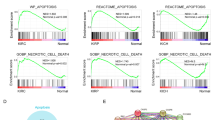
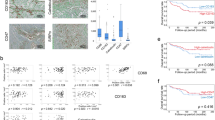
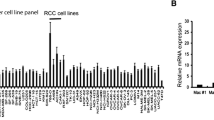
Abstract
Purpose
NOD1 and NOD2 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain)—receptors are intracellular receptors and belong to the family of pattern recognition receptors being present in both human and murine renal tubular cells. Besides, NOD1 has been proved to promote apoptosis, upon its overexpression. Hence, we aimed to investigate NOD1 and NOD2 expression in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
Methods
Tumor and corresponding adjacent healthy tissues from 41 patients with histopathological diagnosis of ccRCC as well as primary isolated renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) and tumor tissue from a murine xenograft model using CAKI-1 ccRCC cells were analyzed.
Results
NOD1 and NOD2 mRNA was constitutively expressed in both tumor and adjacent healthy renal tissue, with NOD1 being significantly lower and in contrast NOD2 significantly higher expressed in tumor tissue compared to healthy tissues. Immunohistochemically, NOD1 was located not only in the cytoplasm, but also in the nucleus in ccRCC tissue whereas NOD2 was solely localized in the cytoplasm in both human ccRCC as well as in the healthy tubular system. Focusing on the vasculature, NOD2 displayed broader expression than NOD1. In primary TECs as well as CAKI-1 cells NOD1 and NOD2 was constitutively expressed and increasable upon LPS stimulation. In the mouse xenograft model, human NOD1 mRNA was significantly higher expressed compared to NOD2. In contrast hereto, we observed a shift towards lower mouse NOD1 compared to NOD2 mRNA expression.
Conclusion
In view of reduced apoptosis-associated NOD1 expression in ccRCC tissue opposed to higher expression of NOD2 in tumor vasculature, inducibility of NOD expression in TECs as well as the detected shift of NOD1 and NOD2 expression in the mouse xenograft model, modulation of NOD receptors might, therefore, provide a molecular therapeutic approach in ccRCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer PC, Nockher WA, Haase W, Scherberich JE (1997) Isolation of proximal and distal tubule cells from human kidney by immunomagnetic separation. Kidney Int 52:1321–1331
Bamias A et al (2017) Current clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and critical evaluation. Oncologist 22:667–679. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0435
Bertin J et al (1999) Human CARD4 protein is a novel CED-4/Apaf-1 cell death family member that activates NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 274:12955–12958
Braunstein MJ, Kucharczyk J, Adams S (2018) Targeting toll-like receptors for cancer therapy. Target Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0589-7
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Caruso R, Warner N, Inohara N, Nunez G (2014) NOD1 and NOD2: signaling, host defense and inflammatory disease. Immunity 41:898–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.010
da Silva Correia J et al (2006) Nod1-dependent control of tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1840–1845. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509228103
Davey MP, Martin TM, Planck SR, Lee J, Zamora D, Rosenbaum JT (2006) Human endothelial cells express NOD2/CARD15 and increase IL-6 secretion in response to muramyl dipeptide. Microvasc Res 71:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2005.11.010
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingber D, Hanahan D (1989) Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 339:58–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/339058a0
Hisamatsu T, Suzuki M, Reinecker HC, Nadeau WJ, McCormick BA, Podolsky DK (2003) CARD15/NOD2 functions as an antibacterial factor in human intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 124:993–1000. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2003.50153
Inohara N et al (1999) Nod1, an Apaf-1-like activator of caspase-9 and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Biol Chem 274:14560–14567
Inohara N, Ogura Y, Chen FF, Muto A, Nunez G (2001) Human Nod1 confers responsiveness to bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Biol Chem 276:2551–2554. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M009728200
Kang MJ et al (2012) Activation of Nod1 and Nod2 induces innate immune responses of prostate epithelial cells. Prostate 72:1351–1358. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22483
Koebel CM et al (2007) Adaptive immunity maintains occult cancer in an equilibrium state. Nature 450:903–907. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06309
Kosugi S, Hasebe M, Tomita M, Yanagawa H (2009) Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:10171–10176. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900604106
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ogura Y, Inohara N, Benito A, Chen FF, Yamaoka S, Nunez G (2001) Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 family member that is restricted to monocytes and activates NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 276:4812–4818. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008072200
Ogura Y et al (2003) Expression of NOD2 in Paneth cells: a possible link to Crohn’s ileitis. Gut 52:1591–1597
Oh HM et al (2005) Induction and localization of NOD2 protein in human endothelial cells. Cell Immunol 237:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2005.09.006
Opitz B et al (2005) Nod1-mediated endothelial cell activation by Chlamydophila pneumoniae. Circ Res 96:319–326. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000155721.83594.2c
Park JH et al (2007) Nod1/RICK and TLR signaling regulate chemokine and antimicrobial innate immune responses in mesothelial cells. J Immunol 179:514–521
Parlato M, Yeretssian G (2014) NOD-like receptors in intestinal homeostasis and epithelial tissue repair. Int J Mol Sci 15:9594–9627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069594
Patard JJ et al (2005) Prognostic value of histologic subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter experience. J Clin Oncol 23:2763–2771. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.07.055
Rini BI (2005) VEGF-targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist 10:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.10-3-191
Schirbel A et al (2013) Pro-angiogenic activity of TLRs and NLRs: a novel link between gut microbiota and intestinal angiogenesis. Gastroenterology 144:613–623 e619. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.11.005
Scurrell E, Stanley R, Schoniger S (2009) Immunohistochemical detection of NOD1 and NOD2 in the healthy murine and canine eye. Vet Ophthalmol 12:269–275 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-5224.2009.00698.x
Shigeoka AA et al (2010) Nod1 and nod2 are expressed in human and murine renal tubular epithelial cells and participate in renal ischemia reperfusion injury. J Immunol 184:2297–2304. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0903065
Stroo I et al (2012) Phenotyping of Nod1/2 double deficient mice and characterization of Nod1/2 in systemic inflammation and associated renal disease. Biol Open 1:1239–1247 https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.2012554
Thoenes W, Storkel S, Rumpelt HJ (1986) Histopathology and classification of renal cell tumors (adenomas, oncocytomas and carcinomas). The basic cytological and histopathological elements and their use for diagnostics. Pathol Res Pract 181:125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0344-0338(86)80001-2
Ting JP, Davis BK (2005) CATERPILLER: a novel gene family important in immunity, cell death and diseases. Annu Rev Immunol 23:387–414. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115616
Tukhvatulin AI et al (2011) A in vitro and in vivo study of the ability of NOD1 Ligands to activate the transcriptional factor NF-kB. Acta Naturae 3:77–84
Uehara A, Fujimoto Y, Fukase K, Takada H (2007) Various human epithelial cells express functional Toll-like receptors, NOD1 and NOD2 to produce anti-microbial peptides but not proinflammatory cytokines Mol Immunol 44:3100–3111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.02.007
Acknowledgements
We especially thank Svenja Stumpf, Melanie Berger and Michael Dreher for their technical support. The study was financed by a grant from the Kulemann-Stiftung, Germany to AU. The foundation had no influence on design of the study, data collection and interpretation or on the decision to publish.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and that the results presented in this paper have not been published previously in whole or part.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mey, L., Jung, M., Roos, F. et al. NOD1 and NOD2 of the innate immune system is differently expressed in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma, corresponding healthy renal tissue, its vasculature and primary isolated renal tubular epithelial cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 1405–1416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02901-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02901-7