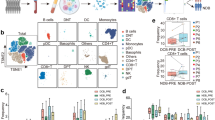
Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether TCF-1+PD-1+CD8+T cells are associated with the response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Methods
We investigated the expression of TCF-1+PD-1+CD8+T cells and elucidated their predictive role in NSCLC patients. Pretreatment specimens from 20 advanced NSCLC patients who underwent PD-1 immunotherapy or combined with chemotherapy were analyzed. The frequencies of TCF-1+ cells in PD-1+CD8+T cells were determined in these biospecimens using multi-label immunofluorescence staining and multi-spectral acquisition technology. The clinical roles of TCF-1+PD-1+CD8+T cells were assessed via analyzing our cases and human NSCLC data collected from public databases.
Results
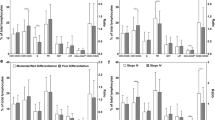
A high frequency of TCF-1+PD-1+CD8+T cells was identified in responders compared with non-responders (p = 0.0024), and the patients with high expression of this cell subset had durable clinical benefit of anti-PD-1 therapy. There were no significant association between the expression of TCF-1+PD-1+CD8+T cells and patients’ age, smoking history, pathologic type, and genetic status. In univariate analysis by the Cox hazard model, high frequency of TCF-1+ PD-1+ CD8+T cells was significantly correlated with patients’ benefit of PD-1 blockade (p = 0.024).
Conclusion
Our study indicated that TCF-1+PD-1+CD8+T cells are associated with the response to PD-1 blockade, and may be a predictor of anti-PD-1 therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The code was analyzed for bioinformation available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahn BC, Pyo KH, Xin CF, Jung D, Shim HS, Lee CY, Park SY, Yoon HI, Hong MH, Cho BC, Kim HR (2019) Comprehensive analysis of the characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 therapy in real-world practice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145:1613–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02899-y
Balatoni T, Mohos A, Papp E, Sebestyén T, Liszkay G, Oláh J, Varga A, Lengyel Z, Emri G, Gaudi I, Ladányi A (2018) Tumor-infiltrating immune cells as potential biomarkers predicting response to treatment and survival in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving ipilimumab therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 67:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-2072-1
Champiat S, Dercle L, Ammari S, Massard C, Hollebecque A, Postel-Vinay S, Chaput N, Eggermont A, Marabelle A, Soria JC, Ferté C (2017) Hyperprogressive disease is a new pattern of progression in cancer patients treated by anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin Cancer Res 23:1920–1928. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1741
Fang X, Chen C, Xia F, Yu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Gu H, Wan J, Zhang X, Weng W, Zhang CC, Chen GQ, Liang A, Xie L, Zheng J (2016) CD274 promotes cell cycle entry of leukemia-initiating cells through JNK/Cyclin D2 signaling. J Hematol Oncol 9:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0350-6
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F et al (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:2078–2092. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1801005
Ganesh K, Massagué J (2018) TGF-β Inhibition and Immunotherapy: checkmate. Immunity 48:626–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.037
Held W, Siddiqui I, Schaeuble K, Speiser DE (2019) Intratumoral CD8+ T cells with stem cell-like properties: Implications for cancer immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med 11:eaay6863. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmedaay6863
Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387:1540–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7
Hwang S, Kwon AY, Jeong JY, Kim S, Kang H, Park J et al (2020) Immune gene signatures for predicting durable clinical benefit of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 10:643. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57218-9
Isaacsson Velho P, Antonarakis ES (2018) PD-1/PD-L1 pathway inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 11:475–486. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2018.1464388
Jansen CS, Prokhnevska N, Master VA, Sanda MG, Carlisle JW, Bilen MA et al (2019) An intra-tumoral niche maintains and differentiates stem-like CD8 T cells. Nature 576:465–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1836-5
Kammerer-Jacquet SF, Deleuze A, Saout J, Mathieu R, Laguerre B, Verhoest G, Dugay F, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Bensalah K, Rioux-Leclercq N (2019) Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 20:1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071692
Kim JY, Lee KH, Kang J, Borcoman E, Saada-Bouzid E, Kronbichler A et al (2019) Hyperprogressive Disease during Anti-PD-1 (PDCD1) / PD-L1 (CD274) therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (basel) 11:1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111699
