Abstract
Purpose
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) have been defined as preinvasive pulmonary adenocarcinoma lesions according to the 2015 World Health Organization lung adenocarcinoma classification. We aimed to search for the most common gene mutations in patients with AAH and AIS and investigate the distinctions between the two groups at the molecular level.
Methods
We performed targeted next-generation sequencing on 18 cases with AAH and 28 cases with AIS to screen for mutations with the Ion Torrent Oncomine Solid Tumor DNA panel. ALK and ROS1 fusions were detected by real-time PCR.
Results
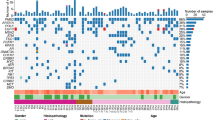
Forty-six mutations were identified in 29 cases (76.1%), including 9 (50%) of 18 cases with AAH and 20 (71.4%) of 28 cases with AIS, in the following genes: EGFR, BRAF, KRAS, ERBB2, TP53, and FGFR3. The mutations in EGFR, BRAF, KRAS, ERBB2, and TP53 genes were more common in AIS lesions than in AAH lesions, whereas the FGFR3 gene was more frequently mutated in AAH compared to AIS. ALK and ROS1 fusions were not detected in any of the lesions.
Conclusions
Based on the molecular evidence, the proposal that AAH and AIS are preinvasive lesions of pulmonary adenocarcinomas is of great significance, and it is necessary to distinguish AAH from AIS. Our study provided insights into the genetic alterations in the early stage of lung adenocarcinoma, which could be beneficial for the pathologic diagnosis and early detection of these lesions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N (2012) Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 489:519–525. doi:10.1038/nature11404
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N (2014) Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 511:543–550. doi:10.1038/nature13385
Carey KD et al (2006) Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Can Res 66:8163–8171. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0453
Casali C et al (2010) A single institution-based retrospective study of surgically treated bronchioloalveolar adenocarcinoma of the lung: clinicopathologic analysis, molecular features, and possible pitfalls in routine practice. J Thorac Oncol 5:830–836
Chiu CH et al (2015) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment response in advanced lung adenocarcinomas with G719X/L861Q/S768I mutations. J Thorac Oncol 10:793–799. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000504
Chung JH et al (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and pathologic–radiologic correlation between multiple lung nodules with ground-glass opacity differentiates multicentric origin from intrapulmonary spread. J Thorac Oncol 4:1490–1495. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181bc9731
Cooper WA, Lam DC, O’Toole SA, Minna JD (2013) Molecular biology of lung cancer. J Thorac Dis 5(Suppl 5):S479–S490. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.03
Dahlman KB et al (2012) BRAF(L597) mutations in melanoma are associated with sensitivity to MEK inhibitors. Cancer Discov 2:791–797. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0097
George J et al (2015) Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 524:47–53. doi:10.1038/nature14664
Greulich H (2010) The genomics of lung adenocarcinoma: opportunities for targeted therapies. Genes Cancer 1:1200–1210. doi:10.1177/1947601911407324
Gu J, Lu C, Guo J, Chen L, Chu Y, Ji Y, Ge D (2013) Prognostic significance of the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification in Chinese patients—a single institution retrospective study of 292 lung adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol 107:474–480. doi:10.1002/jso.23259
Heidorn SJ et al (2010) Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell 140:209–221. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.040
Heigener DF et al (2015) Afatinib in non-small cell lung cancer harboring uncommon EGFR mutations pretreated with reversible EGFR inhibitors. Oncologist 20:1167–1174. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0073
Ikeda K et al (2008) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in multicentric lung adenocarcinomas and atypical adenomatous hyperplasias. J Thorac Oncol 3:467–471. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31816b4b14
Izumchenko E et al (2015) Targeted sequencing reveals clonal genetic changes in the progression of early lung neoplasms and paired circulating DNA. Nat Commun 6:8258. doi:10.1038/ncomms9258
Kandoth C et al (2013) Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature 502:333–339. doi:10.1038/nature12634
Kaneda H, Uemura Y, Nakano T, Taniguchi Y, Saito T, Konobu T, Saito Y (2012) Lesions in patients with multifocal adenocarcinoma are more frequently in the right upper lobes. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 15:627–632. doi:10.1093/icvts/ivs276
Kitaguchi S, Takeshima Y, Nishisaka T, Inai K (1998) Proliferative activity, p53 expression and loss of heterozygosity on 3p, 9p and 17p in atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of the lung. Hiroshima J Med Sci 47:17–25
Kobayashi Y et al (2015) EGFR Exon 18 mutations in lung cancer: molecular predictors of augmented sensitivity to Afatinib or Neratinib as compared with first- or third-generation TKIs. Clin Cancer Res 21:5305–5313. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1046
Korpanty GJ, Graham DM, Vincent M, Leighl NB (2014) Biomarkers that currently effect clinical practice in lung cancer: EGFR, ALK, MET, ROS-1 and KRAS. Front Oncol 4:1–8. doi:10.3389/fonc.2014.00204
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T (2004) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer Res 64:8919–8923. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2818
Kozuki T et al (2007) Mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in the development of adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 58:30–35. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.04.011
