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(18)30056-6
Reddy KR, Beavers KL, Hammond SP, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter YT (2015) American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology 148(1):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.039
Ricci AD, Rizzo A, Rojas Llimpe FL, Di Fabio F, De Biase D, Rihawi K (2021) Novel HER2-directed treatments in advanced gastric carcinoma: another paradigm shift? Cancers (Basel) 13(7):1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071664
Rizvi NA, Mazières J, Planchard D, Stinchcombe TE, Dy GK, Antonia SJ et al (2015) Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): a phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol 16(3):257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70054-9
Rizzo A, Ricci AD (2022) PD-L1, TMB, and other potential predictors of response to immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: how can they assist drug clinical trials? Expert Opin Investig Drugs 31(4):415–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2021.1972969
Rizzo A, Mollica V, Santoni M, Ricci AD, Rosellini M, Marchetti A et al (2021) Impact of clinicopathological features on survival in patients treated with first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors for renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Eur Urol Focus 8(2):514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2021.03.001
Saeidi A, Zandi K, Cheok YY, Saeidi H, Wong WF, Lee CYQ et al (2018) T-cell exhaustion in chronic infections: reversing the state of exhaustion and reinvigorating optimal protective immune responses. Front Immunol 9:2569. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02569
Smalls DJ, Kiger RE, Norris LB, Bennett CL, Love BL (2019) Hepatitis B virus reactivation: risk factors and current management strategies. Pharmacotherapy 39(12):1190–1203. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2340
Tapia Rico G, Chan MM, Loo KF (2020) The safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced cancers and pre-existing chronic viral infections (Hepatitis B/C, HIV): a review of the available evidence. Cancer Treat Rev 86:102011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102011
Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM et al (2018) Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 67(4):1560–1599. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29800
Trépo C, Chan HL, Lok A (2014) Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 384(9959):2053–2063. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60220-8
Watanabe T, Bertoletti A, Tanoto TA (2010) PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis virus infection. J Viral Hepat 17(7):453–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2010.01313.x
Wen X, Wang Y, Ding Y, Li D, Li J, Guo Y et al (2016) Safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors in Chinese patients with melanoma. Melanoma Res 26(3):284–289. https://doi.org/10.1097/cmr.0000000000000256
Wherry EJ, Kurachi M (2015) Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol 15(8):486–499. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3862
Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Rutkowski P, Grob JJ, Cowey CL et al (2017) Overall Survival with combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 377(14):1345–1356. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1709684
Wong GL, Wong VW, Hui VW, Yip TC, Tse YK, Liang LY et al (2021) Hepatitis flare during immunotherapy in patients with current or past hepatitis b virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol 116(6):1274–1283. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001142
Xu F, Zeng Z, Yan B, Fu Y, Sun Y, Yang G et al (2021) Safety and efficacy of anti-PD-1 inhibitors in Chinese patients with advanced lung cancer and hepatitis B virus infection: a retrospective single-center study. Transl Lung Cancer Res 10(4):1819–1828. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-21-79
Yamamoto A, Yano Y, Ueda Y, Yasutomi E, Hatazawa Y, Hayashi H et al (2021) Clinical features of immune-mediated hepatotoxicity induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147(6):1747–1756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03448-8
Yau T, Kang YK, Kim TY, El-Khoueiry AB, Santoro A, Sangro B et al (2020) Efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib: the checkmate 040 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.4564
Yoo S, Lee D, Shim JH, Kim KM, Lim YS, Lee HC et al (2021) Risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients treated with immunotherapy for anti-cancer treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2021.06.019
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Chen C, Fang W, Cai X, Zhang X et al (2019) Hepatitis B virus reactivation in cancer patients with positive Hepatitis B surface antigen undergoing PD-1 inhibition. J Immunother Cancer 7(1):322. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0808-5
Zhong L, Zhong P, Liu H, Li Z, Nie Q, Peng W (2021) Hepatitis B virus infection does not affect the clinical outcome of anti-programmed death receptor-1 therapy in advanced solid malignancies: real-world evidence from a retrospective study using propensity score matching. Medicine 100(49):e28113. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000028113
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82073200 and 81874178), Major basic research of Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR202105070027), Funds for Independent Cultivation of Innovative Team from Universities in Jinan (Grant No. 2020GXRC023), and the grants from the Taishan Scholars Program for Young Expert of Shandong Province (Grant No. tsqn20161064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.L. takes responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, from inception to published article. Z.N.D. and T.L. conceived and designed the study. Z.N.D., J.S.X. independently screened the full text of selected studies to confirm eligibility, assess quality, and extract data. Z.N.D., L.J.Y., G.X.M. and H.L. analyzed the data. Z.N.D., Z.Q.C. and J.G.H. visualize the results. Z.N.D., Y.C.Y., D.X.W. and T.L. wrote reviewed, and/or revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript, including the authorship list.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, ZN., Meng, GX., Xue, JS. et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibition: systematic review with meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 1993–2008 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04133-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04133-8