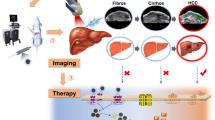
Abstract
Purpose
Presently, liver cancer is still one of the malignant tumors with high mortality. As far as the treatment of liver cancer is concerned, the most effective method is still liver transplantation. But every year, many liver cancer patients die from the lack of a proper liver transplant, or from waiting for a liver transplant. Therefore, it is very important to find new and effective treatment for patients with liver cancer.
Methods
Herein, the cell model and the orthotropic liver tumor mice model have been performed to verify the results of our treatment. We found that the in situ synthesized gold nanocluster–PTEN (GNC–PTEN) complexes can effectively target and realize the fluorescence imaging of the liver tumor.
Results
GNC–PTEN complexes could inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of liver cancer cells. And the results also showed that GNC–PTEN complexes could be well targeted liver tumor at 6 h and the liver tumor in mice group treated with GNC–PTEN complexes almost disappeared.
Conclusion
This is a simply and effectively method to realize liver cancer imaging and inhibition. This may raise the possibility for the accurate image/diagnosis and simultaneously efficient treatment of liver cancer in the relevant clinic application.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed Z, Beik J, Laurent S et al (2019) Iron oxide–gold core–shell nano-theranostic for magnetically targeted photothermal therapy under magnetic resonance imaging guidance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145:1213–1219
Brackenbury WJ, Djamgoz M (2007) Nerve growth factor enhances voltage-gated Na+ channel activity and Transwell migration in Mat-LyLu rat prostate cancer cell line. J Cell Physiol 210:602–608
Cabreara R, Tu Z, Firpi RJ et al (2003) An immunomodulatory role for CD4+ CD25+ T lymphocytes in hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology 124:A710
Chai Y, Xiaoyu L, Haiyan W (2017) Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the clinical features of HBsAg-positive liver cancer. J BUON 22:942
Chen JF, Wu P, Xia R et al (2018) STAT3-induced lncRNA HAGLROS overexpression contributes to the malignant progression of gastric cancer cells via mTOR signal-mediated inhibition of autophagy. Mol Cancer 17:6
Du T, Zhao C, Ur Rehman F et al (2017) Rapid and multimodal in vivo bioimaging of cancer cells through in situ biosynthesis of Zn&Fe nanoclusters. Nano Res 10:2626–2632
Feng J, Dang Y, Zhang W et al (2019) PTEN arginine methylation by PRMT6 suppresses PI3K–AKT signaling and modulates pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116:6868
Gan H, Chen L, Sui X et al (2018) Enhanced delivery of sorafenib with anti-GPC3 antibody-conjugated TPGS-b-PCL/Pluronic P123 polymeric nanoparticles for targeted therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mater Sci Eng 91:395–403
Gerlier D, Thomasset N (1986) Use of MTT colorimetric assay to measure cell activation. J Immunol Methods 9:457–463
Huang C, Zheng J, Ma D et al (2018a) Hypoxia-triggered gene therapy: a new drug delivery system to utilize photodynamic-induced hypoxia for synergistic cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B 6:6424–6430
Huang K-W, Lai Y-T, Chern G-J et al (2018b) Galactose derivative-modified nanoparticles for efficient siRNA delivery to hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomacromolecules 19:2330–2339
Jiang HF, Ren J (2008) Inoculation of murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induces tumor necrosis in mouse with orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 40:453–458
Jiang Z, Zhou Q, Ge C et al (2019) Rpn10 promotes tumor progression by regulating hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha through the PTEN/Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 10:1–11
Lei Y, Tang L, Xie Y (2017) Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nat Commun 8:15130
Mazzaferro V, Chun YS, Poon RTP et al (2008) Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 15:1001–1007
Mcguire S (2016) World cancer report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International agency for research on cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv Nutr 7:418–419
