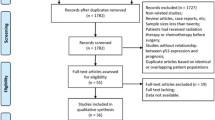
Abstract
Objective
This meta-analysis was conducted to quantitatively assess the prognostic significance of p53 expression in gastric cancer patients.
Methods
A systematic literature search was conducted to identify eligible studies in PubMed and Embase. The pooled hazard ratios (HRs) or odds ratios (ORs) with their corresponding 95 % confidence intervals (95 % CIs) were used to estimate the effect sizes. Moreover, meta-regression analysis and subgroup analysis were carried out.
Results
A total of 34 studies comprising 6,599 patients were subjected to final analysis. Positive/high p53 expression was significantly associated with poorer overall survival (HR 1.56, 95 % CI 1.23–1.98) and disease-specific survival (HR 1.52, 95 % CI 1.35–1.73). The results also indicated that positive/high p53 expression was significantly associated with gender (OR 1.26, 95 % CI 1.09–1.45), Lauren’s classification (OR 1.68, 95 % CI 1.23–2.29), the depth of invasion (OR 0.68, 95 % CI 0.56–0.83), lymph node metastasis (OR 1.56, 95 % CI 1.23–1.97), TNM stage (OR 0.57, 95 % CI 0.47–0.69), vascular invasion (OR 1.51, 95 % CI 1.18–1.92) and lymphatic invasion (OR 1.38, 95 % CI 1.11–1.72), but not with Bormann type (OR 1.24, 95 % CI 0.91–1.70), grade of differentiation (OR 1.08, 95 % CI 0.82–1.44) or distant metastasis (OR 1.37, 95 % CI 0.92–2.03).
Conclusions
This meta-analysis suggests positive/high p53 expression may be a useful biomarker to predict a poorer prognosis for patients with gastric cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HR:
-
Hazard risk
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- DSS:
-
Disease-specific survival
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
References
Al-Moundhri MS et al (2005) The prognostic significance of p53, p27 kip1, p21 waf1, HER-2/neu, and Ki67 proteins expression in gastric cancer: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 121 Arab patients. J Surg Oncol 91:243–252
Anderson C, Nijagal A, Kim J (2006) Molecular markers for gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol Diagn Ther 10:345–352
Baas IO, Mulder JWR, Offerhaus GJA, Vogelstein B, Hamilton SR (1994) An evaluation of six antibodies for immunohistochemistry of mutant p53 gene product in archival colorectal neoplasms. J Pathol 172:5–12
Bani-Hani KE, Almasri NM, Khader YS, Sheyab FM, Karam HN (2005) Combined evaluation of expressions of cyclin E and p53 proteins as prognostic factors for patients with gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:1447–1453
Bataille F et al (2003) Alterations in p53 predict response to preoperative high dose chemotherapy in patients with gastric cancer. Mol pathol 56:286–292
Begg CB (1988) Publication bias: a problem in interpreting medical data. J R Stat Soc A 151:419–463
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Bertuccio P et al (2009) Recent patterns in gastric cancer: a global overview. Int J Cancer 125:666–673
Bria E et al (2013) A clinical–biological risk stratification model for resected gastric cancer: prognostic impact of Her2, Fhit, and APC expression status. Ann Oncol 24:693–701
Chang F, Syrjänen S, Syrjänen K (1995) Implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene in clinical oncology. J Clin Oncol 13:1009–1022
Chen M, Huang J, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Li K (2013) Systematic review and meta-analysis of tumor biomarkers in predicting prognosis in esophageal cancer. BMC Cancer 13:539
Cordon-Cardo C et al (1994) p53 mutations in human bladder cancer: genotypic versus phenotypic patterns. Int J Cancer 56:347–353
De Angelis R et al (2014) Cancer survival in Europe 1999–2007 by country and age: results of EUROCARE–5-a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 15:23–34
De Dosso S et al (2013) ERCC1 predicts outcome in patients with gastric cancer treated with adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72:159–165
Diez M et al (2000) P53 protein expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. Negative predictor of survival after postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. Anticancer Res 20:3929–3933
Drebber U et al (2008) The overexpression of c-met as a prognostic indicator for gastric carcinoma compared to p53 and p21 nuclear accumulation. Oncol Rep 19:1477–1483
Efeyan A, Serrano M (2007) p53: guardian of the genome and policeman of the oncogenes. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 6:1006–1010
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Wang J, Stemmermann GN, Noffsinger A (2003) TP53 and gastric carcinoma: a review. Hum Mutat 21:258–270
Fondevila C et al (2004) p53 and VEGF expression are independent predictors of tumour recurrence and survival following curative resection of gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 90:206–215
Fu H-L, Shao L, Wang Q, Jia T, Li M, Yang D-P (2013) A systematic review of p53 as a biomarker of survival in patients with osteosarcoma. Tumor Biol 34:3817–3821
Gabbert HE, Muller W, Schneiders A, Meier S, Hommel G (1995) The relationship of p53 expression to the prognosis of 418 patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer 76:720–726
Gurel S et al (1999) Expression of p53 protein and prognosis in gastric carcinoma. J Int Med Res 27:85–89
