Abstract
Background
ZMYND8 (Zinc finger MYND (Myeloid, Nervy and DEAF-1)-type containing 8) has been known to play an important role in tumor regulation in various types of cancer. However, the results of ZMYND8 expression and their clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not yet been published. In the present study, we investigate the expression of ZMYND8 protein and mRNA in HCC and elucidate its prognostic significance.
Methods
ZMYND8 protein and mRNA expression in 283 and 234 HCCs were investigated using immunohistochemistry and microarray gene expression profiling data. The relationships between ZMYND8 expression with clinicopathologic features and prognosis of HCC patients were evaluated. Furthermore, we performed the invasion, migration, apoptosis, soft agar formation assay and sphere formation assay in HCC cell lines, and evaluated tumorigenicity in a nude mouse model, after ZMYND8 knockdown.
Results
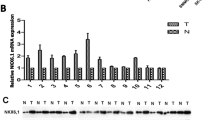
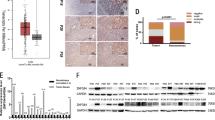
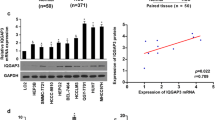
Overexpression of ZMYND8 protein and mRNA was observed in 20.5% and 26.9% of HCC cases, respectively. High ZMYND8 expression showed significant correlations with microvascular invasion, high Edmondson grade, advanced American Joint Committee on Cancer, and increased alpha-fetoprotein level. ZMYND8 mRNA overexpression was an independent prognostic factor for predicting early recurrence as well as short recurrence-free survival (RFS). Downregulation of ZMYND8 reduced migration and invasion of HCC cells, and promoted apoptosis of HCC cells in an in vitro model. In a xenograft nude mouse model, knockdown of ZMYND8 significantly reduced tumor growth.
Conclusion
ZMYND8 mRNA overexpression could be a prognostic marker of shorter RFS in HCC patients after curative resection. ZMYND8 might play an important role in the proliferation and progression of HCC and could be a promising candidate for targeted therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All datasets used and analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- ZMYND8:
-
Zinc finger MYND (Myeloid, Nervy and DEAF-1)-type containing 8
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- AFP:
-
α-Fetoprotein
- HPFs:
-
High-power fields
- AJCC:
-
American Joint Committee on Cancer
- BCLC:
-
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
- DSS:
-
Disease-specific survival
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- FDR:
-
False Discovery Rate
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- GEPIA:
-
Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- RACK:
-
Receptor for activated C-kinase
- PKCβ1:
-
Protein-kinase-C beta I
- ATRA:
-
All-trans retinoic acid
References
Basu M, Khan MW, Chakrabarti P, Das C (2017a) Chromatin reader ZMYND8 is a key target of all trans retinoic acid-mediated inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1860(4):450–459
Basu M, Sengupta I, Khan MW, Srivastava DK, Chakrabarti P, Roy S et al (2017b) Dual histone reader ZMYND8 inhibits cancer cell invasion by positively regulating epithelial genes. Biochem J 474(11):1919–1934
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang Y-H, Bodoky G et al (2017) Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet 389(10064):56–66
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-Tile. A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7252–7259
Chen C, Lou T (2017) Hypoxia inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 8(28):46691–46703
Chen Y, Zhang B, Bao L, Jin L, Yang M, Peng Y et al (2018a) ZMYND8 acetylation mediates HIF-dependent breast cancer progression and metastasis. J Clin Invest 128(5):1937–1955
Chen Y, Wang Y, Luo W (2018b) ZMYND8 is a primary HIF coactivator that mediates breast cancer progression. Mol Cell Oncol 5(4):e1479619
Chen J, Liu J, Chen X, Li Y, Li Z, Shen C et al (2019) Low expression of ZMYND8 correlates with aggressive features and poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 11:7835–7843
Chen J, He Q, Wu P, Fu J, Xiao Y, Chen K et al (2020) ZMYND8 expression combined with pN and pM classification as a novel prognostic prediction model for colorectal cancer: Based on TCGA and GEO database analysis. Cancer Biomark 28(2):201–211
Cho J, Kim KM, Kim HC, Lee WY, Kang WK, Park YS et al (2019) The prognostic role of tumor associated glycoprotein 72 (TAG-72) in stage II and III colorectal adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 215(1):171–176
Edge S, Byrd D, Compton C, Fritz A, Greene F, Trotti IA (2010) AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th edn. Springer, Chicago
Edmondson H, Steiner P (1954) Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer 7:462–503
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C et al (2017) Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. The Lancet 389(10088):2492–2502
Fossey SC, Kuroda S, Price JA, Pendleton JK, Freedman BI, Bowden DW (2000) Identification and characterization of PRKCBP1, a candidate RACK-like protein. Mamm Genome 11(10):919–925
Gong F, Miller KM (2018) Double duty: ZMYND8 in the DNA damage response and cancer. Cell Cycle 17(4):414–420
Gong F, Chiu LY, Cox B, Aymard F, Clouaire T, Leung JW et al (2015) Screen identifies bromodomain protein ZMYND8 in chromatin recognition of transcription-associated DNA damage that promotes homologous recombination. Genes Dev 29(2):197–211
Gong F, Clouaire T, Aguirrebengoa M, Legube G, Miller KM (2017) Histone demethylase KDM5A regulates the ZMYND8-NuRD chromatin remodeler to promote DNA repair. J Cell Biol 216(7):1959–1974
Ha SY, Choi M, Lee T, Park CK (2016) The Prognostic role of Mitotic Index in Hepatocellular Carcinoma patients after curative hepatectomy. Cancer Res Treat 48(1):180–189
