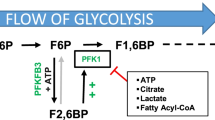
Abstract
Purpose
The unique metabolic profile of cancer (aerobic glycolysis) is an attractive therapeutic target for cancer. Dichloroacetate (DCA), an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, has been shown to reverse glycolytic phenotype and induce mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis. In the present study, we investigated the effects of S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) inhibition on DCA-induced cell death and the underlying mechanisms in breast cancer cells.
Methods
Cell death was evaluated by annexin V and PI staining. The synergistic effects of DCA and PF4708671 were assessed by isobologram analysis. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used for suppressing gene expression. The mRNA and protein levels were measured by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively.
Results
PF4708671, a selective inhibitor of S6K1, and knockdown of S6K1 with specific siRNA enhanced DCA-induced cell death. Interestingly, a combination of DCA/PF4708671 markedly reduced protein expression of a glycolytic enzyme, hexokinase 2 (HK2). Suppression of HK2 activity using specific siRNA and 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) further enhanced cell sensitivity to DCA/PF4708671. Overexpression of Myc-tagged HK2 rescued cell death induced by DCA/PF4708671.
Conclusions
Based on these findings, we propose that inhibition of S6K1, in combination with the glycolytic inhibitor, DCA, provides effective cancer therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayyanathan K, Kesaraju S, Dawson-Scully K, Weissbach H (2012) Combination of sulindac and dichloroacetate kills cancer cells via oxidative damage. PLoS One 7:e39949. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039949
Barger JF, Gallo CA, Tandon P, Liu H, Sullivan A, Grimes HL, Plas DR (2013) S6K1 determines the metabolic requirements for BCR-ABL survival. Oncogene 32:453–461. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.70
Berenbaum MC (1981) Criteria for analyzing interactions between biologically active agents. Adv Cancer Res 35:269–335
Bonnet S et al (2007) A mitochondria-K+ channel axis is suppressed in cancer and its normalization promotes apoptosis and inhibits cancer growth. Cancer Cell 11:37–51. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.020
Cao W et al (2008) Dichloroacetate (DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate 68:1223–1231. doi:10.1002/pros.20788
Cerella C, Dicato M, Diederich M (2014) Modulatory roles of glycolytic enzymes in cell death. Biochem Pharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.07.005
Choi HN et al (2013) Inhibition of S6K1 enhances glucose deprivation-induced cell death via downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 432:123–128. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.074
Ferreira LM (2010) Cancer metabolism: the Warburg effect today. Exp Mol Pathol 89:372–380. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.08.006
Fingar DC, Blenis J (2004) Target of rapamycin (TOR): an integrator of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 23:3151–3171. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207542
Flavin D (2010) Medullary thyroid carcinoma relapse reversed with dichloroacetate: a case report. Oncol Lett 1:889–891. doi:10.3892/ol_00000158
Gimenez-Cassina A, Lim F, Cerrato T, Palomo GM, Diaz-Nido J (2009) Mitochondrial hexokinase II promotes neuronal survival and acts downstream of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Biol Chem 284:3001–3011. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808698200
Hong SE et al (2013) S6K1 inhibition enhances tamoxifen-induced cell death in MCF-7 cells through translational inhibition of Mcl-1 and survivin. Cell Biol Toxicol 29:273–282. doi:10.1007/s10565-013-9253-2
Jha MK, Suk K (2013) Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase as a potential therapeutic target for malignant gliomas. Brain Tumor Res Treat 1:57–63. doi:10.14791/btrt.2013.1.2.57
Jin HO, Seo SK, Woo SH, Choe TB, Hong SI, Kim JI, Park IC (2009) Nuclear protein 1 induced by ATF4 in response to various stressors acts as a positive regulator on the transcriptional activation of ATF4. IUBMB Life 61:1153–1158. doi:10.1002/iub.271
Kim D, Akcakanat A, Singh G, Sharma C, Meric-Bernstam F (2009) Regulation and localization of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 isoforms. Growth Factors 27:12–21. doi:10.1080/08977190802556986
Michelakis ED, Webster L, Mackey JR (2008) Dichloroacetate (DCA) as a potential metabolic-targeting therapy for cancer. Br J Cancer 99:989–994. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604554
Michelakis ED et al (2010) Metabolic modulation of glioblastoma with dichloroacetate. Sci Transl Med 2:31ra34. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3000677
Najafov A, Alessi DR (2010) Uncoupling the Warburg effect from cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19135–19136. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014047107
Noh WC et al (2004) Determinants of rapamycin sensitivity in breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:1013–1023
Pearce LR et al (2010) Characterization of PF-4708671, a novel and highly specific inhibitor of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (S6K1). Biochem J 431:245–255. doi:10.1042/BJ20101024
Pelicano H, Martin DS, Xu RH, Huang P (2006) Glycolysis inhibition for anticancer treatment. Oncogene 25:4633–4646. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209597
Sanchez WY et al (2013) Dichloroacetate inhibits aerobic glycolysis in multiple myeloma cells and increases sensitivity to bortezomib. Br J Cancer 108:1624–1633. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.120
Stockwin LH et al (2010) Sodium dichloroacetate selectively targets cells with defects in the mitochondrial ETC. Int J Cancer 127:2510–2519. doi:10.1002/ijc.25499
Sun RC, Fadia M, Dahlstrom JE, Parish CR, Board PG, Blackburn AC (2010) Reversal of the glycolytic phenotype by dichloroacetate inhibits metastatic breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120:253–260. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0435-9
Tandon P, Gallo CA, Khatri S, Barger JF, Yepiskoposyan H, Plas DR (2011) Requirement for ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 to mediate glycolysis and apoptosis resistance induced by Pten deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2361–2365. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013629108
Vander Heiden MG (2011) Targeting cancer metabolism: a therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:671–684. doi:10.1038/nrd3504
Warburg O (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123:309–314
Wong JY, Huggins GS, Debidda M, Munshi NC, De Vivo I (2008) Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 109:394–402. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.01.038
Zhao Y, Butler EB, Tan M (2013) Targeting cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis 4:e532. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.60
Zheng J (2012) Energy metabolism of cancer: glycolysis versus oxidative phosphorylation (review). Oncol Lett 4:1151–1157. doi:10.3892/ol.2012.928
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by grants from the Radiological Translational Research program Research Program (50451-2014), the National Nuclear R&D program and Basic Science Research Program (A111770) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Radiation Bio-Resource Research Program of the Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences (No. 740802) in the Republic of Korea.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Sung-Eun Hong and Kyung-Sub Shin have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, SE., Shin, KS., Lee, YH. et al. Inhibition of S6K1 enhances dichloroacetate-induced cell death. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 1171–1179 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1887-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1887-9