Abstract
Purpose
A previous study showed that flavopiridol increased doxorubicin sensitivity in hypoxic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells by increasing apoptosis through suppressing hypoxia-inducible N-myc downstream-regulated gene-1 (NDRG1) expression. However, this has not been investigated in an in vivo HCC model. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate whether the combination of doxorubicin and flavopiridol has a synergistic anti-tumor effect in an in vivo HCC model.
Methods
An HCC mouse model was established by implanting C3H/He mouse with MH134 cells. Then, doxorubicin with or without flavopiridol was injected. The anti-tumor efficacy was assessed by evaluating tumor volumes, and the underlying mechanism was investigated by quantifying apoptotic cells, the Ki-67 proliferation index, and microvessel densities (MVDs). Immunohistochemistry of NDRG1 was performed to determine the underlying mechanism.
Results
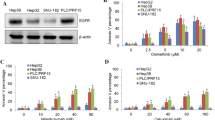
Tumor growth was significantly suppressed in the doxorubicin + flavopiridol combination group compared to the other three groups. The percentage of apoptotic cells was significantly higher, and Ki-67-positive proliferating cells were significantly lower in the combination group compared to the other groups; however, MVDs were not significantly different across the groups. Increased apoptosis by flavopiridol occurred by suppressing hypoxia-inducible NDRG1 expression.
Conclusions
These results show that a combination of doxorubicin and flavopiridol has a synergistic anti-tumor effect in an in vivo HCC model. This synergistic effect of combination therapy was attributed to increased apoptosis and decreased proliferation of tumor cells rather than decreased angiogenesis. These findings suggest that flavopiridol might be an effective adjuvant therapy to doxorubicin-resistant HCC cells by inducing apoptosis through suppression of NDRG1 expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- TACE:
-
Transarterial chemoembolization
- NDRG1:
-
N-myc downstream-regulated gene-1
- NONMEM:
-
Nonlinear mixed effect modeling
- MVD:
-
Microvessel density
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- HK II:
-
Hexokinase II
- SD:
-
Standard deviations
References
Akiba J, Ogasawara S, Kawahara A, Nishida N, Sanada S, Moriya F, Kuwano M, Nakashima O, Yano H (2008) N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 (NDRG1)/Cap43 enhances portal vein invasion and intrahepatic metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 20:1329–1335
Asghar U, Meyer T (2012) Are there opportunities for chemotherapy in the treatment of hepatocellular cancer? J Hepatol 56:686–695. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.07.031
Bagi CM, Gebhard DF, Andresen CJ (2012) Antitumor effect of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor sunitinib in preclinical models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:563–574. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e328350916f
Beal SL (1984) Population pharmacokinetic data and parameter estimation based on their first two statistical moments. Drug Metab Rev 15:173–193. doi:10.3109/03602538409015064
Budak-Alpdogan T, Chen B, Warrier A, Medina DJ, Moore D, Bertino JR (2009) Retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene expression determines the response to sequential flavopiridol and doxorubicin treatment in small-cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15:1232–1240. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0810
Cao H, Phan H, Yang LX (2012) Improved chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 32:1379–1386
Chua MS, Sun H, Cheung ST, Mason V, Higgins J, Ross DT, Fan ST, So S (2007) Overexpression of NDRG1 is an indicator of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod Pathol 20:76–83. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800711
Fan L, Song B, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F, Wei W (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced resistance to doxorubicin is reversed by paeonol treatment in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 8:e62627. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062627
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F (2004) Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology 127:S35–S50
Gladyshev VN, Liu A, Novoselov SV, Krysan K, Sun QA, Kryukov VM, Kryukov GV, Lou MF (2001) Identification and characterization of a new mammalian glutaredoxin (thioltransferase), Grx2. J Biol Chem 276:30374–30380. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100020200
Jung EU, Yoon JH, Lee YJ, Lee JH, Kim BH, Yu SJ, Myung SJ, Kim YJ, Lee HS (2010) Hypoxia and retinoic acid-inducible NDRG1 expression is responsible for doxorubicin and retinoic acid resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 298:9–15. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.05.020
