Abstract
Purpose
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a rare and aggressive soft tissue sarcoma with limited treatment options and a high failure rate during standard therapy. New therapeutic strategies based on targeted immunotherapy are therefore much in demand. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has all the characteristics of an ideal target. It is overexpressed in up to 80 % of embryonal RMS and up to 50 % of alveolar RMS tumors. We therefore tested the activity of the EGFR-specific recombinant immunotoxin (IT) 425(scFv)-ETA′ against EGFR+ RMS cells in vitro and ex vivo.
Methods
We tested the specific binding and internalization behavior of 425(scFv)-ETA′ in RMS cell lines in vitro by flow cytometry, compared to the corresponding imaging probe 425(scFv)-SNAP monitored by live cell imaging. The cytotoxic activity of 425(scFv)-ETA′ was tested using cell viability and apoptosis assays. Specific binding of the IT was confirmed on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples from two RMS patients.
Results
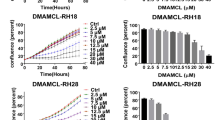
We confirmed the specific binding of 425(scFv)-ETA′ to RMS cells in vitro and ex vivo. Both the IT and the corresponding imaging probe were rapidly internalized. The IT killed EGFR+ RMS cells in a dose-dependent manner, while showing no effect against control cells. It showed specific apoptotic activity against one selected RMS cell line.
Conclusions
This is the first study showing the promising therapeutic potential of a recombinant, EGFR-targeting, ETA′-based IT on RMS cells. We confirmed the selective killing with IC50 values of up to 50 pM, and immunohistochemical staining confirmed the specific ex vivo binding to primary RMS material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham J et al (2011) Preclinical testing of erlotinib in a transgenic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mouse model. Sarcoma 2011:130484. doi:10.1155/2011/130484
Ahmad ZA, Yeap SK, Ali AM, Ho WY, Alitheen NB, Hamid M (2012) scFv antibody: principles and clinical application. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:980250. doi:10.1155/2012/980250
Allen TM (2002) Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2:750–763. doi:10.1038/nrc903
Amoury M et al (2013) SNAP-tag based agents for preclinical in vitro imaging in malignant diseases. Curr Pharm Des 19:5429–5436
Antignani A, Fitzgerald D (2013) Immunotoxins: the role of the toxin. Toxins 5:1486–1502. doi:10.3390/toxins5081486
Armistead PM et al (2007) Expression of receptor tyrosine kinases and apoptotic molecules in rhabdomyosarcoma: correlation with overall survival in 105 patients. Cancer 110:2293–2303. doi:10.1002/cncr.23038
Azemar M et al (2000) Recombinant antibody toxins specific for ErbB2 and EGF receptor inhibit the in vitro growth of human head and neck cancer cells and cause rapid tumor regression in vivo International journal of cancer. J Int Cancer 86:269–275
Bachran D et al (2010) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression affects the efficacy of the combined application of saponin and a targeted toxin on human cervical carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 127:1453–1461. doi:10.1002/ijc.25123
Barth S (2002) Technology evaluation: BL22. NCI current opinion in molecular therapeutics 4:72–75
Barth S, Huhn M, Matthey B, Klimka A, Galinski EA, Engert A (2000) Compatible-solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1572–1579
Becker N, Benhar I (2012) Antibody-based immunotoxins for the treatment of cancer. Antibodies 1:39–69. doi:10.3390/antib1010039
Biberacher V et al (2012) The cytotoxicity of anti-CD22 immunotoxin is enhanced by bryostatin 1 in B-cell lymphomas through CD22 upregulation and PKC-betaII depletion. Haematologica 97:771–779. doi:10.3324/haematol.2011.049155
Bisogno G et al (2012) Rhabdomyosarcoma in adolescents: a report from the AIEOP soft tissue sarcoma committee. Cancer 118:821–827. doi:10.1002/cncr.26355
Brehm H et al (2014) A CSPG4-specific immunotoxin kills rhabdomyosarcoma cells and binds to primary tumor tissues Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.006
Bruell D et al (2003) The recombinant anti-EGF receptor immunotoxin 425(scFv)-ETA′ suppresses growth of a highly metastatic pancreatic carcinoma cell line. Int J Oncol 23:1179–1186
Bruell D et al (2005) Recombinant anti-EGFR immunotoxin 425(scFv)-ETA′ demonstrates anti-tumor activity against disseminated human pancreatic cancer in nude mice. Int J Mol Med 15:305–313