He MM et al (2014) Adjuvant chemotherapy, p53, carcinoembryonic antigen expression and prognosis after D2 gastrectomy for gastric adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 20:264–273
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC (1991) p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 253:49–53
Huang T-J, Wang J-Y, Lin S-R, Lian S-T, Hsieh J-S (2001) Overexpression of the c-met protooncogene in human gastric carcinoma-correlation to clinical features. Acta Oncol 40:638–643
Ide M, Kato T, Ogata K, Mochiki E, Kuwano H, Oyama T (2012) Keratin 17 expression correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 19:3506–3514
Inoue M, Tsugane S (2005) Epidemiology of gastric cancer in Japan. Postgrad Med J 81:419–424. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2004.029330
Ireland AP, Clark G, DeMeester TR (1997) Barrett’s esophagus. The significance of p53 in clinical practice. Ann Surg 225:17
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Joo YE et al (2002) The role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and p53 status for angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Korean J Intern Med 17:211–219
Joypaul BV et al (1994) The prognostic significance of the accumulation of p53 tumour-suppressor gene protein in gastric adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer 69:943–946
Juvan R, Hudler P, Gazvoda B, Repse S, Bracko M, Komel R (2007) Significance of genetic abnormalities of p53 protein in Slovenian patients with gastric carcinoma. Croat Med J 48:207–217
Kasper HU, Schneider-Stock R, Mellin W, Gunther T, Roessner A (1999) P53-protein accumulation and MDM2-protein overexpression in gastric carcinomas. No apparent correlation with survival. Pathol Res Pract 195:815–820
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig RW (1991) Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 51:6304–6311
Kelley JR, Duggan JM (2003) Gastric cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol 56:1–9
Kim HS et al (2011) Advanced detection of recent changing trends in gastric cancer survival: up-to-date comparison by period analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:1344–1350
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Chatzopoulos D (2005) Apoptotic and anti-angiogenic strategies in liver and gastrointestinal malignancies. J Surg Oncol 90:249–259
Ku JH, Byun S-S, Jeong H, Kwak C, Kim HH, Lee SE (2013) The role of p53 on survival of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer 11:221–228
Kubicka S et al (2002) p53 mutation pattern and expression of c-erbB2 and c-met in gastric cancer: relation to histological subtypes, helicobacter pylori infection, and prognosis. Dig Dis Sci 47:114–121
Lane DP (1992) Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 358:15–16
Lauren P (1965) The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 64:31–49
Lazar D et al (2010) The immunohistochemical expression of the p53-protein in gastric carcinomas. Correlation with clinicopathological factors and survival of patients. Rom J Morphol Embryol 51:249–257
Lee WJ, Shun CT, Hong RL, Wu MS, Chang KJ, Chen KM (1998) Overexpression of p53 predicts shorter survival in diffuse type gastric cancer. Br J Surg 85:1138–1142
Lee KE et al (2003) Prognostic significance of p53, nm23, PCNA and c-erbB-2 in gastric cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 33:173–179
Lehrbach DM, Cecconello I, Ribeiro U Jr, Capelozzi VL, Ab’saber AM, Alves VA (2009) Adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction: relationship between clinicopathological data and p53, cyclin D1 and Bcl-2 immunoexpressions. Arq Gastroenterol 46:315–320
Li M, Brooks CL, Kon N, Gu W (2004) A dynamic role of HAUSP in the p53-Mdm2 pathway. Mol Cell 13:879–886
Lim BH, Soong R, Grieu F, Robbins PD, House AK, Iacopetta BJ (1996) p53 accumulation and mutation are prognostic indicators of poor survival in human gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 69:200–204
Liu XP, Tsushimi K, Tsushimi M, Kawauchi S, Oga A, Furuya T, Sasaki K (2001) Expression of p21(WAF1/CIP1) and p53 proteins in gastric carcinoma: its relationships with cell proliferation activity and prognosis. Cancer Lett 170:183–189
Liu J et al (2012a) Alterations of TP53 are associated with a poor outcome for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 48:2328–2338
Liu X et al (2012b) Synergistic role between p53 and JWA: prognostic and predictive biomarkers in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e52348
Maehara Y, Tomoda M, Hasuda S, Kabashima A, Tokunaga E, Kakeji Y, Sugimachi K (1999) Prognostic value of p53 protein expression for patients with gastric cancer: a multivariate analysis. Br J Cancer 79:1255–1261
Malats N et al (2005) P53 as a prognostic marker for bladder cancer: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol 6:678–686
Matturri L et al (1998) Prognostic significance of different biological markers (DNA index, PCNA index, apoptosis, p53, karyotype) in 126 adenocarcinoma gastric biopsies. Anticancer Res 18:2819–2825
Migliavacca M et al (2004) TP53 in gastric cancer: mutations in the l3 loop and LSH motif DNA-binding domains of TP53 predict poor outcome. J Cell Physiol 200:476–485
Mrena J, Wiksten JP, Kokkola A, Nordling S, Ristimaki A, Haglund C (2010) COX-2 is associated with proliferation and apoptosis markers and serves as an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 31:1–7
