Abstract
Purpose
This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the combined effect of anti-PD-1 inhibitor and nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab)-paclitaxel for refractory melanoma among Chinese patients.
Methods
Data from January 2018 to March 2021 were retrospectively collected and analyzed. Sixty-four patients were eligible for analysis from a single Chinese cancer center.
Results
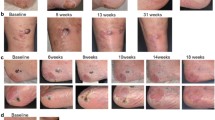
The median follow-up was 16.0 months at data cutoff. The objective response rate (ORR) was 29.7%, and the disease control rate (DCR) was 67.2% in all patients. Treatment-naïve patients had significantly higher ORR than pretreated patients (42.9% vs 13.8%, p = 0.011). Cutaneous melanoma patients with NRAS gene mutation benefited more than non-mutated patients (DCR of 100% vs. 54.5%) (p = 0.030). The median progression-free survival (mPFS) of all patients was 5.2 months and the duration of response was 10.8 months. Median duration of disease control was 7.7 months. Prior treatment-naïve patients had significantly longer PFS than those who accepted prior treatments (7.2 vs. 5.1 months, p = 0.024). Patients with abnormally high LDH level had shorter mPFS (3.6 months vs. 6.6 months, p = 0.020). Median overall survival was not reached in this study. Most patients experienced adverse events (AEs), but only 17.2% of patients experienced grade 3 severe AEs. The most common AEs were alopecia (89.1%), neutropenia (18.8%), pruritus (15.6%), and arthralgia (14.1%). Some patients had immune related AEs (irAEs). No grade 4 or 5 AEs were observed. Patients with ≥ 3 AEs or with irAEs had longer mPFS (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Nab-paclitaxel combined with PD-1 antibody is a well-tolerated and effective regimen for Chinese patients with refractory melanoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AEs:
-
Adverse events
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- BRAF:
-
V-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CR:
-
Complete response
- DCR:
-
Disease control rate
- DDC:
-
Duration of disease control
- ECOG:
-
Eastern cooperative oncology group
- ICIs:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MDM2:
-
Murine double minute 2
- NRAS:
-
Neuroblastoma rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog
- ORR:
-
Objective response rate
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death protein 1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death-ligand 1
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- RECIST:
-
Response evaluation criteria
- PR:
-
Partial response
- SD:
-
Stable disease
- TMB:
-
Tumor mutation burden
- ULN:
-
Upper limits of normal
References
Bracci L, Schiavoni G, Sistigu A, Belardelli F (2014) Immune-based mechanisms of cytotoxic chemotherapy: implications for the design of novel and rationale-based combined treatments against cancer. Cell Death Differ 21:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.67
Champiat S, Dercle L, Ammari S, Massard C, Hollebecque A, Postel-Vinay S (2017) Hyperprogressive disease is a new pattern of progression in cancer patients treated by Anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin Cancer Res 23:1920–1928. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1741
Chi Z, Li S, Sheng X, Si L, Cui C, Han M (2011) Clinical presentation, histology, and prognoses of malignant melanoma in ethnic Chinese: a study of 522 consecutive cases. BMC Cancer 11:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-85
Desai N, Trieu V, Yao Z, Louie L, Ci S, Yang A (2006) Increased antitumor activity, intratumor paclitaxel concentrations, and endothelial cell transport of cremophor-free, albumin-bound paclitaxel, ABI-007, compared with cremophor-based paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 12:1317–1324. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1634
Garbe C, Eigentler TK, Keilholz U, Hauschild A, Kirkwood JM (2011) Systematic review of medical treatment in melanoma: current status and future prospects. Oncologist 16:5–24. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0190
Gardner ER, Dahut WL, Scripture CD, Jones J, Aragon-Ching JB, Desai N (2008) Randomized crossover pharmacokinetic study of solvent-based paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 14:4200–4205. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4592
Garnett CT, Schlom J, Hodge JW (2008) Combination of docetaxel and recombinant vaccine enhances T-cell responses and antitumor activity: effects of docetaxel on immune enhancement. Clin Cancer Res 14:3536–3544. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4025
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu WJ, Kefford R (2013) Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N Engl J Med 369:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1305133
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu WJ, Kefford R (2019) Five-year survival outcomes for patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-001. Ann Oncol 30:582–588. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz011
Hodge JW, Garnett CT, Farsaci B, Palena C, Tsang KY, Ferrone S (2013) Chemotherapy-induced immunogenic modulation of tumor cells enhances killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and is distinct from immunogenic cell death. Int J Cancer 133:624–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28070
