Abstract
Purpose
Oral cancer (OC) patients are at high risk to develop recurrent disease or secondary primary cancers with no available biomarkers to detect these events until a visible lesion is readily present and diagnosed by biopsy. Exosomes secreted by cancer cells are involved in tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. We aimed to determine morphological and molecular differences between oral fluid (OF)-derived exosomes of OC patients and those isolated from healthy individuals (HI).
Methods
OF from OC patients (n = 36) and HI (n = 25) was initially assessed by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). Following ultracentrifugation, exosomal pellets of OC patients and HI were morphologically examined by transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blotting (WB) were used to analyze the expression of exosomal markers—CD9, CD81 and CD63.
Results
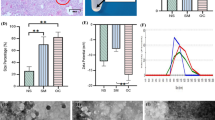
NTA showed that OC samples of OF had a significantly higher concentration of nanoparticles/ml (p = 0.01) and modal nanoparticle size (p = 0.002) compared to HI. The difference in size was structurally highlighted by AFM three-dimensional images applied on exosomal pellets. ELISA and WB showed differential expression of exosomal markers in OC exosomes compared to HI: lower expression of CD81 and CD9 in contrast to a higher expression of CD63 (~53 kDa).
Conclusions
OF-derived exosomes from OC patients differ both morphologically and molecularly from exosomes present in HI. This study is a baseline that provides a starting point for finding exosomal biomarkers for early detection of malignant changes in high-risk patients without overt clinical signs/lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ageberg M, Lindmark A (2003) Characterization of the biosynthesis and processing of the neutrophil granule membrane protein CD63 in myeloid cells. Clin Lab Haematol 25:297–306. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2257.2003.00541.x
Bobrie A, Krumeich S, Reyal F, Recchi C, Moita LF, Seabra MC, Ostrowski M, Théry C (2012) Rab27a supports exosome-dependent and -independent mechanisms that modify the tumor microenvironment and can promote tumor progression. Cancer Res 72:4920–4930. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
Buim ME, Lourenço SV, Carvalho KC, Cardim R, Pereira C, Carvalho AL et al (2010) Downregulation of CD9 protein expression is associated with aggressive behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 46:16. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2009.11.009
Chernousov MA, Stahl RC, Carey DJ (2013) Tetraspanins are involved in Schwann cell-axon interaction. J Neurosci Res 91:1419–1428. doi:10.1002/jnr.23272
Davidovich E, Aframian DJ, Shapira J, Peretz B (2010) A comparison of the sialochemistry, oral pH, and oral health status of Down syndrome children to healthy children. Int J Paediatr Dent 20:235–241. doi:10.1111/j.1365-263X.2010.01045.x
Dayan D, Salo T, Salo S, Nyberg P, Nurmenniemi S, Costea DE et al (2012) Molecular crosstalk between cancer cells and tumor microenvironment components suggests potential targets for new therapeutic approaches in mobile tongue cancer. Cancer Med 1:128–140. doi:10.1002/cam4.24
Erovic BM, Pammer J, Hollemann D, Woegerbauer M, Geleff S, Fischer MB et al (2003) Motility-related protein-1/CD9 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 25:848–857. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601542
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase no. 11 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. http://globocan.iarc.fr. Accessed on 06 Sept 2014
Hemler ME (2003) Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion, and fusion events and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:397–422. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111301.153609
Hirano C, Nagata M, Noman AA, Kitamura N, Ohnishi M, Ohyama T et al (2009) Tetraspanin gene expression levels as potential biomarkers for malignancy of gingival squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 124:2911–2916. doi:10.1002/ijc.24297
Imhof I, Gasper WJ, Derynck R (2008) Association of tetraspanin CD9 with transmembrane TGF{alpha} confers alterations in cell-surface presentation of TGF{alpha} and cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 13):2265–2274. doi:10.1242/jcs.021717
Kademani D (2007) Oral cancer. Mayo Clin Proc 82(7):878–887. doi:10.4065/82.7.878
Kahlert C, Kalluri R (2013) Exosomes in tumor microenvironment influence cancer progression and metastasis. J Mol Med 91:431–437. doi:10.1007/s00109-013-1020-6