Mariathasan S, Turley SJ, Nickles D, Castiglioni A, Yuen K, Wang Y et al (2018) TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 554:544–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25501
Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, Kowalski DM, Cho BC, Turna HZ et al (2019) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEY-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 393:1819–1830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32409-7
Paz-Ares L, Luft A, Vicente D, Tafreshi A, Gümüş M, Mazières J et al (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 379:2040–2051. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1810865
Siddiqui I, Schaeuble K, Chennupati V, Fuertes Marraco SA, Calderon-Copete S, Pais Ferreira D et al (2019) Intratumoral Tcf1+PD-1+CD8+ T cells with stem-like properties promote tumor control in response to vaccination and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Immunity 50:195-211.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.021
Sui H, Ma N, Wang Y, Li H, Liu X, Su Y, Yang J (2018) Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: toward personalized medicine and combination strategies. J Immunol Res 2018:6984948. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6984948
Tanaka Y, Matsubara O, Asada K, Muramatsu A, Suzuki M, Shirai T (2019) Hyperprogressive disease after treatment with pembrolizumab in lung adenocarcinoma: an autopsy case study. Respir Med Case Rep 28:100885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.100885
Tsai KK, Zarzoso I, Daud AI (2019) PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies for melanoma. Hum Vaccin Immunother 10:3111–3116. https://doi.org/10.4161/21645515.2014.983409
Wartewig T, Kurgyis Z, Keppler S, Pechloff K, Hameister E, Öllinger R, Maresch R, Buch T, Steiger K, Winter C, Rad R, Ruland J (2017) PD-1 is a haploinsufficient suppressor of T cell lymphomagenesis. Nature 552:121–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24649
Wu SP, Liao RQ, Tu HY, Wang WJ, Dong ZY, Huang SM et al (2018) Stromal PD-L1-positive regulatory T cells and PD-1-Positive CD8-positive t cells define the response of different subsets of non-small cell lung cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol 13:521–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.11.132
Wu Y, Zhang L, Fan Y, Zhou J, Zhang L, Zhou Q et al (2019) KEYNOTE-042 China study: first-line pembrolizumab vs chemotherapy in chinese patients with advanced nsclc with pd-l1 tps >=1%. J Thorac Oncol 14:s290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.08.584
Xia L, Liu Y, Wang Y (2019) PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: current status and future directions. Oncologist 24:S31–S41. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-IO-S1-s05
Xiong D, Wang Y, Singavi AK, Mackinnon AC, George B, You M (2018) Immunogenomic landscape contributes to hyperprogressive disease after Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy for cancer. iScience 9:258–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2018.10.021
Yaghoubi N, Soltani A, Ghazvini K, Hassanian SM, Hashemy SI (2019) PD-1/ PD-L1 blockade as a novel treatment for colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 110:312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.105
Acknowledgements
We thank Yudong Zhang and Jun Gu (Department of pathology, Shanghai Tongji Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine) for their kind assistant of pathological experiment.
Funding
This study was supported by the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2020M671233), the Youth Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (82103412), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600043, 81800063), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (16ZR1432100, 19ZR1448500), and Shanghai Health Bureau Key Special Fund for Medicine (20134034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XF, SG, XY, and LZ contributed to the conception of the study and manuscript preparation. GW, JH, NW, and PZ contributed to analyze the clinical data. XZ, MC, HZ, TD, and YZ contributed to collect and perform the bioinformation. LZ and YL contributed to the preparation of pathological sections.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethic committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine.
Consent for publication
All subjects were informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2021_3845_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file1 Deconvolution analysis of transcriptomes from human NSCLC with different response to PD-1 blockade (GSE145896) (DOCX 22 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, X., Wu, G., Hua, J. et al. TCF-1+ PD-1+ CD8+T cells are associated with the response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 2653–2660 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03845-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03845-7