Martin B et al (2002) Expression of p53 in preneoplastic and early neoplastic bronchial lesions. Oncol Rep 9:223–229
Matsumoto S et al (2006) Frequent EGFR mutations in noninvasive bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. Int J Cancer 118:2498–2504. doi:10.1002/ijc.21670
Mulloy R et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutants from human lung cancers exhibit enhanced catalytic activity and increased sensitivity to gefitinib. Can Res 67:2325–2330. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4293
Nakamura H, Kawasaki N, Taguchi M, Kato H (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in early pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 13:87–92
Oxnard GR, Binder A, Janne PA (2013) New targetable oncogenes in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:1097–1104. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.42.9829
Pan Y et al (2014) ALK, ROS1 and RET fusions in 1139 lung adenocarcinomas: a comprehensive study of common and fusion pattern-specific clinicopathologic, histologic and cytologic features. Lung Cancer 84:121–126. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.02.007
Russell PA, Wainer Z, Wright GM, Daniels M, Conron M, Williams RA (2011) Does lung adenocarcinoma subtype predict patient survival?: a clinicopathologic study based on the new International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary lung adenocarcinoma classification. J Thorac Oncol 6:1496–1504. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318221f701
Sakamoto H, Shimizu J, Horio Y, Ueda R, Takahashi T, Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y (2007) Disproportionate representation of KRAS gene mutation in atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, but even distribution of EGFR gene mutation from preinvasive to invasive adenocarcinomas. J Pathol 212:287–294. doi:10.1002/path.2165
Sakuma Y et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in atypical adenomatous hyperplasias of the lung. Mod Pathol 20:967–973. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800929
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:169–181. doi:10.1038/nrc2088
Shaw AT, Engelman JA (2013) ALK in lung cancer: past, present, and future. J Clin Oncol 31:1105–1111. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.44.5353
Smalley KS et al (2009) CRAF inhibition induces apoptosis in melanoma cells with non-V600E BRAF mutations. Oncogene 28:85–94. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.362
Takeuchi K et al (2012) RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat Med 18:378–381. doi:10.1038/nm.2658
Travis WD et al (2011) International association for the study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 6:244–285. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221
Travis WD et al (2015) The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol 10:1243–1260. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630
Watanabe S et al (2014) Effectiveness of gefitinib against non-small-cell lung cancer with the uncommon EGFR mutations G719X and L861Q. J Thorac Oncol 9:189–194. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000048
Wen J, Fu J, Zhang W, Guo M (2011) Genetic and epigenetic changes in lung carcinoma and their clinical implications. Mod Pathol 24:932–943. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.46
Yasuda H, Kobayashi S, Costa DB (2012) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: preclinical data and clinical implications. Lancet Oncol 13:e23–e31. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70129-2
Yasuda H et al (2013) Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci Transl Med 5:216ra177. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007205
Yoo SB, Chung JH, Lee HJ, Lee CT, Jheon S, Sung SW (2010) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and p53 overexpression during the multistage progression of small adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol 5:964–969. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181dd15c0
Yoshida Y et al (2005) Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and bronchioloalveolar carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 50:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.04.012
Yoshizawa A et al (2013) Validation of the IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma classification for prognosis and association with EGFR and KRAS gene mutations: analysis of 440 Japanese patients. J Thorac Oncol 8:52–61. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182769aa8
Zhang J, Wu J, Tan Q, Zhu L, Gao W (2013) Why do pathological stage IA lung adenocarcinomas vary from prognosis?: a clinicopathologic study of 176 patients with pathological stage IA lung adenocarcinoma based on the IASLC/ATS/ERS classification. J Thorac Oncol 8:1196–1202. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31829f09a7
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Youhui Hu, Shengji Ma, and Wenjie Ding for excellent technical help. This work was supported by the project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (20164Y0046) and the “Five-New” Clinical and translational Project for Specialized Diseases (16CR3023A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions
XX: sample processing, data analysis and manuscript preparation. NL: sample collection and clinical annotation. RZ: sample processing. LZ and JS: article revision. JZ: study conception and design, pathology assessment, and article revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Li, N., Zhao, R. et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing for analyzing the genetic alterations in atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 2447–2453 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2500-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2500-9