King HW, Michael MZ, Gleadle JM (2012) Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 12:421. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-421
Kovalenko OV, Yang X, Kolesnikova TV, Hemler ME (2004) Evidence for specific tetraspanin homodimers: inhibition of palmitoylation makes cysteine residues available for cross-linking. Biochem J 377:407–417. doi:10.1242/jcs.021717
Krief G, Deutsch O, Zaks B, Wong DT, Aframian DJ, Palmon A (2012) Comparison of diverse affinity based high-abundance protein depletion strategies for improved bio-marker discovery in oral fluids. J Proteomics 75:4165–4175. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2012.05.012
Kusukawa J, Ryu F, Kameyama T, Mekada E (2001) Reduced expression of CD9 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: CD9 expression inversely related to high prevalence of lymph node metastasis. J Oral Pathol Med 30:73–79
Lässer C, Alikhani VS, Ekström K, Eldh M, Paredes PT, Bossios A et al (2011) Human saliva, plasma and breast milk exosomes contain RNA: uptake by macrophages. J Transl Med 9:9. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-9
Lisowska E (2002) The role of glycosylation in protein antigenic properties. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:445–455. doi:10.1007/s00018-002-8437-3
Masaki Nagata, Hajime Fujita, Hiroko Ida, Hoshina H, Inoue T, Seki Y et al (2003) Identification of potential biomarkers of lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by cDNA microarray analysis. Int J Cancer 106:683–689. doi:10.1002/ijc.11283
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ (2010) Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics 73:1907–1920. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.006
Mazzocca A, Liotta F, Carloni V (2008) Tetraspanin CD81-regulated cell motility plays a critical role in intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 135:244–56e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.024
Mhawech P, Dulguerov P, Tschanz E, Verdan C, Ares C, Allal AS (2004) Motility-related protein-1 (MRP-1/CD9) expression can predict disease-free survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Br J Cancer 90:471–475. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601542
Michael A, Bajracharya SD, Yuen PS, Zhou H, Star RA, Illei GG, Alevizos I (2010) Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis 16:34–38. doi:10.1111/j.1601-0825.2009.01604.x
Minciacchi VR, Freemana MR, Di Vizio D (2015) Extracellular vesicles in cancer: exosomes, microvesicles and the emerging role of large oncosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol 40:41–51. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.02.010
Mu W, Rana S, Zöller M (2013) Host matrix modulation by tumor exosomes promotes motility and invasiveness. Neoplasia 15:875–887. doi:10.1593/neo.13786
Nankivell P, Williams H, McConkey C, Webster K, High A, MacLennan K et al (2013) Tetraspanins CD9 and CD151, epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase-2 expression predict malignant progression in oral epithelial dysplasia. Br J Cancer 109:2864–2874. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.600
Ogawa Y, Kanai-Azuma M, Akimoto Y, Kawakami H, Yanoshita R (2008) Exosome-like vesicles with dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human saliva. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1059–1062. doi:10.1248/bpb.31.1059
Ogawa Y, Miura Y, Harazano A, Kanai-Azuma M, Akimoto Y, Kawakami H et al (2011) Proteomic analysis of two types of exosomes in human whole saliva. Biol Pharm Bull 34:13–23. doi:10.1248/bpb.34.13
Ovalle S, Gutierrez-Lopez MD, Olmo N, Turnay J, Lizarbe MA, Majano P et al (2007) The tetraspanin CD9 inhibits the proliferation and tumorigenicity of human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 121:2140–2152. doi:10.1002/ijc.22902
Palanisamy V, Sharma S, Deshpande A, Zhou H, Gimzewski JK, Wong DT (2010) Nanostructural and transcriptomic analyses of human saliva derived exosomes. Plos One 5:e8577. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008577
Principe S, Hui AB, Bruce J, Sinha A, Liu FF, Kislinger T (2013) Tumor-derived exosomes and microvesicles in head and neck cancer: implications for tumor biology and biomarker discovery. Proteomics 13:1608–1623. doi:10.1002/pmic.201200533
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437. doi:10.1038/nm.3394