Camp ER, Summy J, Bauer TW, Liu W, Gallick GE, Ellis LM (2005) Molecular mechanisms of resistance to therapies targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 11:397–405
Cen L et al (2007) Phosphorylation profiles of protein kinases in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Mod Pathol 20:936–946. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800834
Chandramohan V, Bigner D (2013) A novel recombinant immunotoxin-based therapy targeting wild-type and mutant EGFR improves survival in murine models of glioblastoma. OncoImmunology 2(12):e26852
Chong CR, Janne PA (2013) The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med 19:1389–1400. doi:10.1038/nm.3388
Cizeau J, Grenkow DM, Brown JG, Entwistle J, MacDonald GC (2009) Engineering and biological characterization of VB6-845, an anti-EpCAM immunotoxin containing a T-cell epitope-depleted variant of the plant toxin bouganin. J Immunother 32:574–584. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181a6981c
Colcher D, Pavlinkova G, Beresford G, Booth BJ, Choudhury A, Batra SK (1998) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of genetically-engineered antibodies. Q J Nucl Med 42:225–241
Davicioni E et al (2009) Molecular classification of rhabdomyosarcoma–genotypic and phenotypic determinants of diagnosis: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Am J Pathol 174:550–564. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080631
De Giovanni C et al (1996) Antisense epidermal growth factor receptor transfection impairs the proliferative ability of human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Cancer Res 56:3898–3901
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Fehrenbacher B, Schaller M, Kehlbach R, Rodemann HP (2010) Nuclear EGFR shuttling induced by ionizing radiation is regulated by phosphorylation at residue Thr654. FEBS Lett 584:3878–3884. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.08.005
Ganti R et al (2006) Expression and genomic status of EGFR and ErbB-2 in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Mod Pathol 19:1213–1220. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800636
Gattenlohner S et al (2010) A human recombinant autoantibody-based immunotoxin specific for the fetal acetylcholine receptor inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma growth in vitro and in a murine transplantation model. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:187621. doi:10.1155/2010/187621
Ghetie MA, Tucker K, Richardson J, Uhr JW, Vitetta ES (1994) Eradication of minimal disease in severe combined immunodeficient mice with disseminated Daudi lymphoma using chemotherapy and an immunotoxin cocktail. Blood 84:702–707
Green MR, Sambrook J (2012) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Hawkins DS, Gupta AA, Rudzinski ER (2014) What is new in the biology and treatment of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma? Curr Opin Pediatr 26:50–56. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000041
Hristodorov D et al (2013) Microtubule-associated protein tau facilitates the targeted killing of proliferating cancer cells in vitro and in a xenograft mouse tumour model in vivo. Br J Cancer 109:1570–1578. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.457
Hussain AF, Amoury M, Barth S (2013) SNAP-tag technology: a powerful tool for site specific conjugation of therapeutic and imaging agents. Curr Pharm Des 19:5437–5442
Jain S, Xu R, Prieto VG, Lee P (2010) Molecular classification of soft tissue sarcomas and its clinical applications Int J. Clin Exp Pathol 3:416–428
Kamat V et al (2008) Enhanced EGFR inhibition and distinct epitope recognition by EGFR antagonistic mAbs C225 and 425. Cancer Biol Ther 7:726–733
Kampmeier F, Ribbert M, Nachreiner T, Dembski S, Beaufils F, Brecht A, Barth S (2009) Site-specific, covalent labeling of recombinant antibody fragments via fusion to an engineered version of 6-O-alkylguanine DNA alkyltransferase. Bioconjug Chem 20:1010–1015. doi:10.1021/bc9000257
Kampmeier F et al (2010) Rapid optical imaging of EGF receptor expression with a single-chain antibody SNAP-tag fusion protein. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:1926–1934. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1482-5
Koefoed K et al (2011) Rational identification of an optimal antibody mixture for targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. mAbs 3:584–595. doi:10.4161/mabs.3.6.17955
Kreitman RJ (2006) Immunotoxins for targeted cancer therapy. AAPS j 8:E532–E551. doi:10.1208/aapsj080363
