Abstract
Purpose
1% of all breast cancer cases occur in men. There are significant differences regarding clinical behaviour and genetic profiles between female (FBC) and male breast cancer (MBC). Parameters for decision-making on treatment and prognosis are derived from FBC. Ki67 has a high value as a prognostic and predictive factor in FBC, but accurate Ki67 cut-off points for MBC are missing. In this study, we aimed to evaluate adequate examination methods and reliable cut-off points for Ki67 to assess the highest prognostic value for patient’s overall survival (OS).
Methods
In this multicentric retrospective study, histological specimens were obtained from 104 male patients who were diagnosed and treated for primary invasive breast cancer. We applied three methods of Ki67 analysis: Tumor average scoring (TA), tumor border scoring (TB) and hot-spot scoring (HS). Calculated Ki67 cut-off points for each method were assessed as a threshold for patients’ overall survival (OS).
Results
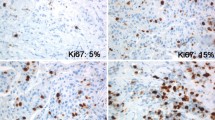
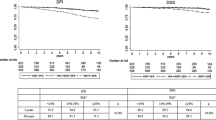
Ki67 cut-off points were 13.5 for the TA group, 22.5 for the HS group and 17.5 for the TB group. Only Ki67 TA cut-off calculations demonstrated statistical significance (p = 0.04). Ki67 expression analysis of TA showed that more than 90% of patients with low Ki67 levels (< 13.5) were alive after 5-year follow-up.
Conclusion
Our findings demonstrate that determination of Ki67 expression in TA is the most reliable to define a cut-off point with high prognostic value. A Ki67 cut-off point of 13.5 shows highest statistical power to define luminal A subgroup and OS.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data and material are available on request.
References
Bustreo S et al (2016) Optimal Ki67 cut-off for luminal breast cancer prognostic evaluation: a large case series study with a long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat 157:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-3817-9
Cardoso F et al (2018) Characterization of male breast cancer: results of the EORTC 10085/TBCRC/BIG/NABCG International Male Breast Cancer Program. Ann Oncol 29:405–417. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx651
Cheang MC et al (2009) Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:736–750. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djp082
Coates AS et al (2015) Tailoring therapies–improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol 26:1533–1546. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv221
Denkert C et al (2013) Ki67 levels as predictive and prognostic parameters in pretherapeutic breast cancer core biopsies: a translational investigation in the neoadjuvant GeparTrio trial. Ann Oncol 24:2786–2793. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt350
Dowsett M et al (2011) Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer working group. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:1656–1664. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djr393
Giordano SH et al (2004) Breast carcinoma in men: a population-based study. Cancer 101:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20312
Goldhirsch A et al (2013) Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol 24:2206–2223. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt303
Hassett MJ et al (2020) Management of male breast cancer: ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.03120
Hoon Tan P et al (2020) The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the breast. Histopathology. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.14091
International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working G (2021) International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. https://www.ki67inbreastcancerwg.org/. Accessed 21 Mar 2021
Jylling AMB, Jensen V, Lelkaitis G, Christiansen P, Nielsen SS, Lautrup MD (2020) Male breast cancer: clinicopathological characterization of a National Danish cohort 1980–2009. Breast Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-020-01066-3
Krebsregisterdaten Zf (2020) Datenabfrage (2020). https://www.krebsdaten.de/Krebs/SiteGlobals/Forms/Datenbankabfrage/datenbankabfrage_stufe2_form.html. Accessed 17 January 2020
Leon-Ferre RA et al (2018) A contemporary review of male breast cancer: current evidence and unanswered questions. Cancer Metastasis Rev 37:599–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-018-9761-x
Leung SCY et al (2019) Analytical validation of a standardised scoring protocol for Ki67 immunohistochemistry on breast cancer excision whole sections: an international multicentre collaboration. Histopathology 75:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.13880
Losurdo A et al (2017) Controversies in clinicopathological characteristics and treatment strategies of male breast cancer: a review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 113:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.013
Maranta AF, Broder S, Fritzsche C, Knauer M, Thurlimann B, Jochum W, Ruhstaller T (2020) Do YOU know the Ki-67 index of your breast cancer patients? Knowledge of your institution’s Ki-67 index distribution and its robustness is essential for decision-making in early breast cancer. Breast 51:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2020.03.005
Masci G et al (2015) Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics in male breast cancer: a retrospective case series. Oncologist 20:586–592. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0243
Nielsen TO et al (2020) Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: updated recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djaa201
Nilsson C et al (2013) Molecular subtyping of male breast cancer using alternative definitions and its prognostic impact. Acta Oncol 52:102–109. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2012.711952
Piccart-Gebhart MJ et al (2005) Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:1659–1672. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa052306
Rakha EA et al (2010) Breast cancer prognostic classification in the molecular era: the role of histological grade. Breast Cancer Res 12:207. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr2607
Remmele W, Stegner HE (1987) Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 8:138–140
Rudlowski C et al (2004) Her-2/neu gene amplification and protein expression in primary male breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 84:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BREA.0000019953.92921.7e
Rudlowski C et al (2006) Comparative genomic hybridization analysis on male breast cancer. Int J Cancer 118:2455–2460. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21646
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Vermeulen MA et al (2017) Pathological characterisation of male breast cancer: results of the EORTC 10085/TBCRC/BIG/NABCG International Male Breast Cancer Program. Eur J Cancer 82:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.01.034
von Minckwitz G et al (2013) Ki67 measured after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:4521–4531. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3628
Williams AD, McGreevy CM, Tchou JC, De La Cruz LM (2020) Utility of oncotype DX in male breast cancer patients and impact on chemotherapy administration: a comparative study with female patients. Ann Surg Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-08473-y
Wittekind C (2012) Lymph nodes, tumour deposits, and TNM: are we getting better? 7th edition of UICC 2010 TNM classification of malignant tumors. Strahlenther Onkol 188:191–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-011-0032-9
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Guido Luechters, Center of Development Research, University Bonn, Germany and Mr. Bernardo Erices for supporting the statistical calculations.
Funding
This work was supported by the German Cancer Foundation (Project Number: 70-3157).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors disclose any financial and personal relationships with other people or organisations that could inappropriately influence (bias) our work. They have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The patient data, histopathological findings as well as treatment reports and follow-up data were collected with the approval of the appropriate institutional review boards from the hospital archives. The study was approved by the institutional local ethics committee. Data were blinded for statistical evaluations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erices-Leclercq, M., Lubig, S., Förster, F. et al. Prognostic relevance of Ki67 expression in primary male breast cancer: determination of cut-off points by different evaluation methods and statistical examinations. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 441–447 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03623-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03623-5