Abstract
Background
The safety and efficacy of transbronchial microwave ablation (TMA) therapy in patients with malignant central airway obstruction (CAO) with respiratory failure remains unclear.
Methods
A total of 38 patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or lung metastases with malignant endoluminal obstruction received TMA therapy under moderate sedation and high fractions of inspired oxygen (FiO2). The success rate of airway patency restoration, complication rate, and overall survival time (OS) from the initiation of TMA therapy were compared in the following two groups of patients with malignant CAO patients: the group with respiratory failure (PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300) (RF group, n = 10) and the group without respiratory failure (PaO2/FiO2 > 300) (non-RF group, n = 28) at the time of the TMA therapy.
Results
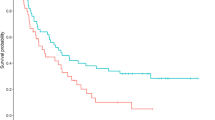
Both the RF group and non-RF group received a median of two sessions of TMA. There was no significant difference in the percentage of patients who showed restored airway patency after the first session of TMA (90% vs. 96%), in the complication rate of TMA therapy (10% vs. 11%), or in the OS (7.1 months vs. 9.1 months) between the RF group and the non-RF group. Multivariate analysis identified no significant association between TMA therapy and the risk of death in malignant CAO patients with respiratory failure (p = 0.196).
Conclusion
TMA therapy under moderate sedation was well tolerated and effective in patients with malignant CAO, including those with respiratory failure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolliger CT, Mathur PN (2002) ERS/ATS statement on interventional pulmonology. Eur Respir J 19(2):356–373
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 40(5):373–383
Chhajed PN, Baty F, Pless M, Somandin S, Tamm M, Brutsche MH (2006) Outcome of treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer with and without central airway obstruction. Chest 130(6):1803–1807
Daneshvar C et al (2019) Prevalence and outcome of central airway obstruction in patients with lung cancer. BMJ Open Respir Res 6(1)
Ernst A, Feller-Kopman D, Becker HD, Mehta AC (2004) Central airway obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169(12):1278–1297
Han CC, Prasetyo D, Wright GM (2007) Endobronchial palliation using Nd:YAG laser is associated with improved survival when combined with multimodal adjuvant treatments. J Thorac Oncol 2(1):59–64
Lubner MG, Brace CL, Hinshaw JL, Lee FT (2010) Microwave tumor ablation: mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21(SUPPL 8):S192–S203
Mahmood K et al (2015) Therapeutic bronchoscopy improves spirometry, quality of life, and survival in central airway obstruction. Respiration 89(5):404–413
Mudambi L, Miller R, Eapen GA (2017) Malignant central airway obstruction. J Thoracic Dis 9(Suppl 10):S1087–S1110 (AME Publishing Company)
Murgu S, Langer S, Colt H (2012) Bronchoscopic intervention obviates the need for continued mechanical ventilation in patients with airway obstruction and respiratory failure from inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Respiration 84(1):55–61
Ost DE et al (2015a) Complications following therapeutic bronchoscopy for malignant central airway obstruction: results of the AQuIRE registry. Chest 148(2):450–471
Ost DE et al (2015b) Therapeutic bronchoscopy for malignant central airway obstruction: success rates and impact on dyspnea and quality of life. Chest 147(5):1282–1298
Shin B, Chang B, Kim H, Jeong BH (2018) Interventional bronchoscopy in malignant central airway obstruction by extra-pulmonary malignancy. BMC Pulm Med 18(1):46
Stephens KE, Wood DE (2000) Bronchoscopic management of central airway obstruction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 119(2):289–296
Stratakos G et al (2016) Survival and quality of life benefit after endoscopic management of malignant central airway obstruction. J Cancer 7(7):794–802
Verma A et al (2018) Outcome of advanced lung cancer with central airway obstruction versus without central airway obstruction. ERJ Open Res 4(2):00173–02017
Verma A et al (2019) Outcome differences between recanalized malignant central airway obstruction from endoluminal disease versus extrinsic compression. Lasers Med Sci 34(5):955–962
Wolf FJ, Grand DJ, Machan JT, DiPetrillo TA, Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE (2008) Microwave ablation of lung malignancies: effectiveness, CT findings, and safety in 50 patients. Radiology 247(3):871–879
Funding
No funding was received from any source for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down by the institutional and/or national research committees and were in compliance with the principle of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashiwabara, K., Fujii, S., Tsumura, S. et al. Efficacy and safety of transbronchial microwave ablation therapy under moderate sedation in malignant central airway obstruction patients with respiratory failure: a single-institution retrospective study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 2751–2757 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03560-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03560-3