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Mazzoleni S et al (2010) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression identifies functionally and molecularly distinct tumor-initiating cells in human glioblastoma multiforme and is required for gliomagenesis. Cancer Res 70:7500–7513. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-10-2353
Mendelsohn J (2002) Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:1s–13s
Missiaglia E et al (2012) PAX3/FOXO1 fusion gene status is the key prognostic molecular marker in rhabdomyosarcoma and significantly improves current risk stratification. J Clin Oncol 30:1670–1677. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.38.5591
Muller KM, Arndt KM, Strittmatter W, Pluckthun A (1998) The first constant domain (C(H)1 and C(L)) of an antibody used as heterodimerization domain for bispecific miniantibodies. FEBS Lett 422:259–264
Murthy U, Basu A, Rodeck U, Herlyn M, Ross AH, Das M (1987) Binding of an antagonistic monoclonal antibody to an intact and fragmented EGF-receptor polypeptide. Arch Biochem Biophys 252:549–560
Pardo A, Stocker M, Kampmeier F, Melmer G, Fischer R, Thepen T, Barth S (2012) In vivo imaging of immunotoxin treatment using Katushka-transfected A-431 cells in a murine xenograft tumour model. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:1617–1626. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1219-3
Pastan I, FitzGerald D (1991) Recombinant toxins for cancer treatment. Science 254:1173–1177
Pastan I, Chaudhary V, FitzGerald DJ (1992) Recombinant toxins as novel therapeutic agents. Annu Rev Biochem 61:331–354. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001555
Pastan I, Hassan R, FitzGerald DJ, Kreitman RJ (2007) Immunotoxin treatment of cancer. Annu Rev Med 58:221–237. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.58.070605.115320
Pedersen MW, Jacobsen HJ, Koefoed K, Hey A, Pyke C, Haurum JS, Kragh M (2010) Sym004: a novel synergistic anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody mixture with superior anticancer efficacy. Cancer Res 70:588–597. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1417
Ratti M, Tomasello G (2014) Emerging combination therapies to overcome resistance in EGFR-driven tumors. Anticancer Drugs 25:127–139. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000000035
Ray A, Huh WW (2012) Current state-of-the-art systemic therapy for pediatric soft tissue sarcomas. Curr Oncol Rep 14:311–319. doi:10.1007/s11912-012-0243-y
Ricci C et al (2002) HER/erbB receptors as therapeutic targets of immunotoxins in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J Immunother 25:314–323
Schiffer S et al (2013) Species-dependent functionality of the human cytolytic fusion proteins granzyme B-H22(scFv) and H22(scFv)-angiogenin in macrophages. Antibodies 2:9–18. doi:10.3390/antib2010009
Sequist LV, Lynch TJ (2008) EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer: an evolving story. Annu Rev Med 59:429–442. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.59.090506.202405
Simon-Keller K, Barth S, Vincent A, Marx A (2013) Targeting the fetal acetylcholine receptor in rhabdomyosarcoma. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17:127–138. doi:10.1517/14728222.2013.734500
Singh R, Samant U, Hyland S, Chaudhari PR, Wels WS, Bandyopadhyay D (2007) Target-specific cytotoxic activity of recombinant immunotoxin scFv(MUC1)-ETA on breast carcinoma cells and primary breast tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 6:562–569. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0604
Singh R, Zhang Y, Pastan I, Kreitman RJ (2012) Synergistic antitumor activity of anti-CD25 recombinant immunotoxin LMB-2 with chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 18:152–160. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1839
Stahnke B et al (2008) Granzyme B-H22(scFv), a human immunotoxin targeting CD64 in acute myeloid leukemia of monocytic subtypes. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2924–2932. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0554
Stocker M, Tur MK, Sasse S, Krussmann A, Barth S, Engert A (2003) Secretion of functional anti-CD30-angiogenin immunotoxins into the supernatant of transfected 293T-cells. Protein Expr Purif 28:211–219
Sumegi J, Streblow R, Frayer RW, Dal Cin P, Rosenberg A, Meloni-Ehrig A, Bridge JA (2010) Recurrent t(2;2) and t(2;8) translocations in rhabdomyosarcoma without the canonical PAX-FOXO1 fuse PAX3 to members of the nuclear receptor transcriptional coactivator family. Genes Chromosom Cancer 49:224–236. doi:10.1002/gcc.20731
Tebbutt N, Pedersen MW, Johns TG (2013) Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: couples therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 13:663–673. doi:10.1038/nrc3559