Mrozek A et al (2003) Combined p53/Bax mutation results in extremely poor prognosis in gastric carcinoma with low microsatellite instability. Cell Death Differ 10:461–467
Muller PA, Vousden KH, Norman JC (2011) p53 and its mutants in tumor cell migration and invasion. J Cell Biol 192:209–218
Ott K et al (2003) Chromosomal instability rather than p53 mutation is associated with response to neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9:2307–2315
Pakos EE, Kyzas PA, Ioannidis JP (2004) Prognostic significance of TP53 tumor suppressor gene expression and mutations in human osteosarcoma a meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res 10:6208–6214
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17:2815–2834
Peng L, Zhan P, Zhou Y, Fang W, Zhao P, Zheng Y, Xu N (2012) Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 39:9473–9484
Pinto-de-Sousa J, Silva F, David L, Leitao D, Seixas M, Pimenta A, Cardoso-de-Oliveira M (2004) Clinicopathological significance and survival influence of p53 protein expression in gastric carcinoma. Histopathology 44:323–331
Potrc S, Gadiijev E, Hajdinjak T, Kavalar R (2007) Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical markers after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 54:308–314
Puhringer-Oppermann F, Stahl M, Keller G, Sarbia M (2006) Lack of prognostic impact of p53 gene mutation and p53 phosphorylation at serine 15 in multimodally treated adenocarcinomas of the gastroesophageal junction. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:433–438
Rivera F, Vega-Villegas ME, López-Brea MF (2007) Chemotherapy of advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 33:315–324
Roder DM (2002) The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 5:5–11
Roviello F, Marrelli D, Vindigni C, De Stefano A, Spina D, Pinto E (1999) P53 accumulation is a prognostic factor in intestinal-type gastric carcinoma but not in the diffuse type. Ann Surg Oncol 6:739–745
Sawada T et al (2014) New molecular staging with G-factor supplements TNM classification in gastric cancer: a multicenter collaborative research by the Japan society for gastroenterological carcinogenesis G-project committee. Gastric Cancer. doi:10.1007/s10120-014-0338-2
Sgambato A et al (2000) Loss of p27Kip1 expression is a strong independent prognostic factor of reduced survival in N0 gastric carcinomas. Cancer 89:2247–2257
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29
Solcia E et al (2009) A combined histologic and molecular approach identifies three groups of gastric cancer with different prognosis. Virchows Arch 455:197–211
Song KY, Jung CK, Park WS, Park CH (2009) Expression of the antiapoptosis gene survivin predicts poor prognosis of stage III gastric adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 39:290–296
Song J, Su H, Y-y Zhou, L-l Guo (2013) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is associated with poor overall survival of patients with gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 59:436–445
Soussi T (2000) The p53 tumor suppressor gene: from molecular biology to clinical investigation. Ann NY Acad Sci 910:121–137
Soussi T (2005) The p53 pathway and human cancer. Br J Surg 92:1331–1332. doi:10.1002/bjs.5177
Steels E et al (2001) Role of p53 as a prognostic factor for survival in lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 18:705–719
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR (2007) Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 8:16
Toledo F, Wahl GM (2006) Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat Rev Cancer 6:909–923
Tsujitani S et al (2012) Relationship between expression of apoptosis-related proteins and the efficacy of postoperative chemotherapy in patients with T3 gastric cancer. Surg Today 42:225–232
Wang J et al (2011) p53 status and its prognostic role in extrahepatic bile duct cancer: a meta-analysis of published studies. Dig Dis Sci 56:655–662
Xiao LJ, Zhao S, Zhao EH, Zheng X, Gou WF, Takano Y, Zheng HC (2013) Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of Ki-67, caspase-3 and p53 expression in gastric carcinomas. Oncol Lett 6:1277–1284
Xing X, Tang YB, Yuan G, Wang Y, Wang J, Yang Y, Chen M (2013) The prognostic value of E-cadherin in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 132:2589–2596
Yoo C, Noh S, Shin D, Choi S, Min J (2000) Recurrence following curative resection for gastric carcinoma. Br J Surg 87:236–242
Zafirellis K, Karameris A, Milingos N, Androulakis G (2005) Molecular markers in gastric cancer: can p53 and bcl-2 protein expressions be used as prognostic factors? Anticancer Res 25:3629–3636
Zha Y, Cun Y, Zhang Q, Li Y, Tan J (2012) Prognostic value of expression of Kit67, p53, TopoIIa and GSTP1 for curatively resected advanced gastric cancer patients receiving adjuvant paclitaxel plus capecitabine chemotherapy. Hepatogastroenterology 59:1327–1332
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Number: lzujbky-2013-160).
Conflict of interest
All the authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, K., Jiang, L., Wei, Y. et al. The prognostic significance of p53 expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 735–748 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1844-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1844-7