Kim W, Yoon JH, Kim JR, Jang IJ, Bang YJ, Kim YJ, Lee HS (2009) Synergistic anti-tumor efficacy of lovastatin and protein kinase C-beta inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64:497–507. doi:10.1007/s00280-008-0897-1
Lai CL, Wu PC, Chan GC, Lok AS, Lin HJ (1988) Doxorubicin versus no antitumor therapy in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. A prospective randomized trial. Cancer 62:479–483
Li W, Fan J, Bertino JR (2001) Selective sensitization of retinoblastoma protein-deficient sarcoma cells to doxorubicin by flavopiridol-mediated inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 kinase activity. Cancer Res 61:2579–2582
Lillig CH, Lonn ME, Enoksson M, Fernandes AP, Holmgren A (2004) Short interfering RNA-mediated silencing of glutaredoxin 2 increases the sensitivity of HeLa cells toward doxorubicin and phenylarsine oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13227–13232. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401896101
Melotte V, Qu X, Ongenaert M, van Criekinge W, de Bruine AP, Baldwin HS, van Engeland M (2010) The N-myc downstream regulated gene (NDRG) family: diverse functions, multiple applications. FASEB J 24:4153–4166. doi:10.1096/fj.09-151464
Motwani M, Sirotnak FM, She Y, Commes T, Schwartz GK (2002) Drg1, a novel target for modulating sensitivity to CPT-11 in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 62:3950–3955
Newcomb EW (2004) Flavopiridol: pleiotropic biological effects enhance its anti-cancer activity. Anticancer Drugs 15:411–419
Richard C, Matthews D, Duivenvoorden W, Yau J, Wright PS, Th’ng JP (2005) Flavopiridol sensitivity of cancer cells isolated from ascites and pleural fluids. Clin Cancer Res 11:3523–3529. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2507
Wall NR, O’Connor DS, Plescia J, Pommier Y, Altieri DC (2003) Suppression of survivin phosphorylation on Thr34 by flavopiridol enhances tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Res 63:230–235
Xiang QF, Zhang DM, Wang JN, Zhang HW, Zheng ZY, Yu DC, Li YJ, Xu J, Chen YJ, Shang CZ (2014) Cabozantinib reverses multidrug resistance of human hepatoma HepG2/adr cells by modulating the function of P-glycoprotein. Liver Int. doi:10.1111/liv.12524
Yamashita YI, Shimada M, Hasegawa H, Minagawa R, Rikimaru T, Hamatsu T, Tanaka S, Shirabe K, Miyazaki JI, Sugimachi K (2001) Electroporation-mediated interleukin-12 gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in the mice model. Cancer Res 61:1005–1012
Yan X, Chua MS, Sun H, So S (2008) N-Myc down-regulated gene 1 mediates proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 262:133–142. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.12.010
Yeo W, Mok TS, Zee B, Leung TW, Lai PB, Lau WY, Koh J, Mo FK, Yu SC, Chan AT, Hui P, Ma B, Lam KC, Ho WM, Wong HT, Tang A, Johnson PJ (2005) A randomized phase III study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon alpha-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1532–1538. doi:10.1093/jnci/dji315
Yu SJ, Yoon JH, Yang JI, Cho EJ, Kwak MS, Jang ES, Lee JH, Kim YJ, Lee HS, Kim CY (2012) Enhancement of hexokinase II inhibitor-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via augmenting ER stress and anti-angiogenesis by protein disulfide isomerase inhibition. J Bioenerg Biomembr 44:101–115. doi:10.1007/s10863-012-9416-5
Zhai S, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Figg WD (2002) Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in clinical development. Ann Pharmacother 36:905–911
Zhou J, Zheng W, Cao L, Liu M, Han F, Li A (2010) Antiangiogenic tumor treatment: noninvasive monitoring with contrast pulse sequence imaging for contrast-enhanced grayscale ultrasound. Acad Radiol 17:646–651. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2010.01.008
Zhou J, Wan B, Liu XM, Li R, Wang Y, Yu L (2012) MK5 is degraded in response to doxorubicin and negatively regulates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:581–586. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.101
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Liver Research Foundation of Korea. The funding organizations had no role in the study design; collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Authors have full control of all primary data and that authors agree to allow the journal to review these data if requested.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Min-Sun Kwak and Su Jong Yu have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwak, MS., Yu, S.J., Yoon, JH. et al. Synergistic anti-tumor efficacy of doxorubicin and flavopiridol in an in vivo hepatocellular carcinoma model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 2037–2045 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1990-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1990-6