Thorpe SJ, Turner C, Heath A, Feavers I, Vatn I, Natvig JB, Thompson KM (2003) Clonal analysis of a human antimouse antibody (HAMA) response. Scand J Immunol 57:85–92
Tur MK et al (2003) Recombinant CD64-specific single chain immunotoxin exhibits specific cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res 63:8414–8419
Wachtel M et al (2006) Subtype and prognostic classification of rhabdomyosarcoma by immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol 24:816–822. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.03.4934
Walter D et al (2011) CD133 positive embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma stem-like cell population is enriched in rhabdospheres. PLoS ONE 6:e19506. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019506
Wayne AS, Fitzgerald DJ, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I (2014) Immunotoxins for leukemia. Blood 123:2470–2477. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-01-492256
Wei BR, Ghetie MA, Vitetta ES (2000) The combined use of an immunotoxin and a radioimmunoconjugate to treat disseminated human B-cell lymphoma in immunodeficient mice. Clin Cancer Res 6:631–642
Weidle UH, Tiefenthaler G, Schiller C, Weiss EH, Georges G, Brinkmann U (2014) Prospects of bacterial and plant protein-based immunotoxins for treatment of cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 11:25–38
Weiss A, Gill J, Goldberg J, Lagmay J, Spraker-Perlman H, Venkatramani R, Reed D (2014) Advances in therapy for pediatric sarcomas. Curr Oncol Rep 16:395. doi:10.1007/s11912-014-0395-z
Weldon JE, Pastan I (2011) A guide to taming a toxin–recombinant immunotoxins constructed from Pseudomonas exotoxin A for the treatment of cancer. FEBS J 278:4683–4700. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08182.x
Wels W et al (2004) Recombinant immunotoxins and retargeted killer cells: employing engineered antibody fragments for tumor-specific targeting of cytotoxic effectors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:217–226. doi:10.1007/s00262-003-0482-8
Williamson D et al (2010) Fusion gene-negative alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is clinically and molecularly indistinguishable from embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Oncol 28:2151–2158. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.26.3814
Yamamoto Y et al (2013) Cetuximab promotes anticancer drug toxicity in rhabdomyosarcomas with EGFR amplification in vitro. Oncol Rep 30:1081–1086. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2588
Yewale C, Baradia D, Vhora I, Patil S, Misra A (2013) Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer: a review of trends and strategies. Biomaterials 34:8690–8707. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.100
Yip WL, Weyergang A, Berg K, Tonnesen HH, Selbo PK (2007) Targeted delivery and enhanced cytotoxicity of cetuximab-saporin by photochemical internalization in EGFR-positive cancer cells. Mol Pharm 4:241–251. doi:10.1021/mp060105u
Yokota T, Milenic DE, Whitlow M, Schlom J (1992) Rapid tumor penetration of a single-chain Fv and comparison with other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res 52:3402–3408
Yun CH et al (2008) The T790 M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2070–2075. doi:10.1073/pnas.0709662105
Zanola A, Rossi S, Faggi F, Monti E, Fanzani A (2012) Rhabdomyosarcomas: an overview on the experimental animal models. J Cell Mol Med 16:1377–1391. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01518.x
Acknowledgments
Christoph Stein was supported by the INTERREG IV A project Microbiomed. We would like to thank Radoslav Mladenov for his help with the tissue sections. We thank Dr. Agnieszka Weinandy (University Hospital Aachen, Neurosurgery Clinic, Aachen, Germany) for providing cetuximab, and we also thank Dr. Richard M. Twyman for the critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standard
Primary tissue samples were obtained during routine clinical practice at the University Hospital Giessen approved by the appropriate ethics committee, in accordance with the principles and the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Judith Niesen and Hannes Brehm shared first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niesen, J., Brehm, H., Stein, C. et al. In vitro effects and ex vivo binding of an EGFR-specific immunotoxin on rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 1049–1061 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1884-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1884-z