Hoshida Y, Villanueva A, Kobayashi M, Peix J, Chiang DY, Camargo A et al (2008) Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(19):1995–2004
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S et al (2003) Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol 38(2):200–207
Inagaki Y, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Yada T, Tameda M, Ogura S et al (2016) Epigenetic regulation of proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by CBP/p300 histone acetyltransferase activity. Int J Oncol 48(2):533–540
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han K-H, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F et al (2018) Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. The Lancet 391(10126):1163–1173
Kuroyanagi J, Shimada Y, Zhang B, Ariyoshi M, Umemoto N, Nishimura Y et al (2014) Zinc finger MYND-type containing 8 promotes tumour angiogenesis via induction of vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression. FEBS Lett 588(18):3409–3416
Li M, Luo RZ, Chen JW, Cao Y, Lu JB, He JH et al (2011) High expression of transcriptional coactivator p300 correlates with aggressive features and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med 9:5
Li N, Li Y, Lv J, Zheng X, Wen H, Shen H et al (2016) ZMYND8 Reads the Dual Histone Mark H3K4me1-H3K14ac to antagonize the expression of metastasis-linked genes. Mol Cell 63(3):470–484
Lim HY, Sohn I, Deng S, Lee J, Jung SH, Mao M et al (2013) Prediction of disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Ann Surg Oncol 20(12):3747–3753
Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan (2003) The general rules for the clinical and pathological study of primary liver cancer, 2nd edn. Tokyo, Kanahara
Llovet JM, Bru C, Bruix J (1999) Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: the BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis 19(3):329–338
Ma L, Li G, Zhu H, Dong X, Zhao D, Jiang X et al (2014) 2-Methoxyestradiol synergizes with sorafenib to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma by simultaneously dysregulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and -2. Cancer Lett 355(1):96–105
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF, Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J et al (2003) PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet 34(3):267–273
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S, Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GA et al (2006) Early and late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg 243(2):229–235
Qin LX, Tang ZY (2004) Recent progress in predictive biomarkers for metastatic recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of the literature. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130(9):497–513
Remmele W, Stegner HE (1987) Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 8(3):138–140
Shen H, Xu W, Guo R, Rong B, Gu L, Wang Z et al (2016) Suppression of enhancer overactivation by a RACK7-histone demethylase complex. Cell 165(2):331–342
Sherman M (2008) Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(19):2045–2047
Shimada M, Hamatsu T, Yamashita Y, Rikimaru T, Taguchi K, Utsunomiya T et al (2001) Characteristics of multicentric hepatocellular carcinomas: comparison with intrahepatic metastasis. World J Surg 25(8):991–995
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(43):15545–15550
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102
Wang Y, Luo M, Chen Y, Wang Y, Zhang B, Ren Z et al (2020) ZMYND8 expression in breast cancer cells blocks T-lymphocyte surveillance to promote tumor growth. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1710
Xiang ZL, Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, He J, Zeng HY et al (2012) The expression of HIF-1alpha in primary hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with radiotherapy response and clinical outcome. Mol Biol Rep 39(2):2021–2029
Yeo S-Y, Lee K-W, Shin D, An S, Cho K-H, Kim S-H (2018) A positive feedback loop bi-stably activates fibroblasts. Nat Commun 9(1):1–16
Yu H, Jiang Y, Liu L, Shan W, Chu X, Yang Z et al (2017) Integrative genomic and transcriptomic analysis for pinpointing recurrent alterations of plant homeodomain genes and their clinical significance in breast cancer. Oncotarget 8(8):13099–13115
Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S, Ogasawara S, Palmer D et al (2018) Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 19(7):940–952
Funding
This study was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2017R1C1B5017890 and NRF-2018R1C1B6006428).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC performed data analysis, generated tables and figures, and drafted the manuscript. KWL performed in vitro and in vivo assays, analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. HHK analyzed data. SP, SYY, JWJ, MSC supported data acquisition. SHK and CKP contributed to knowledge. SYH conceptualized and designed the study, collected and analyzed the data, drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All contributing authors have no financial support relevant to this article and no competing interests to declare.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The Institutional Review Board of Samsung Medical Center approved this study and waived informed consent for this study.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to publish the article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S., Lee, KW., Koh, H.H. et al. Validation of ZMYND8 as a new treatment target in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 3517–3534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03768-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03768-3