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1003466
Karimkhani C, Green AC, Nijsten T, Weinstock MA, Dellavalle RP, Naghavi M (2017) The global burden of melanoma: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Br J Dermatol 177:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15510
Kato S, Goodman A, Walavalkar V, Barkauskas DA, Sharabi A, Kurzrock R (2017) Hyperprogressors after Immunotherapy: analysis of genomic alterations associated with accelerated growth rate. Clin Cancer Res 23:4242–4250. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3133
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Lao CD (2019) Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 381:1535–1546. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1910836
Ng HY, Li J, Tao L, Lam AK, Chan KW, Ko JMY (2018) Chemotherapeutic treatments increase PD-L1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through EGFR/ERK activation. Transl Oncol 11:1323–1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2018.08.005
Paz-Ares L, Luft A, Vicente D, Tafreshi A, Gumus M, Mazieres J (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 379:2040–2051. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1810865
Perlstein D, Shlagman O, Kogan Y, Halevi-Tobias K, Yakobson A, Lazarev I (2019) Personal response to immune checkpoint inhibitors of patients with advanced melanoma explained by a computational model of cellular immunity, tumor growth, and drug. PLoS ONE 14:e0226869. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226869
Robert C, Long GV, Brady B, Dutriaux C, Maio M, Mortier L (2015) Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N Engl J Med 372:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1412082
Rossi E, Schinzari G, Maiorano BA, Indellicati G, Di Stefani A, Pagliara MM (2020) Efficacy of i- mmune checkpoint inhibitors in different types of melanoma. Hum Vaccin Immunother: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2020.1771986
Si L, Zhang X, Shu Y, Pan H, Wu D, Liu J (2019) A phase Ib study of pembrolizumab as second-line therapy for chinese patients with advanced or metastatic melanoma (KEYNOTE-151). Transl Oncol 12:828–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2019.02.007
Soliman HH (2017) nab-Paclitaxel as a potential partner with checkpoint inhibitors in solid tumors. Onco Targets Ther 10:101–112. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S122974
Tang B, Chi Z, Chen Y, Liu X, Wu D, Chen J (2020) Safety, efficacy, and biomarker analysis of toripalimab in previously treated advanced melanoma: results of the POLARIS-01 multicenter phase II trial. Clin Cancer Res 26:4250–4259. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3922
Tumeh PC, Hellmann MD, Hamid O, Tsai KK, Loo KL, Gubens MA (2017) Liver metastasis and treatment outcome with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody in patients with melanoma and NSCLC. Cancer Immunol Res 5:417–424. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0325
Tyrrell H, Payne M (2018) Combatting mucosal melanoma: recent advances and future perspectives. Melanoma Manag 5:MMT11. https://doi.org/10.2217/mmt-2018-0003
Ugurel S, Paschen A, Becker JC (2013) Dacarbazine in melanoma: from a chemotherapeutic drug to an immunomodulating agent. J Invest Dermatol 133:289–292. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.341
Zhang P, Su DM, Liang M, Fu J (2008) Chemopreventive agents induce programmed death-1-ligand 1 (PD-L1) surface expression in breast cancer cells and promote PD-L1-mediated T cell apoptosis. Mol Immunol 45:1470–1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.08.013
Zhang F, Huang D, Li T, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhang Y (2020) Anti-PD-1 therapy plus chemotherapy and/or bevacizumab as second line or later treatment for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer 11:741–749. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.37966
Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G (2013) Mechanism of action of conventional and targeted anticancer therapies: reinstating immunosurveillance. Immunity 39:74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.06.014
Acknowledgements
No.
Funding
This study was funded by the Foundation of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center for Distinguished Young Scholar (grant number: PT04180201), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 81802725) and Foundation of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (grant number: Y-SY201901-0247).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X-sZ: study design and concepts. J-jL, J-hW, YD, D-dL, X-zW, J-jZ, HJ, XL, F-xH: data acquisition. J-jL, J-hW, YD: quality control of data, algorithms, data analysis, and interpretation. J-jL, J-hW: statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, and manuscript editing. J-jL, J-hW and YD contribute equally to this article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all authors and participants in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Jj., Wang, Jh., Dingv, Y. et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1 inhibitor combined with nab-paclitaxel in Chinese patients with refractory melanoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 1159–1169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03700-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03700-9