Radford KJ, Thorne RF, Hersey P (1996) CD63 associates with transmembrane 4 superfamily members, CD9 and CD81, and with beta 1 integrins in human melanoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 222:13–18
Rosell R, Wei J, Taron M (2009) Circulating microRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes for early diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 10:8–9. doi:10.3816/CLC.2009.n.001
Salo T, Vered M, Bello IO, Nyberg P, Bitu CC, Zlotogorski-Hurvitz A et al (2014) Insights into the role of components of the tumor microenvironment in oral carcinoma call for new therapeutic approaches. Exp Cell Res 325:58–64. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.12.029
Sharma S, Rasool HI, Palanisamy V, Mathisen C, Schmidt M, Wong DT et al (2010) Structural-mechanical characterization of nanoparticle exosomes in human saliva, using correlative AFM, FESEM, and force spectroscopy. ACS Nano 4:1921–1926. doi:10.1021/nn901824n
Sharma S, Gillespie BM, Palanisamy V, Gimzewski JK (2011) Quantitative nanostructural and single-molecule force spectroscopy biomolecular analysis of human-saliva-derived exosomes. Langmuir 27:14394–14400. doi:10.1021/la2038763
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes—vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007
Simple M, Suresh A, Das D, Kuriakose MA (2015) Cancer stem cells and field cancerization of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 51:643–651. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.006
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110:13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.04.033
Tominaga N, Hagiwara K, Kosaka N, Honma K, Nakagama H, Ochiya T (2014) RPN2-mediated glycosylation of tetraspanin CD63 regulates breast cancer cell malignancy. Mol Cancer 31:134. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-134
Vered M, Lehtonen M, Hotakainen L, Pirilä E, Teppo S et al (2015) Caveolin-1 accumulation in the tongue cancer tumor microenvironment is significantly associated with poor prognosis: an in-vivo and in-vitro study. BMC Cancer 15:25. doi:10.1186/s12885-015-1030-6
Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R (2012) Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:940–948. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.017
Zhang HG, Grizzle WE (2014) Exosomes: a novel pathway of local and distant intercellular communication that facilitates the growth and metastasis of neoplastic lesions. Am J Pathol 184:28–41. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.09.027
Zhou H, Yuen PS, Pisitkun T, Gonzales PA, Yasuda H, Dear JW et al (2006) Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery. Kidney Int 69:1471–1476. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5000273
Zhu L, Qu XH, Sun YL, Qian YM, Zhao XH (2014) Novel method for extracting exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 20:6651–6657. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6651
Zlotogorski-Hurvitz A, Dayan D, Chaushu G, Korvala J, Salo T, Sormunen R et al (2015) Human saliva-derived exosomes: comparing methods of isolation. J Histochem Cytochem 63:181–189. doi:10.1369/0022155414564219
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Ronit Galron from the Department of Neurobiology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Tel Aviv University for her valuable technical assistance, Dr. Artium Khatchtouriants, from The Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Tel Aviv University, for his AFM analysis and Mr. Ariel Roytman, from Merkel Technologies, Yehud, Israel, for his assistance with the NTA. Special thanks go to Dr. Ran Yahalom, Head of the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Sheba Medical Center, for his assistance in collecting the saliva samples. The authors also want to thank Ms. Esther Eshkol for editorial assistance. The study was supported in part by the Dave and Sarah Babish Fund in Oral Pathology, Tel- Aviv University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
This work was performed in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a Ph.D. degree of Ayelet Zlotogorski- Hurvitz, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Israel
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zlotogorski-Hurvitz, A., Dayan, D., Chaushu, G. et al. Morphological and molecular features of oral fluid-derived exosomes: oral cancer patients versus healthy individuals. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 101–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2005-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2005-3