Menon MB, Ronkina N, Schwermann J et al (2009) Fluorescence-based quantitative scratch wound healing assay demonstrating the role of MAPKAPK-2/3 in fibroblast migration. Cytoskeleton 66:1041–1047
Okada S, Vaeteewoottacharn K, Kariya R (2018) Establishment of a patient-derived Tumor Xenograft model and application for precision cancer medicine. Chem Pharm Bull 66:225–230
Sadauskas E, Wallin H, Stoltenberg M et al (2007) Kupffer cells are central in the removal of nanoparticles from the organism. Part Fibre Toxicol 4(1):10
Sana S, Ur RF, Tianyu Du et al (2018) Real-time multimodal bioimaging of cancer cells and exosomes through biosynthesized iridium and iron nanoclusters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:26056–26063
Surnar B, Basu U, Banik B et al (2018) Nanotechnology-mediated crossing of two impermeable membranes to modulate the stars of the neurovascular unit for neuroprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115:E12333–E12342
Thalheimer A, Otto C, Bueter M et al (2009) Tumor cell dissemination in a human colon cancer animal model: orthotopic implantation or intraportal injection? Eur Surg Res 42:195–200
Tian Yu, Gujie Mi, Qian C et al (2018) Acid-induced activated cell-penetrating peptide-modified cholesterol-conjugated polyoxyethylene sorbitol oleate mixed micelles for pH-triggered drug release and efficient brain tumor targeting based on a charge reversal mechanism. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:43411–43428
Vega JM, Grande AM, van der Zwaag S et al (2014) On the role of free carboxylic groups and cluster conformation on the surface scratch healing behaviour of ionomers. Eur Polym J 57:121–126
Wan H, Yue J, Zhu S et al (2018) A bright organic NIR-II nanofluorophore for three-dimensional imaging into biological tissues. Nat Commun 9:1171
Wang J, Zhang G, Li Q et al (2013) In vivo self-bio-imaging of tumors through in situ biosynthesized fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Sci Rep 3:1157
Wang M, Yu Z, Feng H et al (2019) In situ biosynthesized gold nanoclusters inhibiting cancer development via the PI3K–AKT signaling pathway. J Mater Chem B 7:5336–5344
Wang M, Chen Y, Cai W et al (2020) In situ self-assembling Au-DNA complexes for targeted cancer bioimaging and inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 117:308
Woroniecka K, Chongsathidkiet P, Rhodin KE et al (2018) T-cell exhaustion signatures vary with tumor type and are severe in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 24:1846–2017
Xin X, Mengying W, Qiuyu M (2018) Long noncoding RNA HULC accelerates liver cancer by inhibiting PTEN via autophagy cooperation to miR15a. Mol Cancer 17:94
Xu J, Cheng X, Tan L et al (2019) Microwave responsive nanoplatform via P-selectin mediated drug delivery for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with distant metastasis. Nano Lett 19:2914–2927
Yidi H, Meizhu C, Aili W et al (2019) STAT3-induced upregulation of lncRNA CASC11 promotes the cell migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by epigenetically silencing PTEN and activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:472–479
Zhang Z, Cai M, Bao C et al (2019) Endoscopic Cerenkov luminescence imaging and image-guided tumor resection on hepatocellular carcinoma-bearing mouse models. Nanomedicine 17:62–70
Zhao C, Du T, Rehman FU et al (2016) Biosynthesized gold nanoclusters and iron complexes as scaffolds for multimodal cancer bioimaging. Small 12:6255–6265
Zheng Q, Lin Z, Xu J et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA MEG3 suppresses liver cancer cells growth through inhibiting β-catenin by activating PKM2 and inactivating PTEN. Cell Death Dis 9:253
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91753106, 21675023, and 81325011), Primary Research & Development Plan of Jiangsu Province (BE2019716), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0205300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Wang, L., Feng, H. et al. Precise therapeutic effect of self-assembling gold nanocluster–PTEN complexes on an orthotropic model of liver cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 875–882 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03163-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03163-4